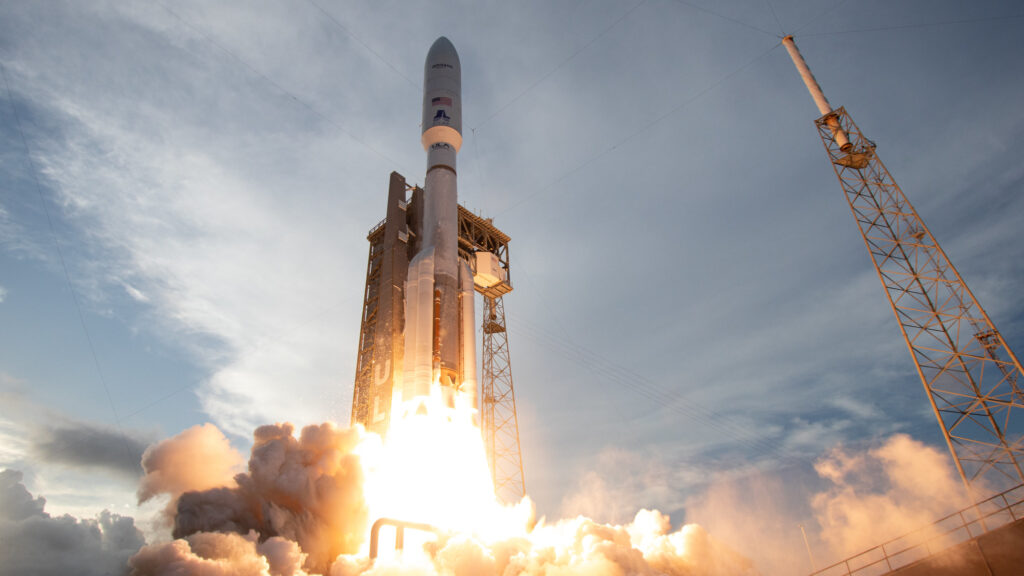
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — A SpaceX rocket launched a new space telescope into orbit Saturday (July 1) on a mission to map the “dark universe” like never before.
The European Space Agency observatory, called Euclid, soared to space today aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 11:11 a.m. EDT (1511 GMT) from Space Launch Complex 40 here at the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.
Spectators here at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex cheered and applauded as the Falcon 9 booster carried Euclid aloft, with the first stage handily touching down just eight minutes later on a drone ship stationed nearby in the Atlantic Ocean.
“We have a mission,” ESA Director-General Josef Aschbacher said during a live webcast just after liftoff. “I’m so excited for this mission now, knowing its on its way to Lagrange point 2 … amazing, I’m very happy and very thrilled.”
“I’m totally addicted, a launch junkie,” joked Nicola Fox, NASA’s associate administrator for science, at a press conference here after the launch Saturday (July 1). “It’s just the most exciting day where you realize all the work, all the teams, all the thousands of people that put their life into this mission and for them to see that take flight today.”
The Euclid space observatory, which is designed to seek out invisible dark matter and dark energy, separated from its rocket about 41 minutes after liftoff and is now making the journey to the sun-Earth Lagrange point 2, which is roughly 1 million miles (1.5 million km) away from our planet on the opposite side of the sun. Lagrange points are relatively stable orbits where satellites use a minimum of fuel, and Euclid’s destination is a popular location: NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope also orbits at L2, for example.
Related: We’ve never seen dark matter and dark energy. Does it really exist?
Unveiling the ‘dark universe’

Dark matter and dark energy are believed to make up most of the universe, but we can’t see these phenomena in wavelengths of light. Rather, we can track the dark universe through its effects on other objects. (Gravitational lensing is one example, when a massive object bends the light of a distant object behind through the force of gravity, bringing otherwise faraway stars or galaxies into sharp focus.)
Cosmologists — scientists studying the history of space — seek to understand how the dark universe behaves to chart the effects of time on our cosmos. The mergers of galaxies, the expansion of the universe and the movements of individual stars are all subject to the forces of dark energy and dark matter.
Carole Mundell, ESA’s director of science, added at the press conference that one of her priorities is making sure there is a robust data archive that will last even beyond Euclid’s six years of gathering science.
Calling herself a “custodian” as she has just taken on the director role, she said she would rather pass any baton of congratulations “to all of our science communities who now will work very hard to commission this mission.”
Euclid will aim its telescope eye to regions outside of the Milky Way, our own galaxy, to map over a third of the “extragalactic” sky. In its six-year mission, the deep space explorer will map billions of targets like galaxies and stars. Euclid’s two instruments, focusing respectively on visible and infrared (heat-seeking) light wavelengths, will record the information for scientists.
The long survey mission will uncover the movements of these distant objects, along with their chemical makeup. From space, Euclid’s sharp eyes will allow for images at least four times more clear than what telescopes achieve from the ground, given the spacecraft will be far away from Earth’s interfering atmosphere and stray light.
Carole Mundell, ESA’s director of science, said the Euclid mission is one 15 years in the making, but still she was holding her breath waiting for signal acquisition after a prefect launch and spacecraft separation.
“In the next six years of this mission, we will unravel the mysteries of the dark universe,” Mundell said. “So, a huge honor to be here. I think there’ll be some partying tonight.”
Related: The Euclid spacecraft will transform how we view the ‘dark universe’

The 1.4 billion Euro ($1.5 billion USD) Euclid has been in the works for nearly two decades. It was forged from two mission concepts proposed in 2007: Dune (Dark Universe Explorer) and Space (Spectroscopic All Sky Cosmic Explorer), which used different but complementing ways of looking at dark energy. Given how well the two missions worked with each other, they were combined into one powerful observatory: Euclid.
The European Space Agency‘s (ESA) science program committee selected Euclid for space in 2011 and formally adopted the program in 2012. The larger Euclid consortium today includes more than 2,000 scientists from Europe, the U.S. (including NASA), Canada and Japan contributing both instruments and analysis. Thales Alenia Space was the satellite’s prime contractor, while Airbus Defence and Space contributed the payload module and 4-foot (1.2-meter) telescope.

Euclid’s work follows on from several ground-based and space-based surveys of the universe. Among them is the Chilean Victor M. Blanco telescope’s Dark Energy Survey that mapped 100 million galaxies; a 2022 study of that team’s work will serve as a pathfinder both for Euclid and for NASA’s Roman Space Telescope.
ESA’s still-active Gaia satellite (also at Lagrange Point 2) is another recent example, having mapped the movements of nearly 2 billion bright stars since 2015. Gaia, however, focuses on the Milky Way and that will make it a complementary mission to Euclid’s deep space focus.
A rocket swap for Euclid

RELATED STORIES:
Incidentally, Euclid was not supposed to launch aboard SpaceX at all. As late as February 2022, the mission was manifested upon an Arianespace Soyuz (provided by Russia) for a March 2023 launch in French Guiana. Russia’s unsanctioned invasion of Ukraine forced a stop to most such space collaborations aside from the International Space Station, pushing Euclid’s team to look for another ride to space.
Arianespace has been ESA’s launch partner for decades and as a French vendor, it is the preferred route for European space access. Yet there was no room left on the retiring Ariane 5 rocket line, and the new Ariane 6 was still in a late stage of development, reported SpaceNews, which was at the meeting.
Even U.S. options were few, as United Launch Alliance’s trusty Atlas V and Delta IV Heavy rockets also had full manifests ahead of their retirement. ULA’s new Vulcan Centaur will not fly until this year at least, leaving SpaceX as the only viable short-term option, according to ESA comments last year.
To get to its new site, Euclid made its way from Italy to its Floridian launch site under sail. It took roughly two weeks to voyage across the Atlantic by boat, yet just minutes to cross that same ocean again in the air by rocket.
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that launched Euclid made its second flight to space with this launch. The mission marked SpaceX’s 44th mission of 2023 and 243rd mission to date. It was the also the 204th successful landing of an orbital class rocket by SpaceX.
Euclid will take about 30 days to commute to its deep-space site. Investigators have not yet released the date for the first science image, but say it will be in a few months.
This story was updated at 2:08 p.m. EDT with information from the post-launch press conference.
Elizabeth Howell’s Florida coverage was co-sponsored by Canadian Geographic magazine and Canada’s University of Waterloo, where Euclid’s primary science coordinator (Will Percival) is based. Space.com has independent control of news coverage.