In a historic first, all six radio frequency antennas at the Madrid Deep Space Communication Complex – part of NASA’s Deep Space Network (DSN) – carried out a test to receive data from the agency’s Voyager 1 spacecraft at the same time on April 20, 2024. Known as “arraying,” combining the receiving power of several antennas allows the DSN to collect the very faint signals from faraway spacecraft. A five-antenna array is currently needed to downlink science data from the spacecraft’s Plasma Wave System instrument. As Voyager gets further way, six antennas will be needed.
Related posts
-

Marvel delays ‘Avengers: Doomsday’ and ‘Avengers: Secret Wars’ by 7 months each
Marvel maniacs are going to have to muster more patience to watch “Avengers: Doomsday” and “Avengers:... -
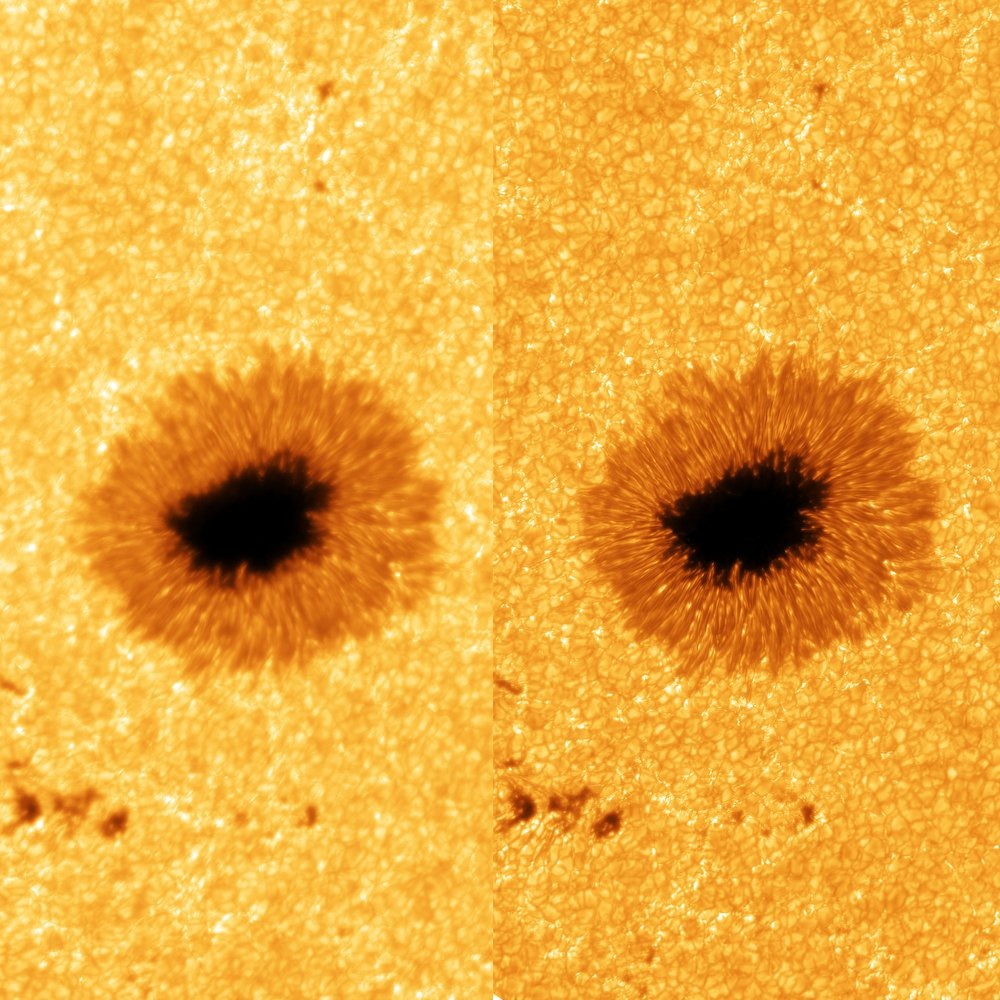
New 8K-resolution photos of the sun show off incredible details of raging sunspots
Incredible new images of the sun’s surface provide an unprecedented view of raging sunspots and solar... -
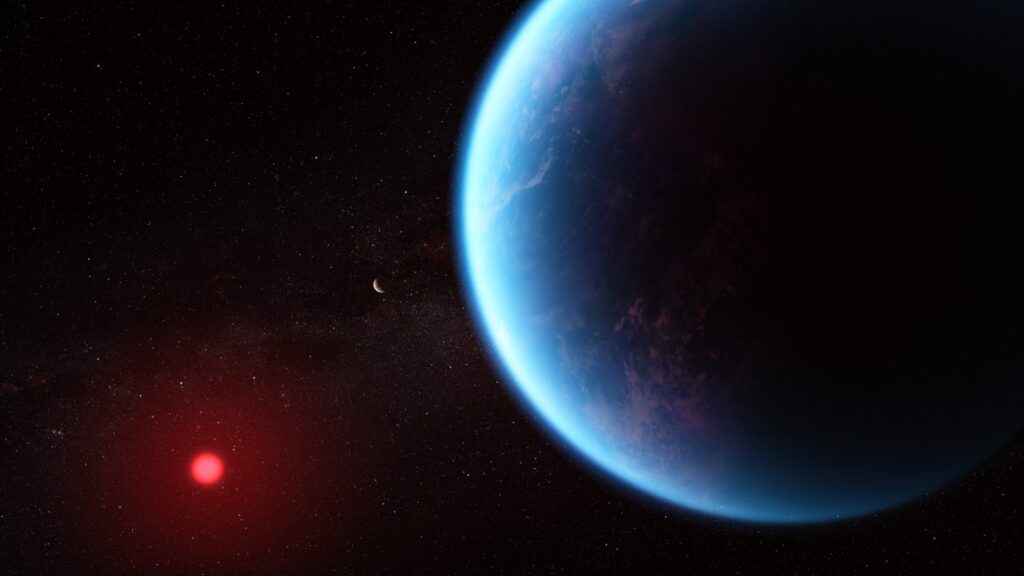

Scientists question possible signs of life on exoplanet K2-18b in new study: ‘We never saw more than insignificant hints’
In 2023, scientists from Cambridge University reported what appeared to be very exciting news. NASA’s James...