The surface of Mars is littered with examples of glacier-like landforms. While surface ice deposits are mostly limited to the polar caps, patterns of slow, viscous flow abound in many non-polar regions of Mars. Streamlines that appear as linear ridges in the surface soils and rocky debris are often exposed on top of infilling deposits that coat crater and valley floors. We see such patterns on the surfaces of Earth’s icy glaciers and debris-covered “rock glaciers.” As ice flows downhill, rock and soil are plucked from the surrounding landscape and ferried along the flowing ice surface and within the icy subsurface. While this process is gradual, taking perhaps thousands of years or longer, it creates a network of linear patterns that reveal the history of ice flow.
Related posts
-
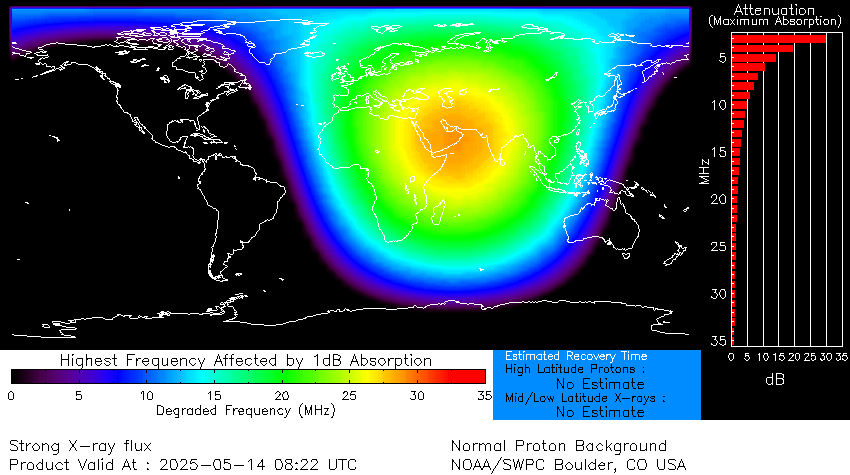
Strongest solar flare of 2025 erupts from sun, sparking radio blackouts across Europe, Asia and the Middle East
The sun roared to life early Tuesday (May 14), unleashing a powerful X-class solar flare from... -
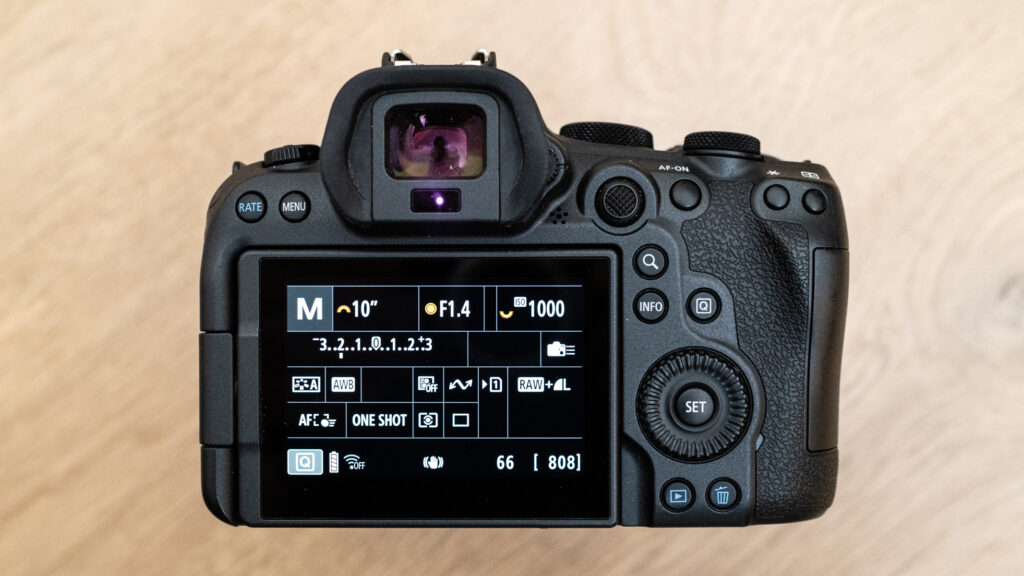

Canon EOS R6 Mark II review
Key specs Type: Mirrorless Sensor: 24.2MP full-frame CMOS sensor Lens mount: RF/RF-S ISO range: 100-102,400 Viewfinder... -
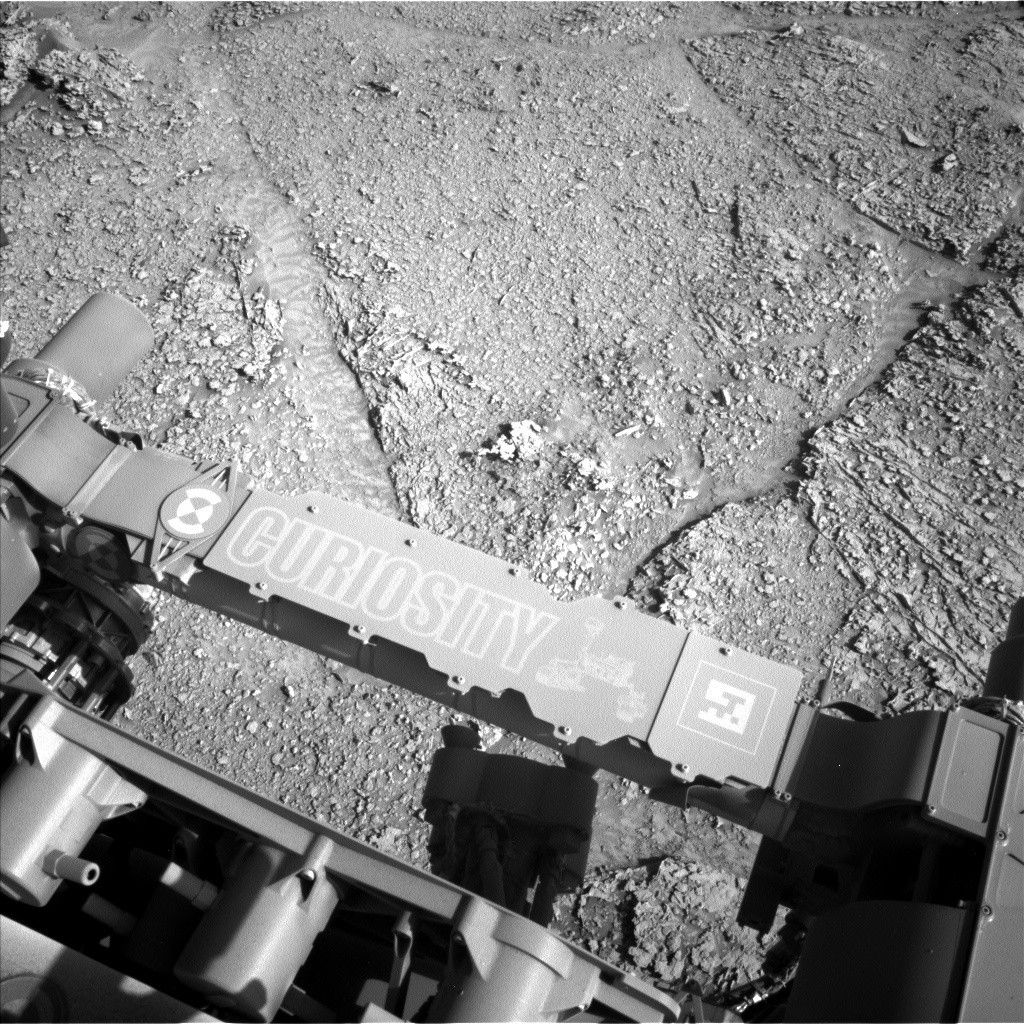

Sols 4539-4540: Back After a Productive Weekend Plan
Curiosity Navigation Curiosity Home Mission Overview Where is Curiosity? Mission Updates Science Overview Instruments Highlights Exploration...