5 min read
Sketch the Shape of the Sun for Science During the Solar Eclipse
Calling all eclipse admirers!
The SunSketcher team is looking for one million volunteers to capture photos on their cell phones during the April 8 total solar eclipse. These images will help scientists learn about the size, shape, and inner structure of the Sun.
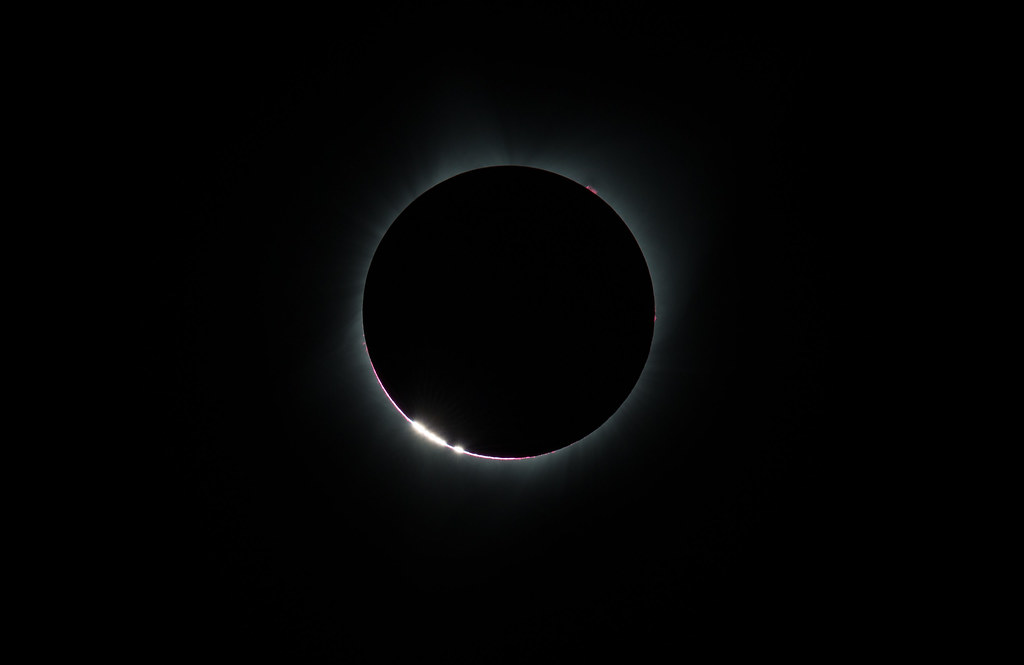
This NASA-funded citizen science project invites anyone who will be within the path of totality in the U.S. to take photos of the Baily’s Beads effect, which occurs when little points of sunlight pass through the valleys in between the mountains on the edge of the Moon. It’s the last piece of the Sun seen before totality and the first to appear after totality. For a few seconds, these glimmers of light look like beads along the Moon’s edge.
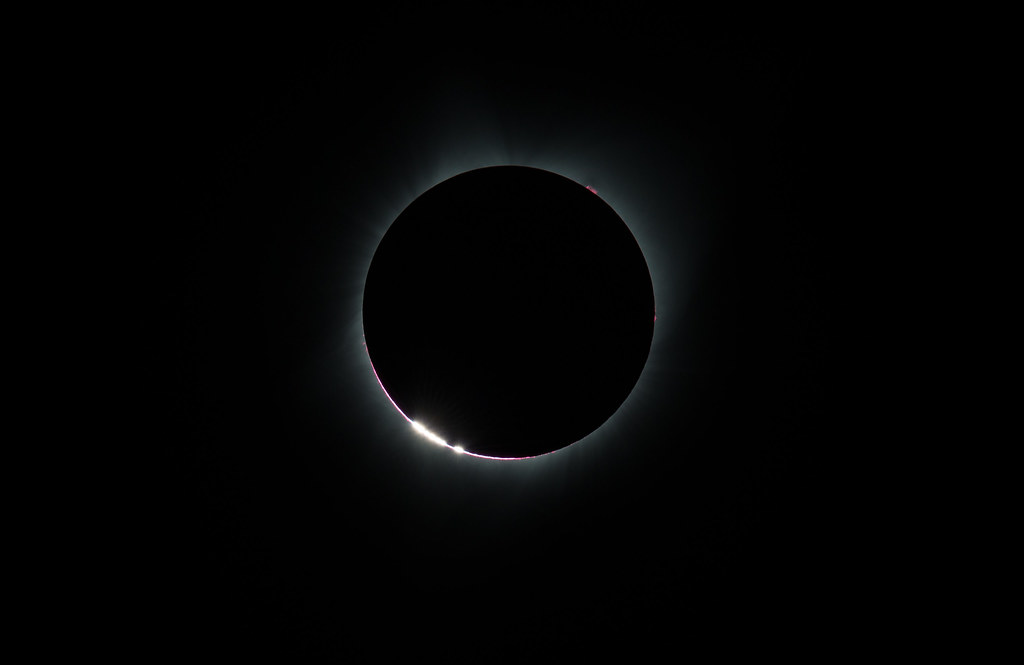

The SunSketcher app will use smartphones to automatically take a sequence of images as Baily’s Beads appear. Volunteers will simply download a free app, activate it just before totality, set the phone down with the rear camera pointed at the Sun, and leave it alone. The app will use the phone’s GPS location to calculate when Baily’s Beads will be visible.
“All you need is a cell phone,” says Gordon Emslie, SunSketcher’s project lead and professor of physics and astronomy at Western Kentucky University. “How many science projects can you do with the equipment you already have in your pocket?”
Emslie says the cell phone images of Baily’s Beads will look fairly simple, but the tiny dots of light will provide crucial data about our star.
“It’s the precise timing of when these flashes appear and disappear that can tell you how big the Sun is and what shape it is,” Emslie says.
The SunSketcher team will merge the images collected from various viewpoints on the eclipse path to create an evolving pattern of beads. This pattern will be compared with 3D maps that show the exact locations and distances between lunar craters, mountains, and valleys on the surface of the Moon from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. The combined measurements will allow researchers to calculate the precise size and shape of the Sun based on the timing of the images captured over 90 minutes of eclipse observations.
“The fascinating thing about this is you can really only do this by having observers stretched over the whole eclipse path,” Emslie explains. “No one observer can monitor an eclipse for more than about four or five minutes.”
The Sun is round but not a perfect sphere. It bulges out slightly along the equator with a diameter of about 865,000 miles. Scientists suspect the shape of the Sun changes slightly as it goes through 11-year cycles of fluctuating solar activity. The Sun is a rotating ball of gas and plasma with complicated internal flows of material, energy, and magnetic fields beneath the surface that vary over that cycle and impact its overall shape.
“All of these flows connect to the surface somehow, and so the shape of the surface is determined by the details of the flows,” Emslie says. “If we can understand the subsurface flows, we can better understand the Sun’s internal structure.”
The Sun’s shape also determines its gravitational field, which affects the motions of the planets, so measuring the Sun’s precise shape will help scientists test theories of gravity.
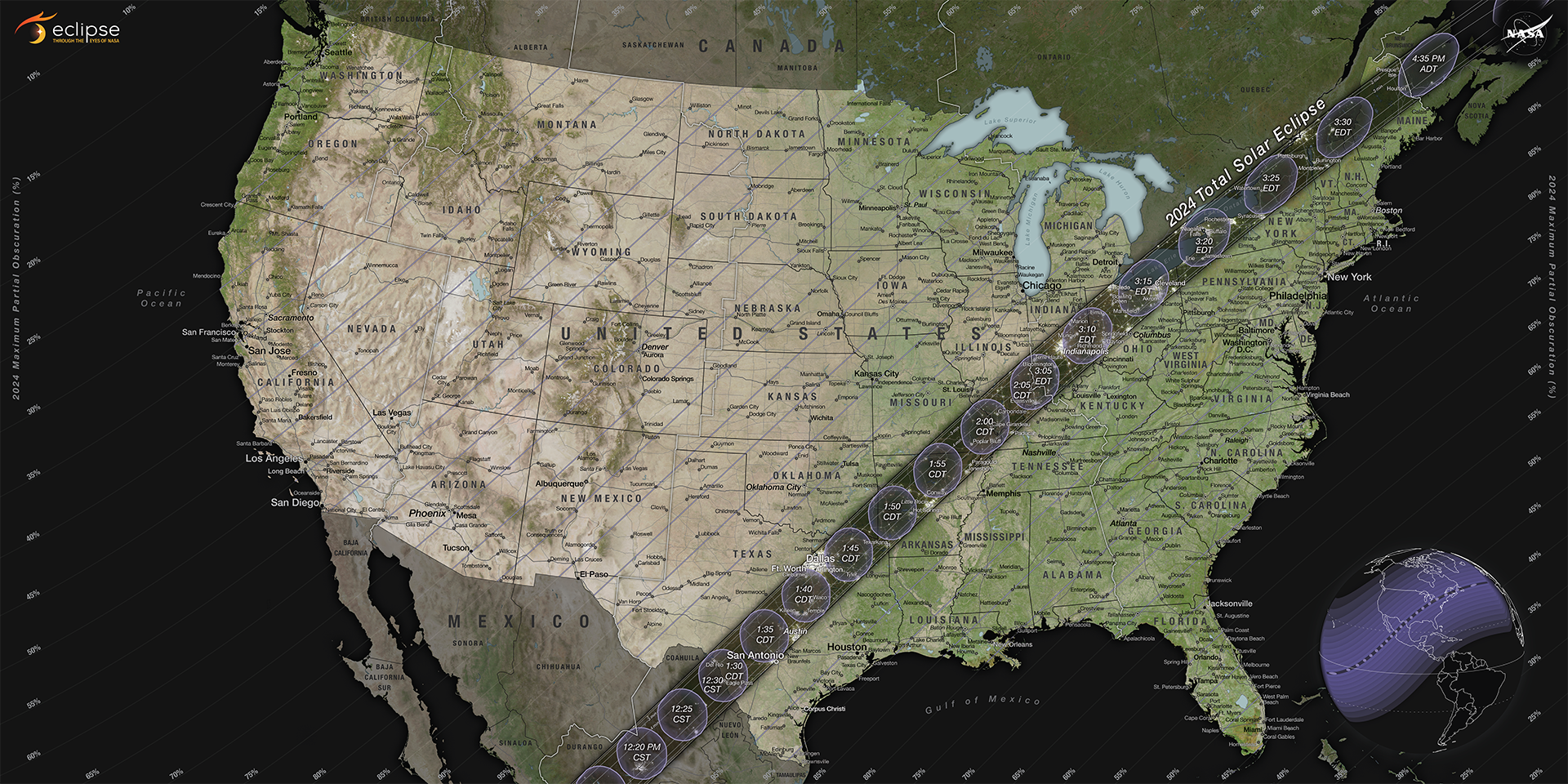
Participants in the SunSketcher project can be located anywhere in the eclipse’s path of totality in the U.S., which stretches from Texas to Maine, on April 8. Emslie says the more people involved, the more worthwhile the project will be. “Literally, we’re looking for a million people to play.”
For more info on SunSketcher, visit: https://sunsketcher.org/
How to Become a SunSketcher and Be a Part of History
Animation credit: SunSketcher/Tabby Cline
Before the Eclipse
- Download the free app from your phone’s app store (available now on iOS and coming soon on Android).
- Initiate the app around five minutes before totality. No internet connection is required.
- If possible, turn on “Do Not Disturb” in your phone’s settings to prevent vibrations that could disturb the image sequence.
- Prop the phone against a steady surface (such as a rock, book, phone stand, or tripod) with the rear (back-facing) camera pointed at the Sun.
- Let it be! The app will automatically take images of Baily’s Beads at the correct times.
- Enjoy the eclipse! Remember to use specialized eye protection for solar viewing except during the brief total phase of a total solar eclipse, when the Moon completely blocks the Sun.
After the Eclipse
- The app will show a directory of images taken and will request user permission to share them. Only time and location data will be recorded with the images. No personally identifiable or private information will be collected.
- Once an internet connection is established, the images will be automatically uploaded to a central server and a screen will appear with a thank-you message.
By Rose Brunning
Communications Lead, NASA Heliophysics Digital Resource Library (HDRL)










