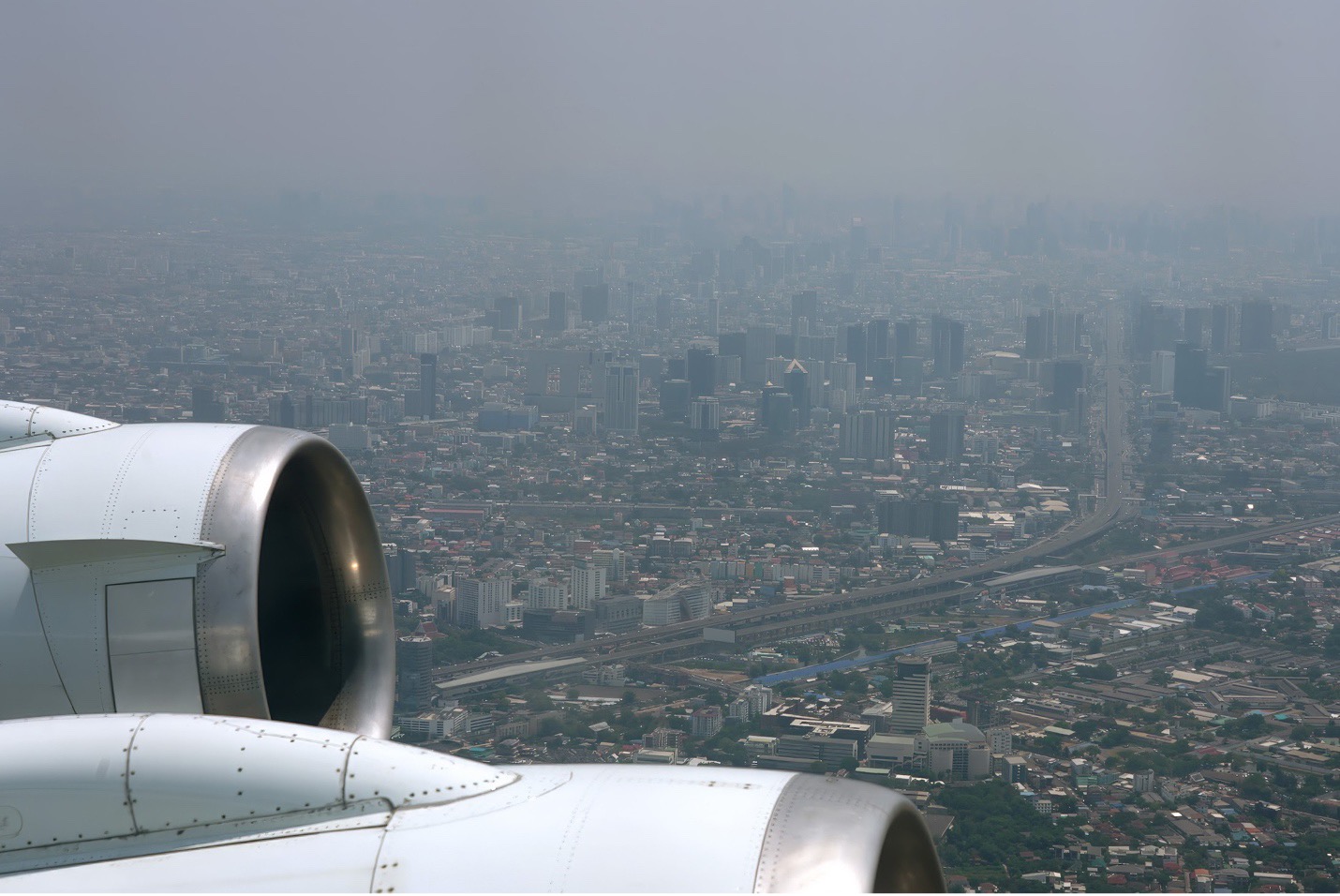
ASIA-AQ DC-8 aircraft flies over Bangkok, Thailand to monitor seasonal haze from fire smoke and urban pollution. Photo credit: Rafael Luis Méndez Peña. Tracking the spread of harmful air pollutants across large regions requires aircraft, satellites, and diverse team of scientists. NASA’s global interest in the threat of air pollution extends into Asia, where it works with partners on the Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality (ASIA-AQ). This international mission integrates satellite data and aircraft measurements with local air quality ground monitoring and modeling efforts across Asia. Orchestrating…
Read MoreDay: June 21, 2024
South Central US Students to Hear from NASA Astronaut Aboard Station
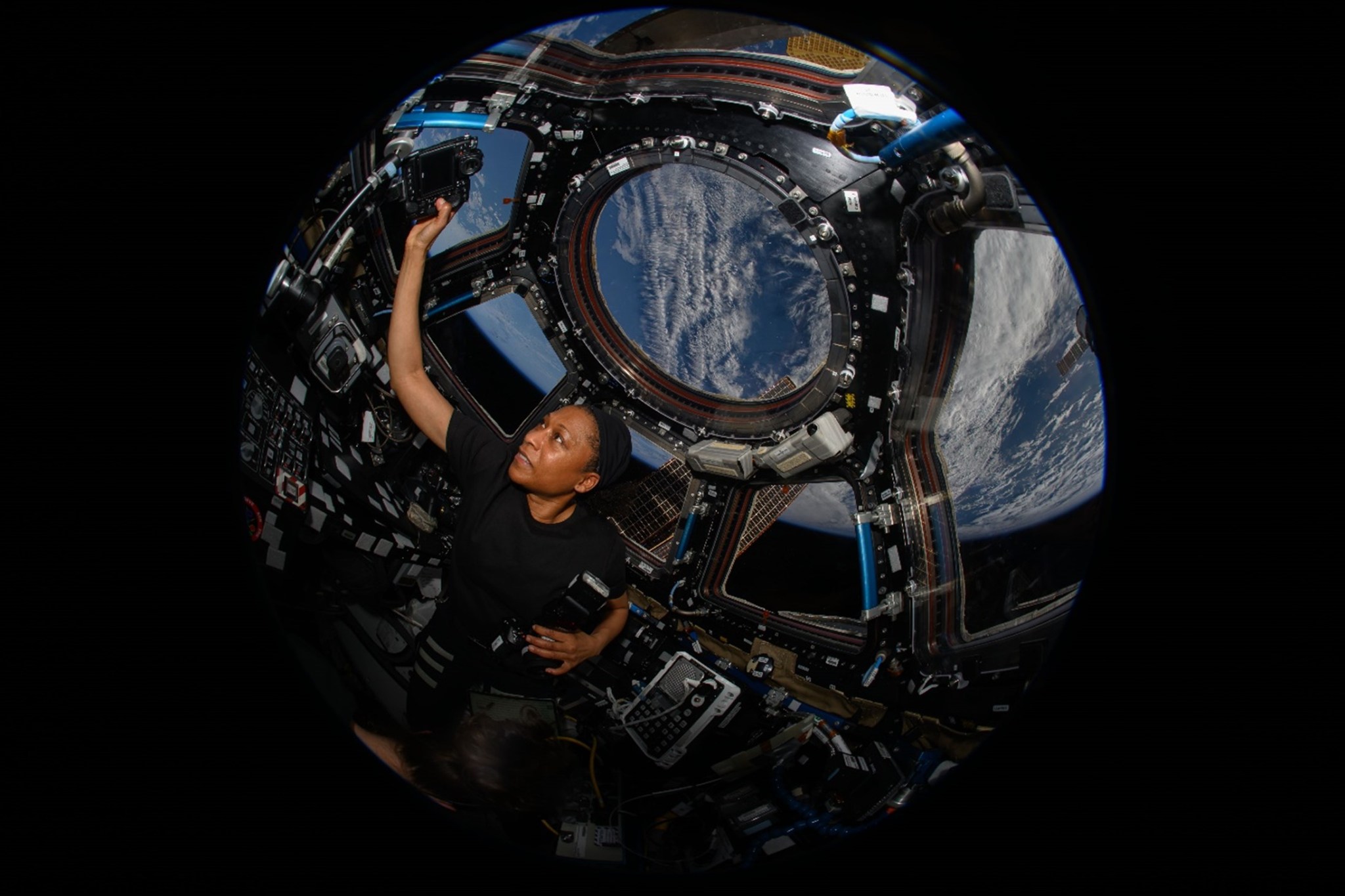
(April 8, 2024) NASA astronaut Jeanette Epps uses a camera in the International Space Station’s cupola to take photographs of the Moon’s shadow umbra as a total solar eclipse moves across Earth’s surface during Expedition 71. Credits: NASA/Matthew Dominick Students from Louisiana, New Mexico, and Texas will have an opportunity to hear from a NASA astronaut aboard the International Space Station. The 20-minute Earth-to-space call will stream live at 9:10 a.m. EDT, Wednesday, June 26, on NASA+, NASA Television, the NASA app, and the agency’s website. Learn how to stream…
Read MoreWhy smaller planets are better at building large moons
New simulations that describe how moons, including Earth‘s own moon, formed strongly imply that exomoons are more likely to be found around rocky exoplanets. Our moon is thought to have formed when a Mars-size planetesimal called Theia slammed into Earth, gouging out a huge wound in our planet and rendering its entire surface molten. It’s believed that the moon then coalesced from debris that settled into a ring around our planet. Those are the generally accepted details, but the specifics are still hotly debated. The angle and velocity with which…
Read MoreTeachers Bring Student Teams to GLOBE Research Symposia
5 min read Teachers Bring Student Teams to GLOBE Research Symposia A year-long professional development experience for teachers resulted in participation of 10 student teams at Global Learning & Observations to Benefit the Environment (GLOBE) student research symposia. Teachers from the ENGAGE (Earth, NASA, GLOBE, and Guided Explorations) GLOBE Mission Earth 2023-2024 virtual educator cohort have been connecting throughout the school year to learn GLOBE protocols, identify opportunities for students to present GLOBE research, and to share lessons learned. The NASA Science Activation Langley Research Center (LaRC) team led the…
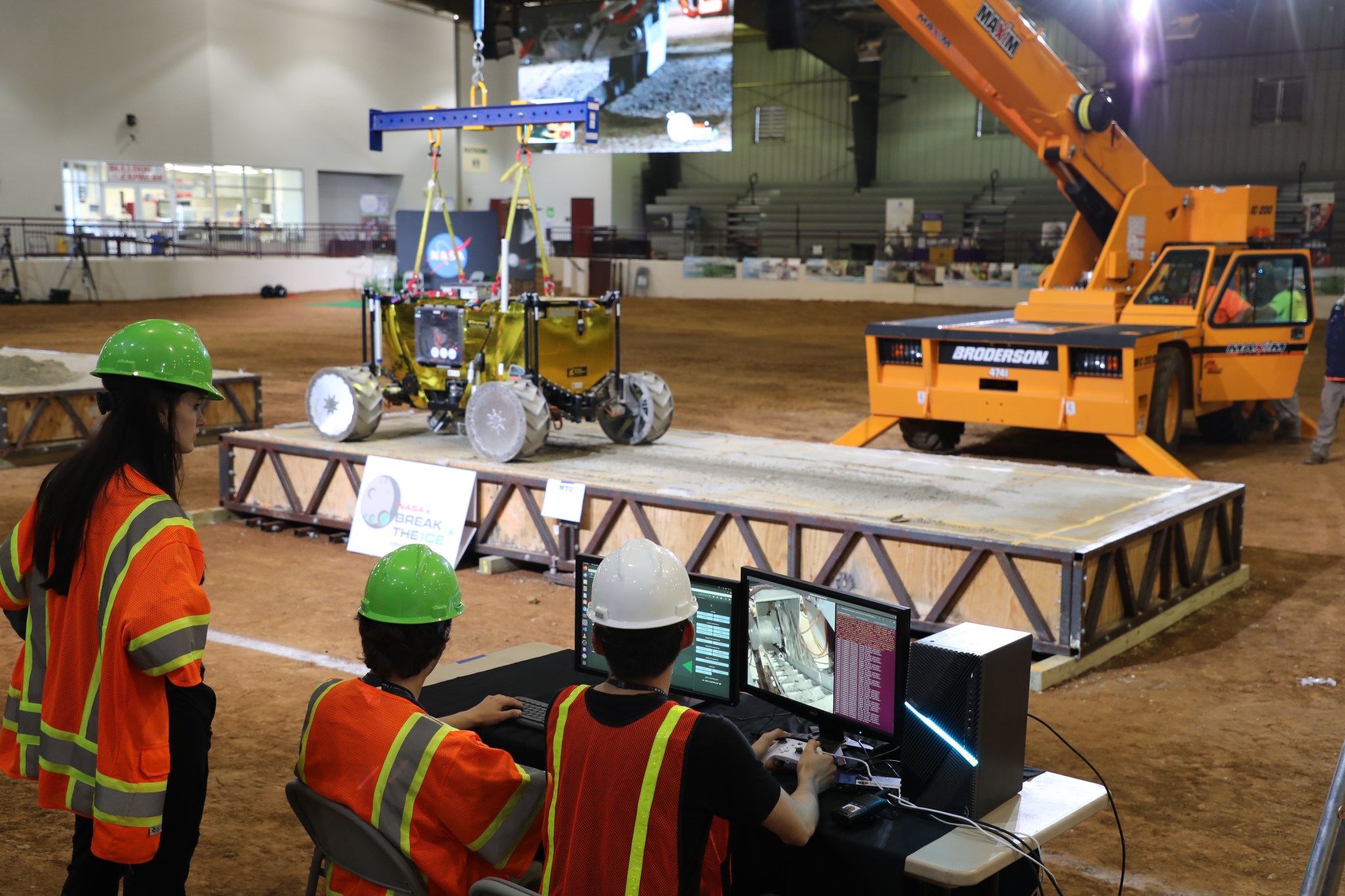
Read MoreHuskyWorks During Rover Testing
“HuskyWorks,” a team from Michigan Technological University’s Planetary Surface Technology Development Lab, tests the excavation tools of a robot on a concrete slab, held by a gravity-offloading crane on June 12 at NASA’s Break the Ice Lunar Challenge at Alabama A&M’s Agribition Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Led by Professor Paul van Susante, the team aimed to mimic the conditions of the lunar South Pole, winning an invitation to use the thermal vacuum chambers at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center to continue robotic testing. Read more about NASA’s Break the Ice Lunar Challenge. NASA/Jonathan Deal
Read More