The distorted spiral galaxy at center, the Penguin, and the compact elliptical at left, the Egg, are locked in an active embrace. This near- and mid-infrared image combines data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), and marks the telescope’s second year of science. Webb’s view shows that their interaction is marked by a glow of scattered stars represented in blue. Known jointly as Arp 142, the galaxies made their first pass by one another between 25 and 75 million years ago, causing “fireworks,” or new star formation, in the Penguin. The galaxies are approximately the same mass, which is why one hasn’t consumed the other.
Related posts
-
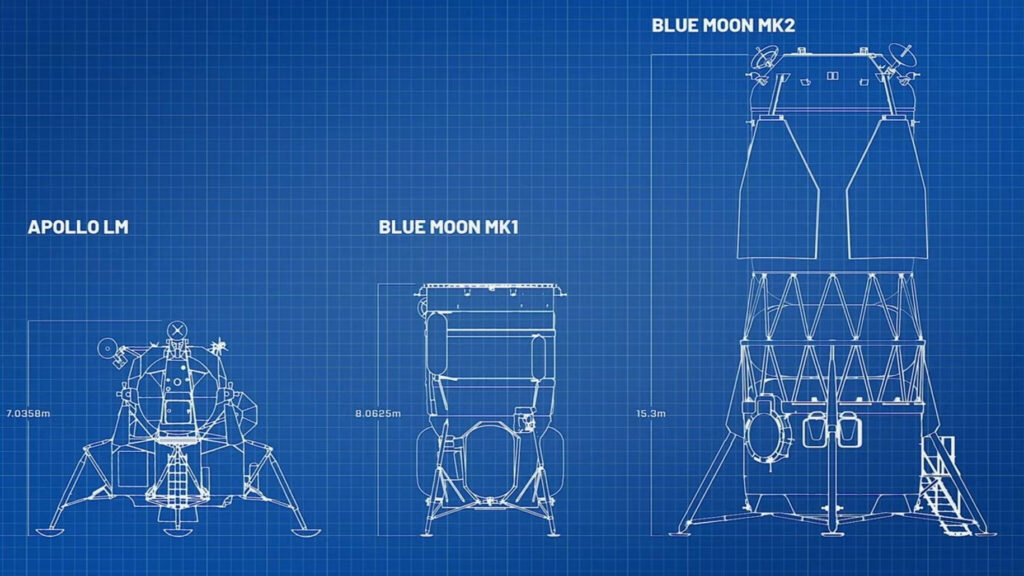
Lunar landers and ‘Transporter’ tankers: Blue Origin unveils its blueprint for the moon
Blue Origin has begun revealing how it plans to establish itself as a provider of hardware... -

How a Childhood Telescope Launched a NASA Career
Christina Zeringue is the chief safety and mission assurance officer at NASA’s Stennis Space Center. She... -

You can beat the Father’s Day and Prime Day rush with one of the best VR headset deals available, perfect for entertainment and beginners
If you’re looking for one of the best VR headsets on the market but you don’t...