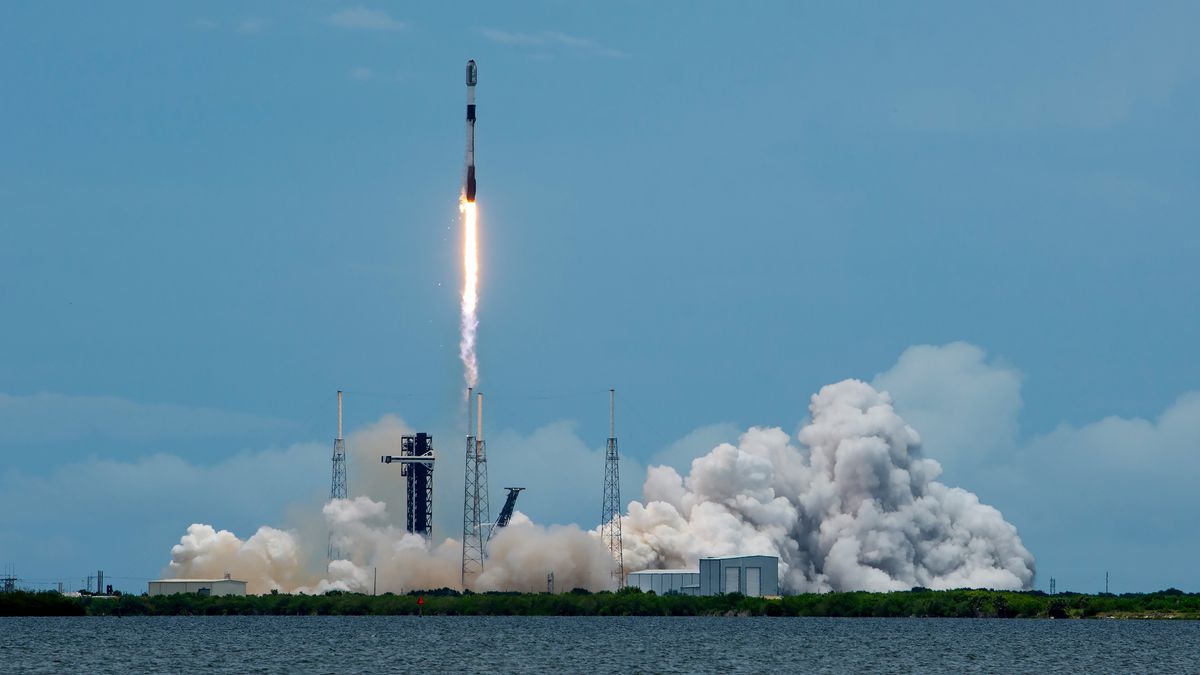
SpaceX just added another mission to its already crowded launch manifest.
Elon Musk‘s company won the launch contract for the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) JPSS-4 satellite. If all goes according to plan, JPSS-4 will lift off atop a Falcon 9 rocket from California’s Vandenberg Space Force Base in 2027.
The firm, fixed-price contract is worth $112.7 million, “which includes launch services and other mission-related costs,” NASA officials wrote in an update on Monday (July 22).
The JPSS (“Joint Polar Satellite System”) program is a cooperative effort of NOAA and NASA (which awarded the JPSS-4 launch contract on NOAA’s behalf). The constellation collects a variety of information about Earth’s land, sea and air.
“These data support NOAA’s mission for continuous observation of Earth’s environment to understand and predict changes in weather, climate, oceans and coasts to support the nation’s economy and protect lives and property,” NASA officials wrote in the same update. “NASA uses the instruments aboard the JPSS satellites to continue decades of Earth science research for the betterment of humanity.”
Three JPSS satellites have launched to date, and all remain operational today: Suomi NPP in October 2011, JPSS-1 (renamed NOAA-20 upon reaching its final orbit) in November 2017 and JPSS-2 (NOAA-21) in November 2022. All three lifted off atop United Launch Alliance rockets — a Delta II for Suomi NPP and JPSS-1 and an Atlas V for JPSS-2.
The JPSS fleet will eventually consist of five satellites; JPSS-3 is scheduled to lift off in 2032, rounding out the constellation.
Related: SpaceX: Facts about Elon Musk’s private spaceflight company
RELATED STORIES:
The Falcon 9 has already launched 69 times in 2024. But it’s grounded for the time being after suffering a failure on its most recent flight, which took place on July 11.
The rocket’s upper stage sprang a leak of liquid oxygen on that mission and could not complete an orbit-raising engine burn as planned. The Falcon 9 therefore deployed its payloads — 20 of SpaceX’s Starlink internet satellites — too low. All 20 spacecraft are presumed doomed, fated to be dragged down to a fiery death in Earth’s atmosphere.