Student-Built Capsules Endure Heat of Re-entry for NASA Science
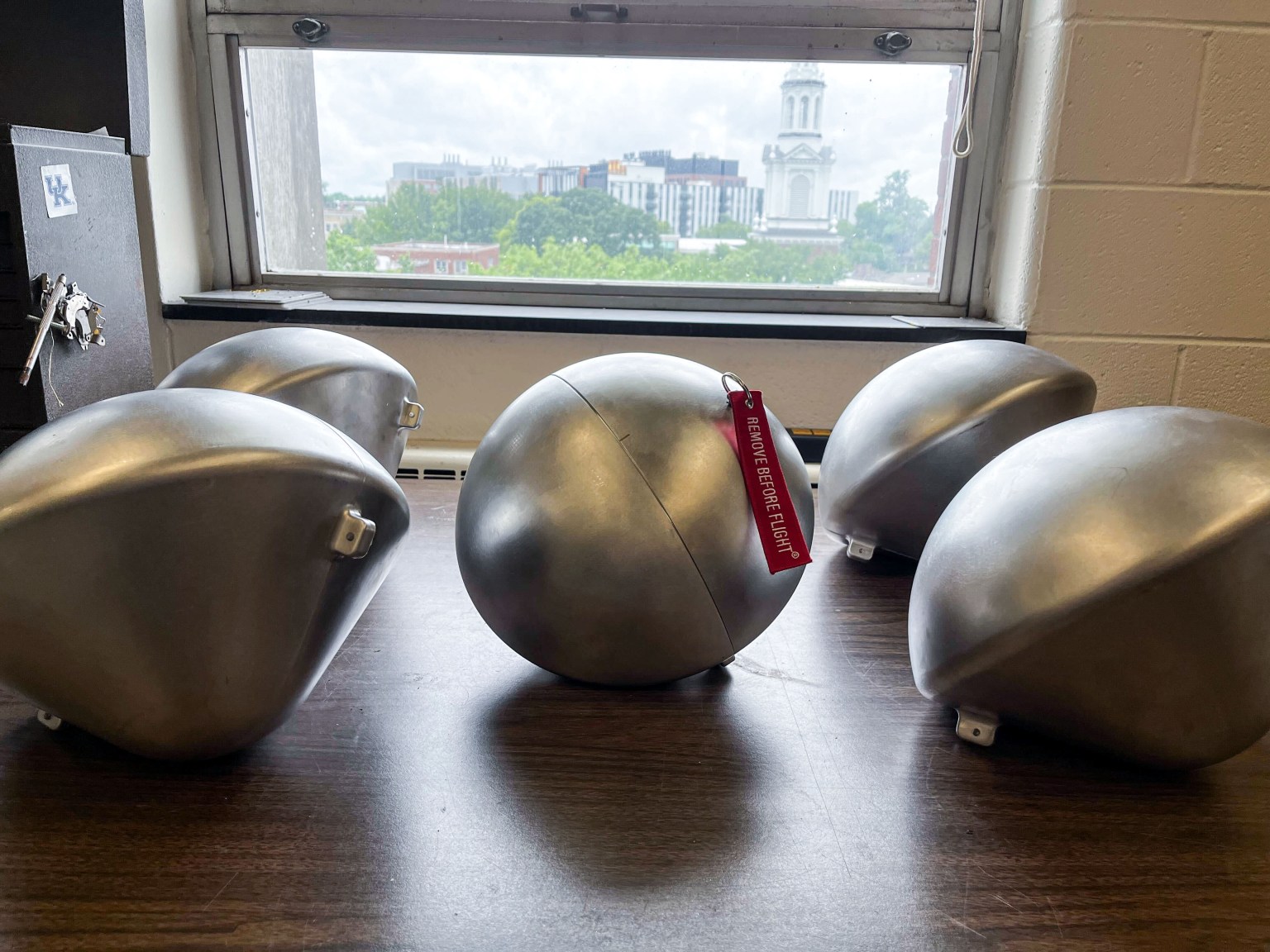

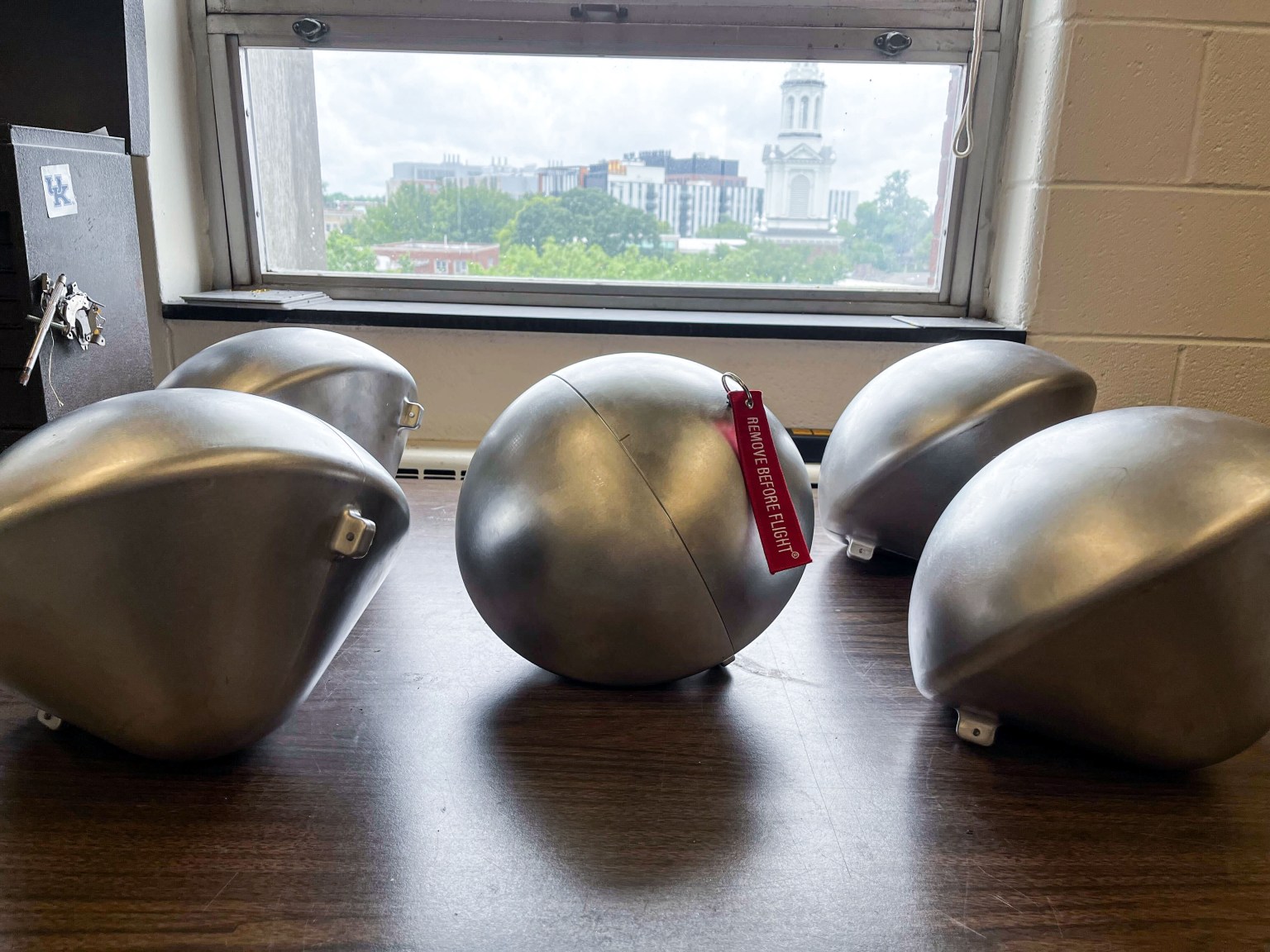
In July 2024, five student-built capsules endured the scorching heat of re-entry through Earth’s atmosphere as part of the second Kentucky Re-Entry Probe Experiment (KREPE-2). Scientists are now analyzing the data from the KREPE-2 experiments, which could advance the development of heat shields that protect spacecraft when they return to Earth.
The mission was designed to put a variety of heat shield prototypes to the test in authentic re-entry conditions to see how they would perform. These experimental capsules, which were built by students at the University of Kentucky and funded by the NASA Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR) within NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, all survived more than 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit during descent.
The football-sized capsules also successfully transmitted valuable data via the Iridium satellite network along their fiery journey. The trove of information they provided is currently being analyzed to consider in current and future spacecraft design, and to improve upon designs for future experiments.
“These data – and the instruments used to obtain the data – assist NASA with designing and assessing the performance of current and new spacecraft that transport crew and cargo to and from space,” said Stan Bouslog, thermal protection system senior discipline expert at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston who served as the agency’s technical monitor for the project.
Taking the Plunge: Communicating Through a Fiery Descent
“The only way to ‘test like you fly’ a thermal protection system is to expose it to actual hypersonic flight through an atmosphere,” Bouslog said.
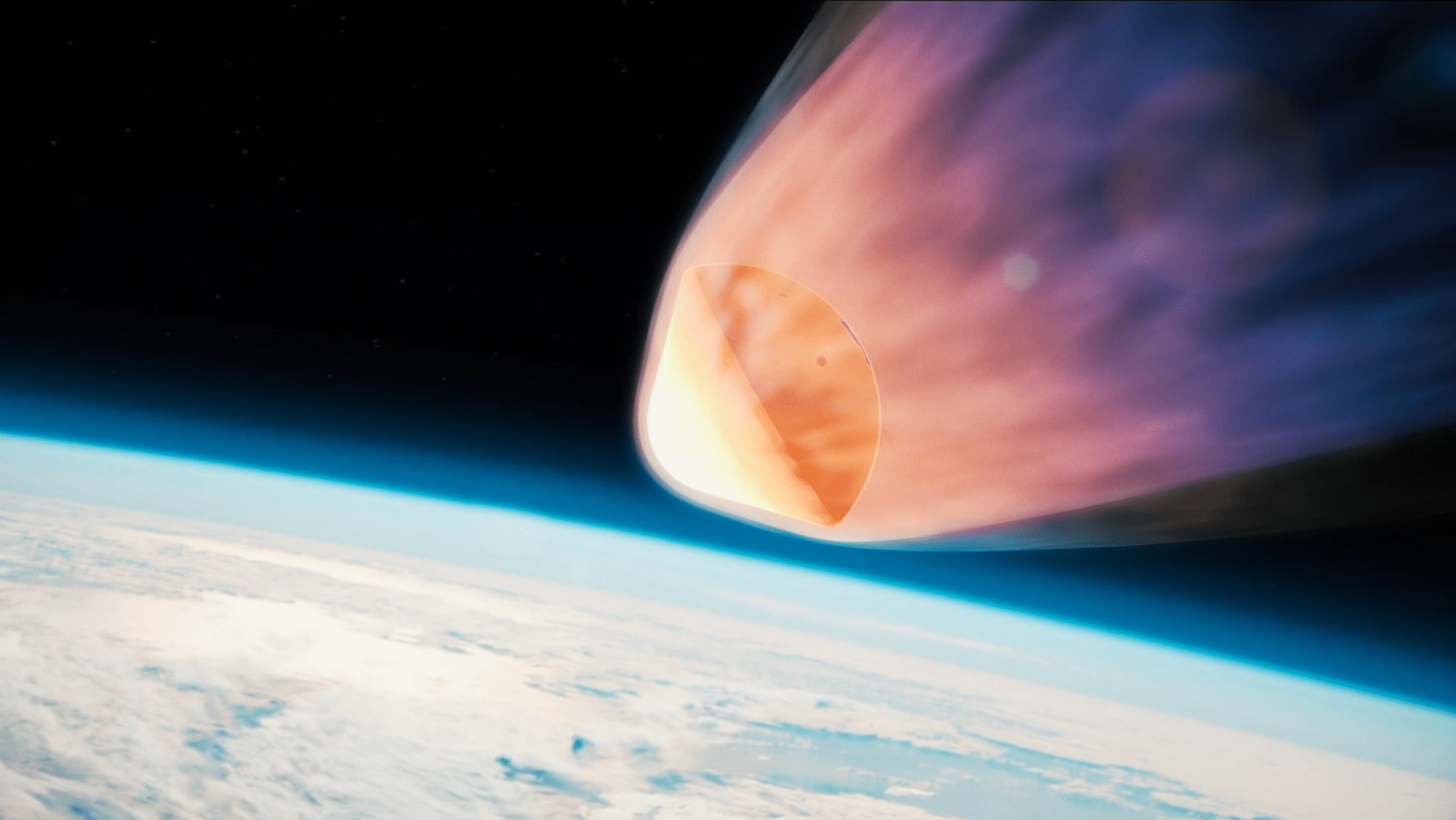
The self-contained capsules launched aboard an uncrewed Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft in January 2024 along with other cargo bound for the International Space Station. The cargo craft detached from the space station July 12 as the orbiting laboratory flew above the south Atlantic Ocean. As the Cygnus spacecraft began its planned breakup during re-entry, the KREPE-2 capsules detected a signal – a temperature spike or acceleration – to start recording data and were released from the vehicle. At that point, they were traveling at a velocity of about 16,000 miles per hour at an altitude of approximately 180,000 feet.
The University of Kentucky student team and advisors watched and waited to learn how the capsules had fared.
As the capsules descended through the atmosphere, one group watched from aboard an aircraft flying near the Cook Islands in the south Pacific Ocean, where they tracked the return of the Cygnus spacecraft. The flight was arranged in partnership with the University of Southern Queensland in Toowoomba, Queensland, Australia, and the University of Stuttgart in Stuttgart, Germany. Alexandre Martin, professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the University of Kentucky and the principal investigator for the experiment, was on that flight.
“We flew in close to the re-entry path to take scientific measurements,” Martin said, adding that they used multiple cameras and spectrometers to observe re-entry. “We now have a much better understanding of the break-up event of the Cygnus vehicle, and thus the release of the capsules.”
Meanwhile, members of the University of Kentucky’s Hypersonic Institute had gathered at the university to watch as KREPE-2 data arrived via email. All five successfully communicated their flight conditions as they hurtled to Earth.
“It will take time to extract the data and analyze it,” Martin said. “But the big accomplishment was that every capsule sent data.”
Members of the University of Kentucky student team have begun analyzing the data to digitally reconstruct the flight environment at the time of transmission, providing key insights for future computer modeling and heat shield design.
Building on Student Success
The mission builds on the accomplishments of KREPE-1, which took place in December 2022. In that experiment, two capsules recorded temperature measurements as they re-entered Earth’s atmosphere and relayed that data to the ground.
The extensive dataset collected during the KREPE-2 re-entry includes heat shield measurements, such as temperature, as well as flight data including pressure, acceleration, and angular velocity. The team also successfully tested a spectrometer that provided spectral data of the shockwave in front of a capsule.
“KREPE-1 was really to show we could do it,” Martin said. “For KREPE-2, we wanted to fully instrument the capsules and really see what we could learn.”
KREPE-3 is currently set to take place in 2026.
The ongoing project has provided valuable opportunities for the University of Kentucky student team, from undergrads to PhD students, to contribute to spaceflight technology innovation.
“This effort is done by students entirely: fabrication, running simulations, handling all the NASA reviews, and doing all the testing,” Martin said. “We’re there supervising, of course, but it’s always the students who make these missions possible.”
Related links: