Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have discovered distant, overly massive supermassive black holes in the early universe. The black holes seem way too massive compared to the mass of the stars in the galaxies that host them. In the modern universe, for galaxies close to our own Milky Way, supermassive black holes tend to have masses equal to around 0.01% of the stellar mass of their host galaxy. Thus, for every 10,000 solar masses attributed to stars in a galaxy, there is around one solar mass of…
Read MoreTag: Black Holes
Astronomers Catch Unprecedented Features at Brink of Active Black Hole
International teams of astronomers monitoring a supermassive black hole in the heart of a distant galaxy have detected features never seen before using data from NASA missions and other facilities. The features include the launch of a plasma jet moving at nearly one-third the speed of light and unusual, rapid X-ray fluctuations likely arising from near the very edge of the black hole. Radio images of 1ES 1927+654 reveal emerging structures that appear to be jets of plasma erupting from both sides of the galaxy’s central black hole following a…
Read MoreAstronaut Set to Patch NASA’s X-ray Telescope Aboard Space Station
4 min read Astronaut Set to Patch NASA’s X-ray Telescope Aboard Space Station NASA astronaut Nick Hague will install patches to the agency’s NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) X-ray telescope on the International Space Station as part of a spacewalk scheduled for Jan. 16. Hague, along with astronaut Suni Williams, will also complete other tasks during the outing. NICER will be the first NASA observatory repaired on-orbit since the last servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope in 2009. Hague and other astronauts, including Don Pettit, who is also currently on the…
Read MoreSmall satellite constellation could reveal black holes like never before
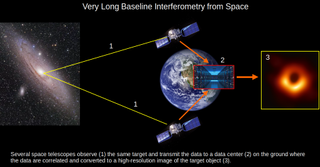
Researchers in South Korea are developing a constellation of satellites that could reveal what goes on in the vicinity of supermassive black holes like never before. The constellation, dubbed Capella, is a brainchild of Seoul National University astronomy professor Sascha Trippe. An expert in black holes, Trippe has grown frustrated with the limitations of humanity’s existing instruments for observing black holes and concerned that unless major technological advances are made, research may soon reach a “dead end.” When the first-ever image of a supermassive black hole — the one at…
Read MoreBlack hole paradox that stumped Stephen Hawking may have a solution, new paper claims
Nothing is supposed to escape a black hole’s event horizon — yet new research suggests it may secretly leak information. That leakage would appear in subtle signatures in gravitational waves, and now we know how to look for them, the study authors say. In 1976, Stephen Hawking rocked the astrophysics world with his discovery that black holes aren’t entirely black. Instead, they emit tiny amounts of radiation and, given enough time, can give off so much that they disappear entirely. But this introduced a massive problem. Information flows into black…
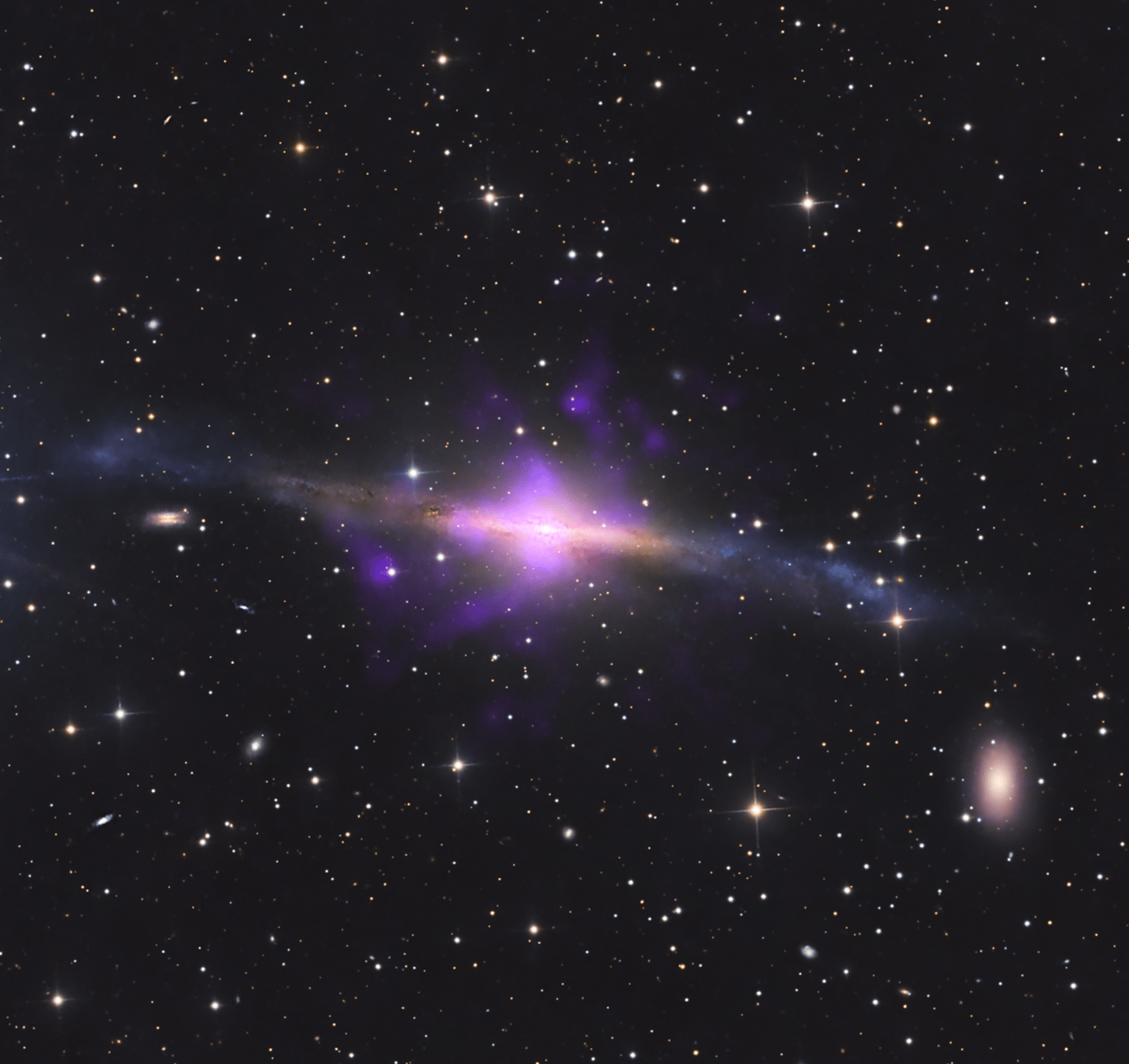
Read MoreNASA Finds ‘Sideways’ Black Hole Using Legacy Data, New Techniques
4 Min Read NASA Finds ‘Sideways’ Black Hole Using Legacy Data, New Techniques Image showing the structure of galaxy NGC 5084, with data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory overlaid on a visible-light image of the galaxy. Chandra’s data, shown in purple, revealed four plumes of hot gas emanating from a supermassive black hole rotating “tipped over” at the galaxy’s core. Credits: X-ray: NASA/CXC, A. S. Borlaff, P. Marcum et al.; Optical full image: M. Pugh, B. Diaz; Image Processing: NASA/USRA/L. Proudfit NASA researchers have discovered a perplexing case of a black hole that appears to…
Read MoreAstronomers discover 1st binary stars orbiting supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way
Astronomers have discovered the first binary stars orbiting a supermassive black hole. The stellar pairing in question orbits the cosmic titan at the heart of the Milky Way, Sagittarius A*. The binary stars, designated D9, were found in data collected by the Very Large Telescope (VLT), located atop Cerro Paranal, an 8,645-foot-tall (2,635-meter) mountain in Chile’s Atacama Desert. By measuring their velocity, the team behind the discovery was surprised to find they were two stars, not one. The fact that these binary stars so near Sgr A* have survived the…
Read More1st monster black hole ever pictured erupts with surprise gamma-ray explosion
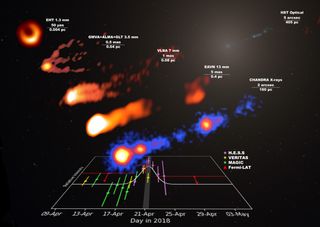
In 2018, it was revealed that a pioneering telescope the size of Earth had taken, for the first time, an image of a black hole. That same instrument, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT), has now witnessed the same black hole erupt with a powerful and unexpected explosion. Scientists hope that by studying this emission, they can better model the structure surrounding supermassive black holes. The flare, which lasted for about three days in April and May 2018, erupted from the supermassive black hole designated M87*, which liesat the heart of…
Read MoreUnusual black hole light bursts puzzle astronomers: ‘We are finding a lot of weird stuff’
Astronomers have stumbled upon a pair of massive black holes in a distant galaxy that are triggering unusual bursts of light. These bright emissions, which appear to peak on a regular cycle, may be caused by the black hole duo disrupting a massive gas cloud — a phenomenon researchers say is the first of its kind to be detected. The cosmic behemoths reside at the center of a galaxy named 2MASX J21240027+3409114, located roughly 1 billion light-years away in the northern constellation Cygnus. These black holes complete an orbit once…
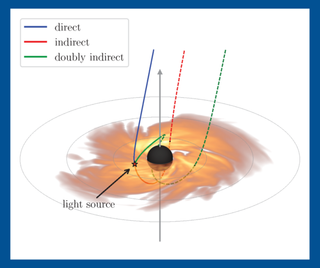
Read MoreA black hole’s secrets could hide in its dizzying light ‘echoes’
To measure the masses and spins of black holes, scientists want to follow clues left behind by light that takes a round-a-bout journey, bends around these voids, and ultimately shines toward us. The crew, from Princeton University and Los Alamos National Laboratory, has performed complex computer simulations to show how two telescopes — one on Earth, the other in space — can work together to make the idea a reality. In other words, these devices could help us detect light that has basically been on a trip around a black…
Read More