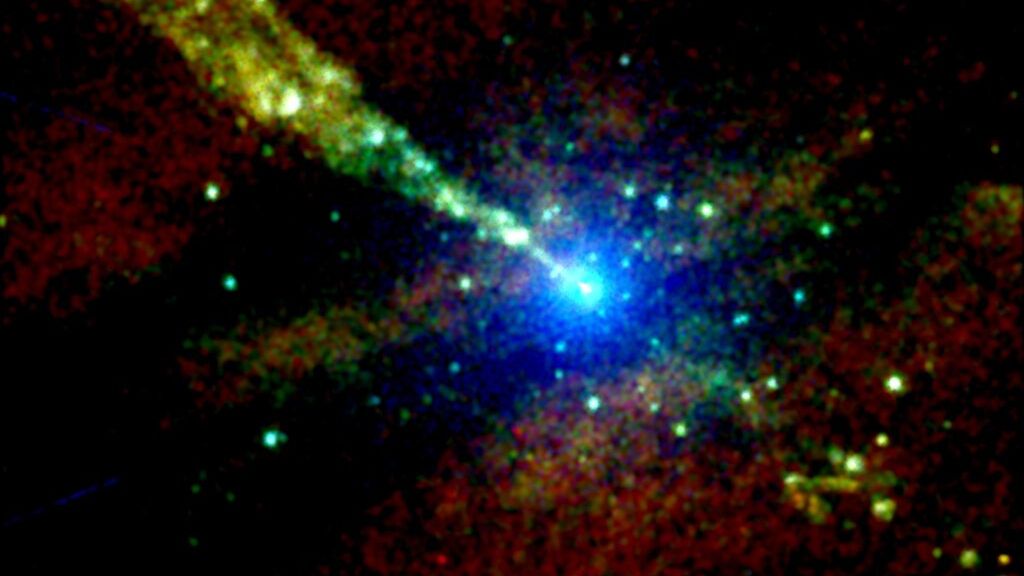
Black holes exert a tremendous influence on their surroundings, meaning that when they spin, they literally drag the very fabric of space and time around with them. That means nothing can sit still around a rotating black hole, including the “plates” that these cosmic titans feed from. Those flattened clouds of gas and dust surrounding supermassive black holes are known as accretion disks. Around some supermassive black holes, the churning of these disks is one of the most efficient ways of converting energy in the known universe — changing gravitational…
Read MoreTag: Black Holes
NASA’s Chandra X-ray telescope sees ‘knots’ blasting from nearby black hole jets
Astronomers have scoured decades-old data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, finding bright, lumpy features dotting a jet of energy spit out by a nearby black hole. Puzzlingly, the “knots” clock a faster speed when seen in X-rays than they do in radio wavelengths. scientists said. “The X-ray data traces a unique picture that you can’t see in any other wavelength,” study lead author David Bogensberger, an astrophysicist at the University of Michigan, who led the new study, said in a recent news release. “We’ve shown a new approach to studying…
Read MoreBlack holes that form in ‘reverse Big Bang replays’ could account for dark energy
Scientists have strengthened the potential connection between dark energy and black holes. New research suggests that as more black holes were born in “little Big Bang reverse replays” in the 14.6 billion-year-old cosmos, the strength of dark energy grew to dominance and continues to change to this day. Dark energy is the placeholder name given to the mysterious force driving the acceleration of the universe’s expansion in its current epoch. It is troubling because scientists have no idea what dark energy is, yet it dominates our universe, accounting for around…
Read More1st image of our Milky Way’s black hole may be inaccurate, scientists say
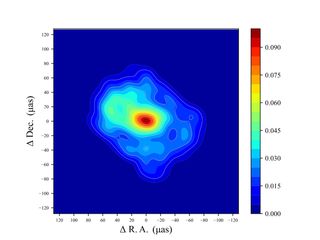
What does the supermassive black hole lurking at the center of our galaxy look like?It’s a deceptively simple question. Although our local cosmic abyss, named Sgr A* (short for Sagittarius A*), resides just 26,000 light-years from Earth, it has proven to be a very difficult object to image. This is thanks in part to material whipping around it at near light-speeds. However, after years of trying, scientists with the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) project succeeded in 2022.The black hole’s silhouette emerged from the shadows, appearing like a fuzzy orange doughnut.…
Read MoreJames Webb Space Telescope sees lonely supermassive black hole-powered quasars in the early universe
Using the James Webb Space Telescope, astronomers have peered back 13 billion years to discover surprisingly lonely supermassive black hole-powered quasars. The James Webb Space Telescope’s (JWST) observations are confusing because isolated black holes should struggle to gather enough mass to reach supermassive status, especially just a few hundred million years after the Big Bang. The discovery further muddies the waters when it comes to the puzzle of how some black holes grew to masses equivalent to millions or even billions of suns when the universe was less than a…
Read MoreWhat happens when black holes merge?
Black hole mergers are beautiful — and some of the most violent events in the cosmos. Here’s how the process unfolds. The story begins with two black holes orbiting far from each other in long, lazy circles. They could have been born as a binary pair of stars, or they may have just randomly encountered each other in the depths of interstellar space. Either way, to merge, they must get close, which means losing a lot of orbital energy. The first step in stealing energy from the system is through…
Read MoreAncient supermassive black hole is blowing galaxy-killing wind, James Webb Space Telescope finds
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have spotted the earliest powerful “galaxy-size” wind blowing from a feeding supermassive black hole-powered quasar. The powerful wind is pushing gas and dust from its galaxy at incredible speeds, killing star birth in its host galaxy. This quasar, designated J1007+2115, is so distant that it is seen as it was just 700 million years after the Big Bang — when the 13.8 billion-year-old universe was just around 5% of its current age. Though this makes J1007+2115 just the third-earliest quasar ever seen,…
Read MoreA ‘primordial’ black hole may zoom through our solar system every decade
If microscopic black holes born a fraction of a second after the Big Bang exist, as some researchers suspect, then at least one may fly through the solar system per decade, generating tiny gravitational distortions that scientists can detect, a new study finds. These findings suggest that if astronomers can discover and confirm the existence of such gravitational disruptions, they may be able to solve the mystery behind the nature of dark matter, the unseen material that many researchers suspect makes up about five-sixths of all matter in the cosmos.…
Read MoreScientists make lab-grown black hole jets
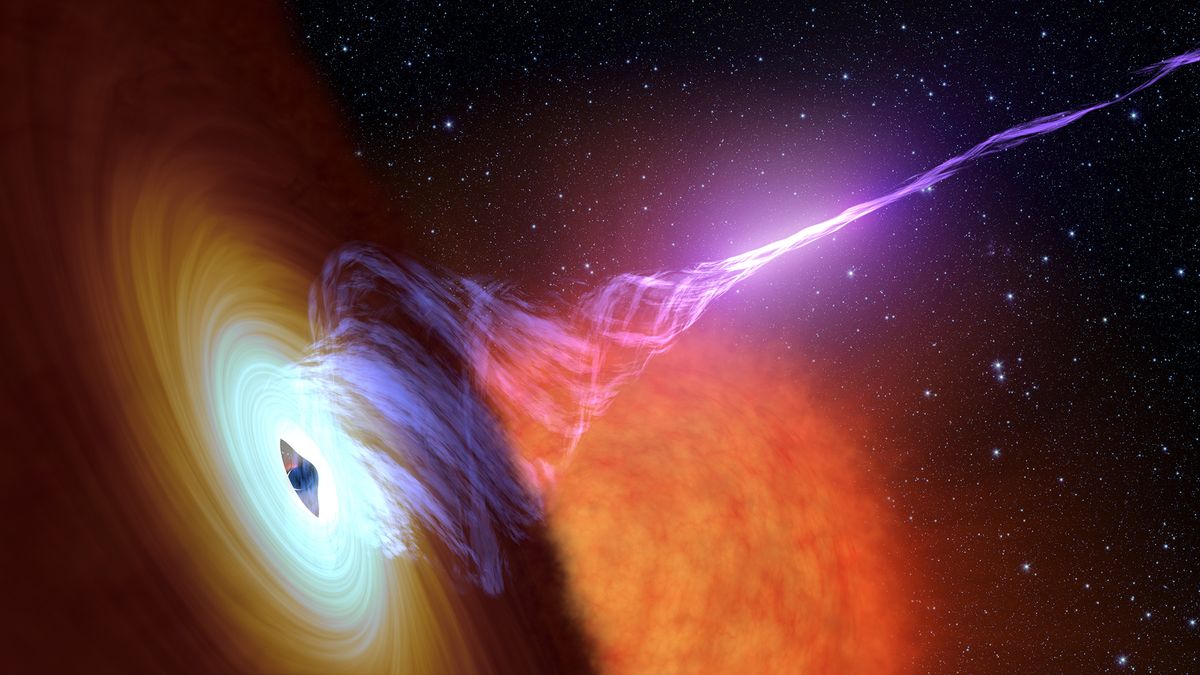
An experiment using beams of protons to probe how plasma and magnetic fields interact may have just solved the mystery of how quasars and other active supermassive black holes unleash their relativistic jets. Let’s picture the scene at the heart of a quasar. A supermassive black hole, perhaps hundreds of millions — or even billions — of times the mass of our sun, is ravenously devouring matter that is streaming into its maw from a spiraling, ultra-hot disk. That charged matter is called plasma, and it gets gravitationally drawn into…
Read MoreSupermassive black holes have masses of more than a million suns – but their growth has slowed as the universe aged
This article was originally published at The Conversation. The publication contributed the article to Space.com’s Expert Voices: Op-Ed & Insights. Fan Zou is a graduate student at Penn State University while W. Neil Brandt is a professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State. Black holes are remarkable astronomical objects with gravity so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape them. The most gigantic ones, known as “supermassive” black holes, can weigh millions to billions times the mass of the Sun. These giants usually live in the centers of galaxies. Our own galaxy, the Milky…
Read More