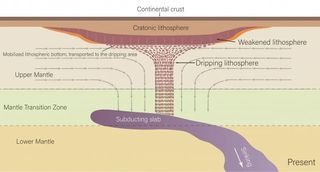
An ancient slab of Earth’s crust buried deep beneath the Midwest is sucking huge swatches of present-day’s North American crust down into the mantle, researchers say. The slab’s pull has created giant “drips” that hang from the underside of the continent down to about 400 miles (640 kilometers) deep inside the mantle, according to a new study. These drips are located beneath an area spanning from Michigan to Nebraska and Alabama, but their presence appears to be impacting the entire continent. The dripping area looks like a large funnel, with…
Read MoreTag: Earth
Earth’s sea ice hits all-time low, NASA satellites reveal
New research from NASA and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) in Colorado measured Arctic sea ice cover on March 22, during what should’ve been its annual peak. In conclusion, the agency reported seeing 5.53 million square miles (14.33 million square kilometers) of sea ice — for context, that’s the lowest Arctic winter sea ice levels have ever been. To make matters worse, NASA scientists also discovered that, this year, summer ice in the Antarctic retreated to 764,000 square miles (1.98 million square kilometers) as of March 1,…
Read MoreNext-Generation Water Satellite Maps Seafloor From Space
6 min read Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater) Located off the coast of Ecuador, Paramount seamount is among the kinds of ocean floor features that certain ocean-observing satellites like SWOT can detect by how their gravitational pull affects the sea surface. NOAA Okeanos Explorer Program More accurate maps based on data from the SWOT mission can improve underwater navigation and result in greater knowledge of how heat and life move around the world’s ocean. There are better maps of the Moon’s surface than of the bottom of…
Read MoreNASA Researchers Study Coastal Wetlands, Champions of Carbon Capture
Earth (ESD) Earth Explore Explore Earth Science Climate Change Air Quality Science in Action Multimedia Image Collections Videos Data For Researchers About Us 8 Min Read NASA Researchers Study Coastal Wetlands, Champions of Carbon Capture Florida’s coastal wetlands are a complex patchwork of ecosystem — consisting of sawgrass marshland, hardwood hammocks, freshwater swamps, and mangrove forests. Credits: NASA/ Nathan Marder Across the street from the Flamingo Visitor’s Center at the foot of Florida’s Everglades National Park, there was once a thriving mangrove population — part of the largest stand of…
Read MoreNASA-ISRO Mission Will Map Farmland From Planting to Harvest
The NISAR mission will help map crops and track their development through the entire growing season. Using synthetic aperture radar, the satellite will be able to observe both small plots of farmland and monitor trends across broad regions, gathering data to in-form agricultural decision making. Adobe Stock/Greg Kelton Data from the NISAR satellite will be used to map crop growth, track plant health, and monitor soil moisture — offering detailed, timely information for decision making. When it launches this year, the NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) satellite will provide a…
Read MoreWorld’s largest iceberg runs aground in South Atlantic after 1,200-mile journey (satellite photos)
Earth’s largest iceberg has run aground off the coast of South Georgia Island, a common rendezvous spot for large icebergs, new satellite images show. Measuring 1,240 square miles (3,460 square kilometers), the Antarctic iceberg A-23A has come to a grinding halt after a long and winding journey across the Scotia Sea, also known as “iceberg alley.” Satellite images taken at the beginning of March show the iceberg parked on a shallow underwater shelf off the coast of South Georgia Island, which is a British overseas territory in the South Atlantic…
Read MoreScientists discover Earth’s oldest impact crater in Australia
Geologists have discovered the world’s oldest known impact crater; it sits in the heart of Western Australia’s ancient Pilbara region. An analysis of rock layers in the region suggests a crater at least 62 miles (100 kilometers) wide was carved after a large space rock struck Earth roughly 3.47 billion years ago, when our planet was almost completely covered in water. The discovery pushes back the record for the oldest impact crater on Earth by more than 1 billion years — the previous record holder, the Yarrabubba impact structure, also…
Read MoreScientists warn of consequences as over 800 NOAA workers are fired: ‘Censoring science does not change the facts’
Scientists warn that the Trump administration’s abrupt firing of hundreds of weather forecasters and climate experts across NOAA will curtail important climate research and could result in preventable deaths during extreme weather events and related disasters. Over 800 employees across most divisions of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) — a premier U.S. federal agency at the forefront of climate research that provides timely weather forecasts to the public for free — were dismissed in mass layoffs that began Thursday afternoon (Feb. 27). The cuts targeted probationary employees, a…
Read MoreOur Pale Blue Dot
This updated version of “the Pale Blue Dot,” made for the photo’s 30th anniversary in 2020, uses modern image-processing software and techniques to revisit the well-known Voyager view while attempting to respect the original data and intent of those who planned the images. NASA/JPL-Caltech Earth is but a tiny light blue dot in this 30th anniversary version of the iconic “Pale Blue Dot” image. The original photo, taken by NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft on Feb. 14, 1990, is now 35 years old. Voyager 1 was 3.7 billion miles (6 billion…
Read MoreContinent-size blobs in Earth’s mantle are a billion years old, ancient crystals reveal
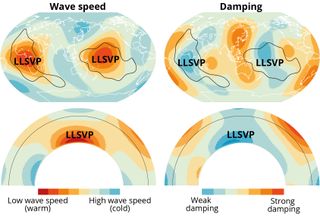
Continent-size islands deep inside Earth’s mantle could be more than a billion years old, a new study finds. Known as large low-seismic-velocity provinces (LLSVPs), these blobs are both hotter and older than nearby areas of the mantle. The findings, published Jan. 22 in the journal Nature, shed light on Earth’s deep interior and could help explain how the mantle moves over time. Scientists have known about these LLSVPs for a few decades. The two giant blobs — one beneath the Pacific Ocean and one beneath Africa — lie at the…
Read More