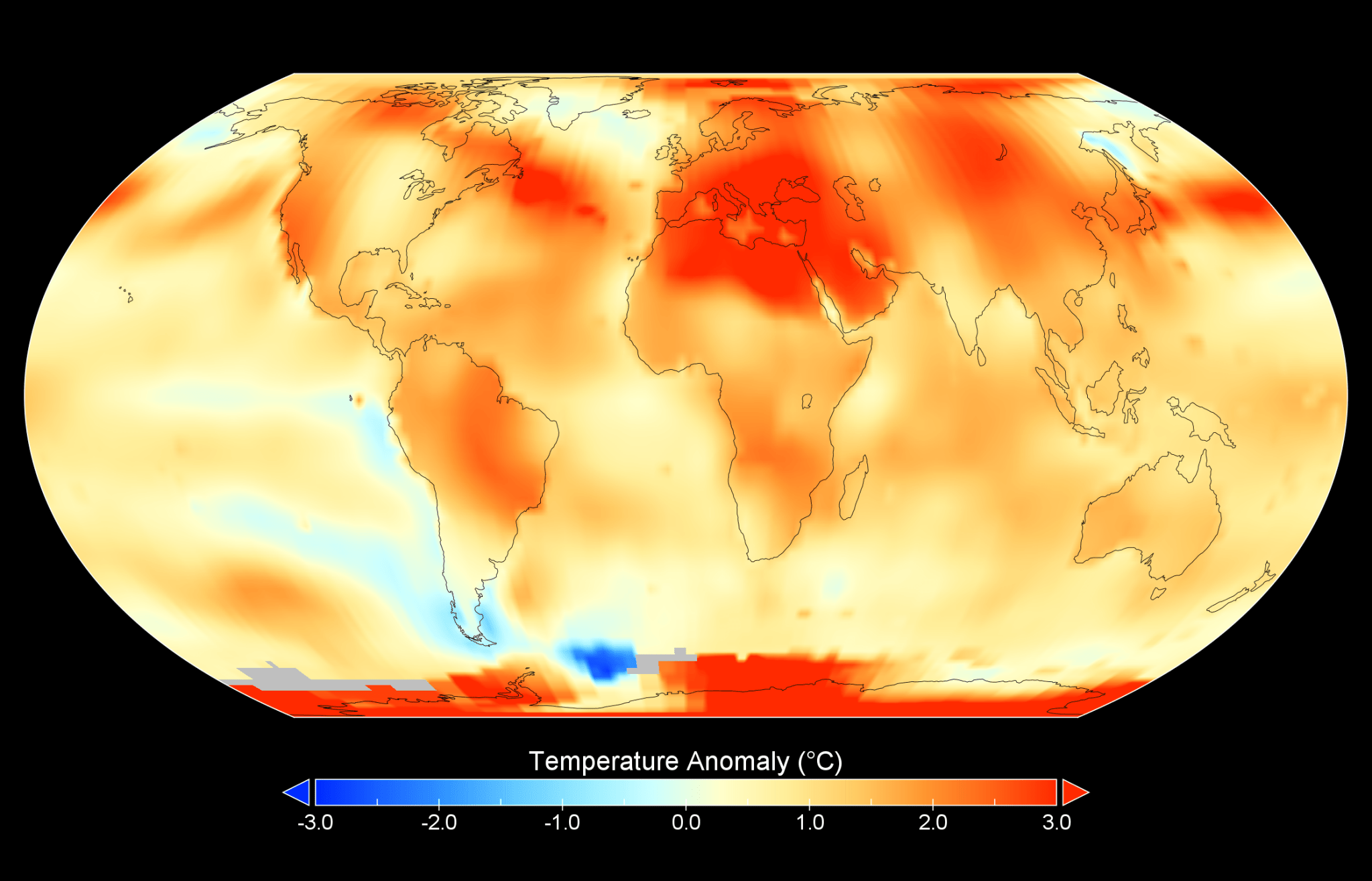
This map depicts global temperature anomalies for meteorological summer in 2024 (June, July, and August). It shows how much warmer or cooler different regions of Earth were compared to the baseline average from 1951 to 1980. (Credit: NASA/NOAA) Climate researchers from NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) will release their annual assessments of global temperatures and discuss the major climate trends of 2024 during a media briefing at 12 p.m. EST Friday, Jan. 10. NASA will share the briefing on the agency’s website at: https://www.nasa.gov/live. Participants will include:…
Read MoreTag: Earth
‘Ambitious climate action is more urgent than ever:’ 3 Climate records broken in 2024
The year 2024 has been another challenging one for Earth’s climate, marked by record temperatures, extreme weather events, and urgent warnings from scientists about the accelerating pace of global warming. An analysis by the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), the European Union agency that tracks global warming, suggests this year will be the hottest since instrument record keeping began more than a century ago — beating climate records set just last year. 2024 will also be the first calendar year in which the global average temperature exceeded 1.5 degrees Celsius…
Read MoreJust a fraction of the hydrogen hidden beneath Earth’s surface could power Earth for 200 years, scientists find
A mountain of hydrogen is lurking beneath Earth’s surface — and scientists say that just a fraction of it could break our dependence on fossil fuels for 200 years. New research suggests the planet holds around 6.2 trillion tons (5.6 trillion metric tons) of hydrogen in rocks and underground reservoirs. That’s roughly 26 times the amount of oil known to be left in the ground (1.6 trillion barrels, each weighing approximately 0.15 tons) — but where these hydrogen stocks are located remains unknown. Most of the hydrogen is likely too…
Read MoreNASA Accelerates Space Exploration, Earth Science for All in 2024
With a look back at 2024, NASA is celebrating its many innovative and inspiring accomplishments this year including for the first time, landing new science and technology on the Moon with an American company, pushing the boundaries of exploration by launching a new mission to study Jupiter’s icy moon Europa; maintaining 24 years of continuous human exploration off the Earth aboard the International Space Station, and unveiling the first look at its supersonic quiet aircraft for the benefit of humanity. The agency also shared the wonder of a total eclipse…
Read MoreDeclassified spy satellite images reveal 1,400-year-old battle site in Iraq that set off the Muslim conquest
Declassified spy images of Iraq have helped archaeologists find a historic Islamic battlefield. Upon analyzing the images, which were taken in 1973 by a U.S. satellite system named KH-9 (Hexagon), the team found remnants of a 1,400-year-old settlement. This helped them match the site to the lost location of the Battle of al-Qadisiyyah, the researchers reported in a study published Nov. 12 in the journal Antiquity. The Battle of al-Qadisiyyah took place in A.D. 636 or 637 between the Arab Muslim army and the Sasanian Empire, which ruled the area…
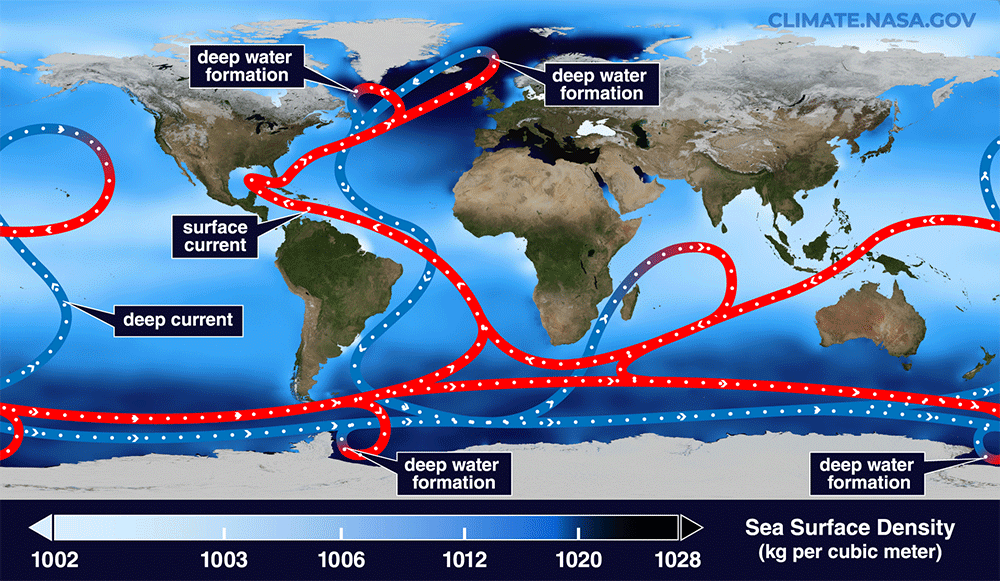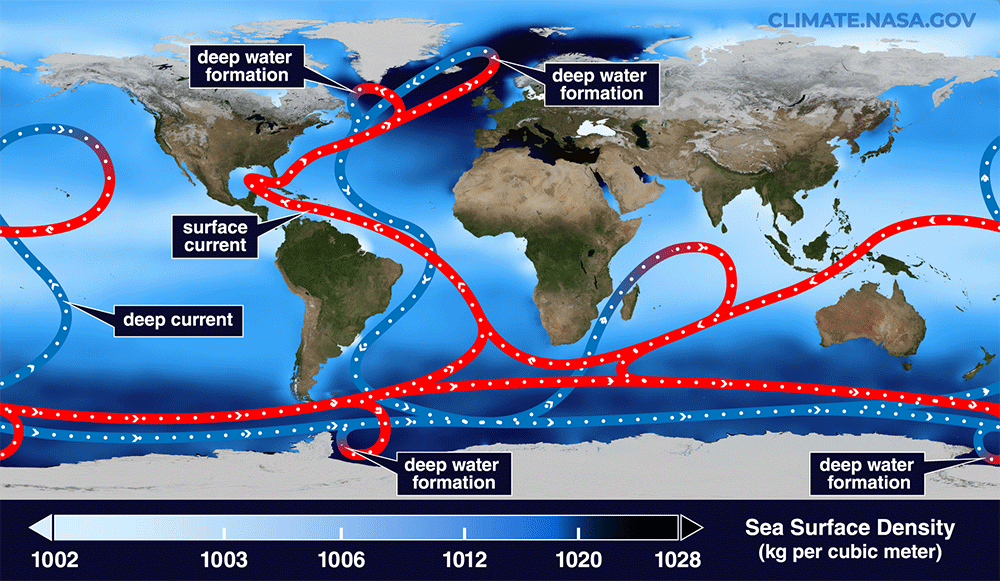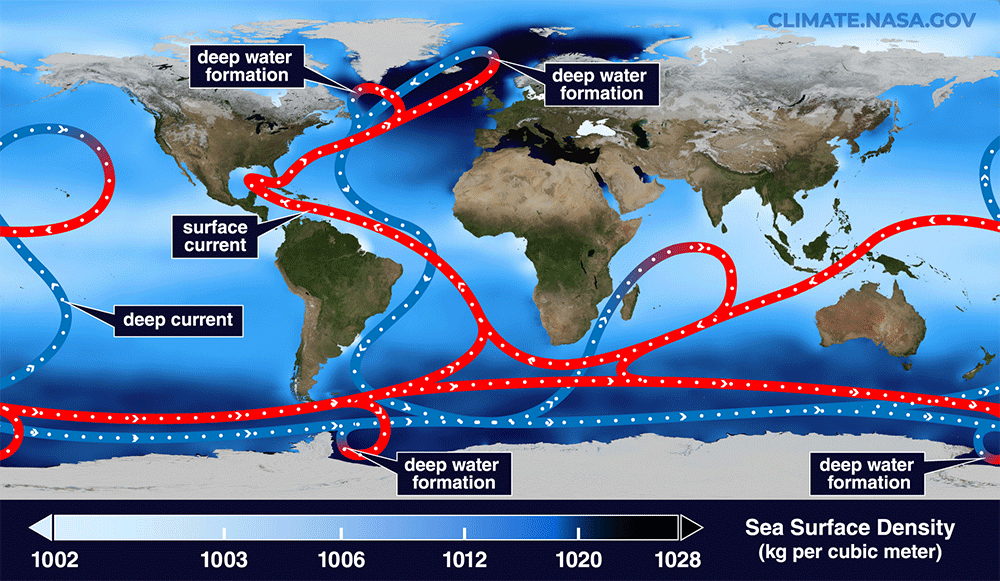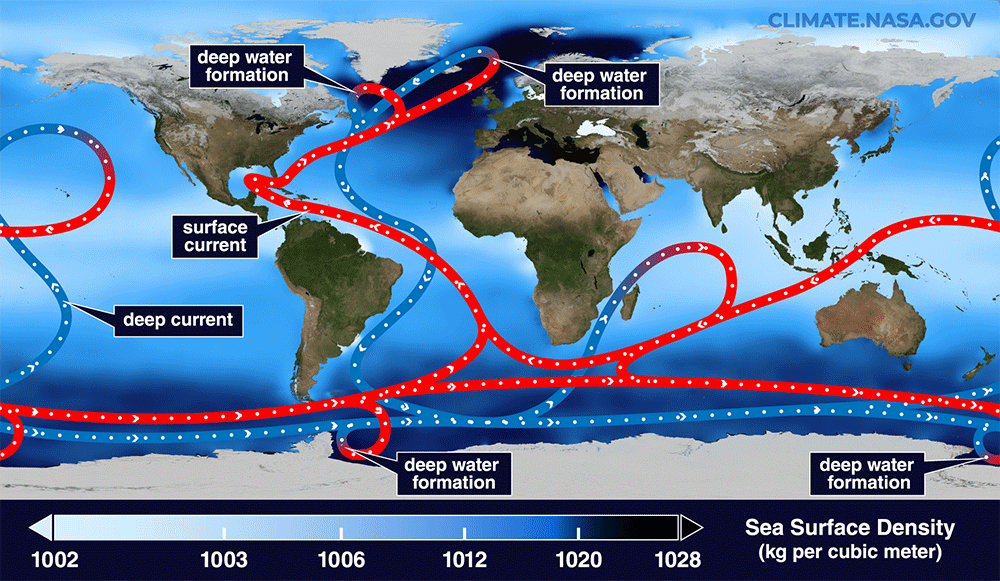
Read MoreThis spot will be key to the inevitable collapse of a key Atlantic current
Scientists have pinpointed the ocean engine with the biggest role in driving key Atlantic currents that regulate Earth’s climate, new research suggests. The Irminger Sea off southeastern Greenland is where warm waters that transport heat northwards from the Southern Hemisphere sink and then return south along the bottom of the ocean. As such, this region plays a critical role in powering the ocean conveyor belt known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). “The key finding of this study is that the Irminger Basin (eastern Greenland) plays a crucial role…
Read MoreNASA AI, Open Science Advance Disaster Research and Recovery
4 min read NASA AI, Open Science Advance Disaster Research and Recovery Hurricane Ida is pictured as a category 2 storm from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above the Gulf of Mexico. In the foreground is the Canadarm2 robotic arm with Dextre, the fine-tuned robotic hand, attached. NASA By Lauren Perkins When you think of NASA, disasters such as hurricanes may not be the first thing to come to mind, but several NASA programs are building tools and advancing science to help communities make more informed…
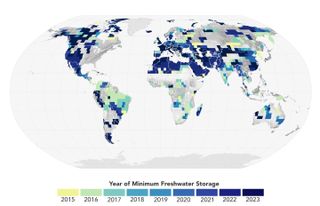
Read MoreNASA satellites reveal Earth’s continents are getting drier
The amount of freshwater found on our planet has dropped significantly in the last decade, NASA satellites have found. An international team of scientists reviewed observations taken by the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellites operated by NASA, the German Aerospace Center and the German Research Center for Geosciences. The data collected by GRACE revealed that beginning in May 2014, there was a plunge in Earth’s freshwater supply, and the planet has still not recovered. The researchers suggest that this evidence could also mean Earth is undergoing a drier…
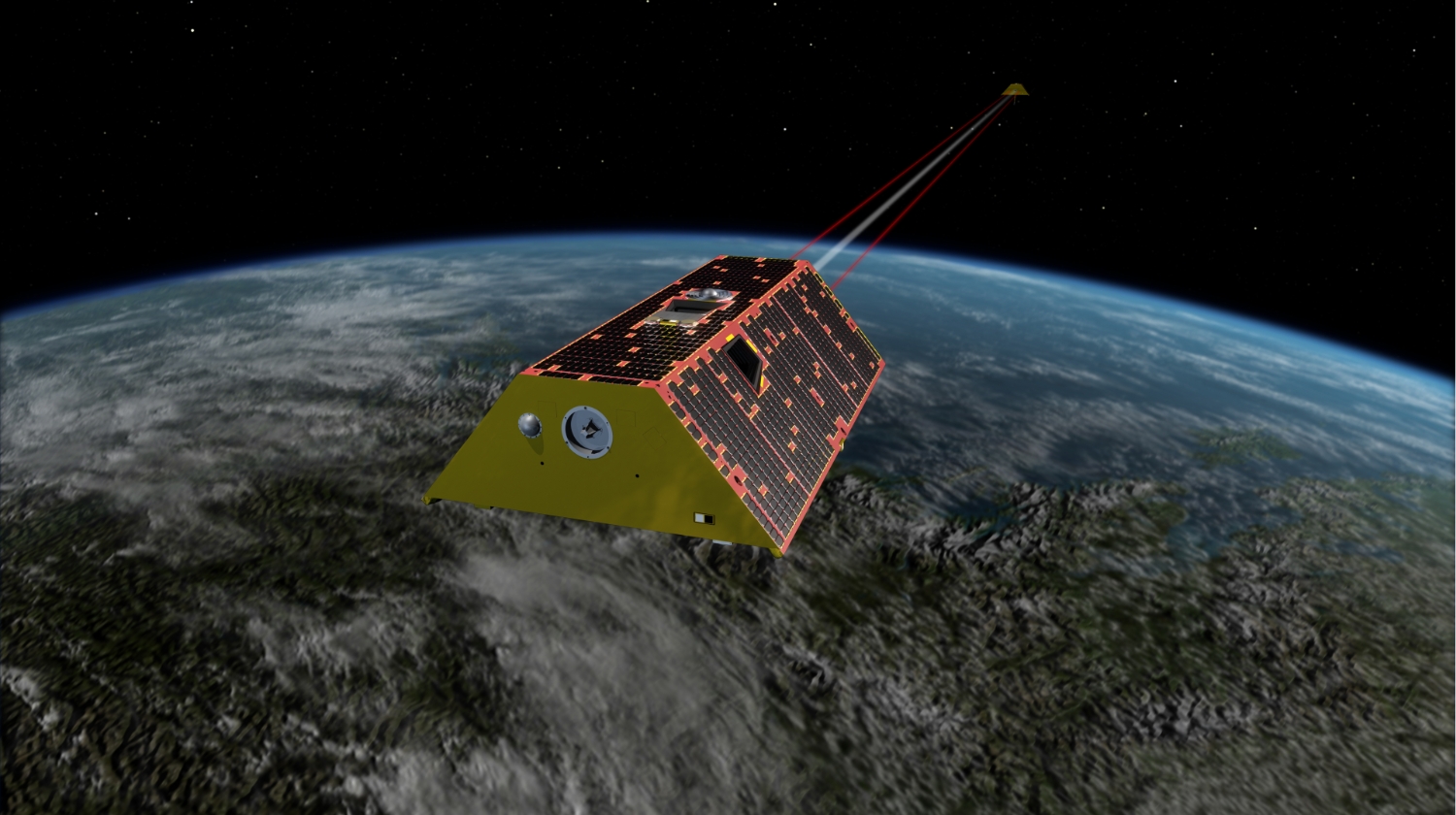
Read MoreNASA Satellites Reveal Abrupt Drop in Global Freshwater Levels
4 min read NASA Satellites Reveal Abrupt Drop in Global Freshwater Levels Earth (ESD) Earth Home Explore Climate Change Science in Action Multimedia Data For Researchers GRACE satellites measure gravity as they orbit the planet to reveal shifting levels of water on the Earth (artist’s concept). NASA/JPL-Caltech An international team of scientists using observations from NASA-German satellites found evidence that Earth’s total amount of freshwater dropped abruptly starting in May 2014 and has remained low ever since. Reporting in Surveys in Geophysics, the researchers suggested the shift could indicate Earth’s…
Read MoreHurricane Helene’s Gravity Waves Revealed by NASA’s AWE
2 min read Hurricane Helene’s Gravity Waves Revealed by NASA’s AWE On Sept. 26, 2024, Hurricane Helene slammed into the Gulf Coast of Florida, inducing storm surges and widespread impacts on communities in its path. At the same time, NASA’s Atmospheric Waves Experiment, or AWE, recorded enormous swells in the atmosphere that the hurricane produced roughly 55 miles above the ground. Such information helps us better understand how terrestrial weather can affect space weather, part of the research NASA does to understand how our space environment can disrupt satellites, communication…
Read More