A subduction zone below the Gibraltar Strait is creeping westward and could one day “invade” the Atlantic Ocean, causing the ocean to slowly close up, new research suggests. The subduction zone, also known as the Gibraltar arc or trench, currently sits in a narrow ocean corridor between Portugal and Morocco. Its westward migration began around 30 million years ago, when a subduction zone formed along the northern coast of what is now the Mediterranean Sea, but it has stalled in the last 5 million years, prompting some scientists to question whether…
Read MoreTag: Earth
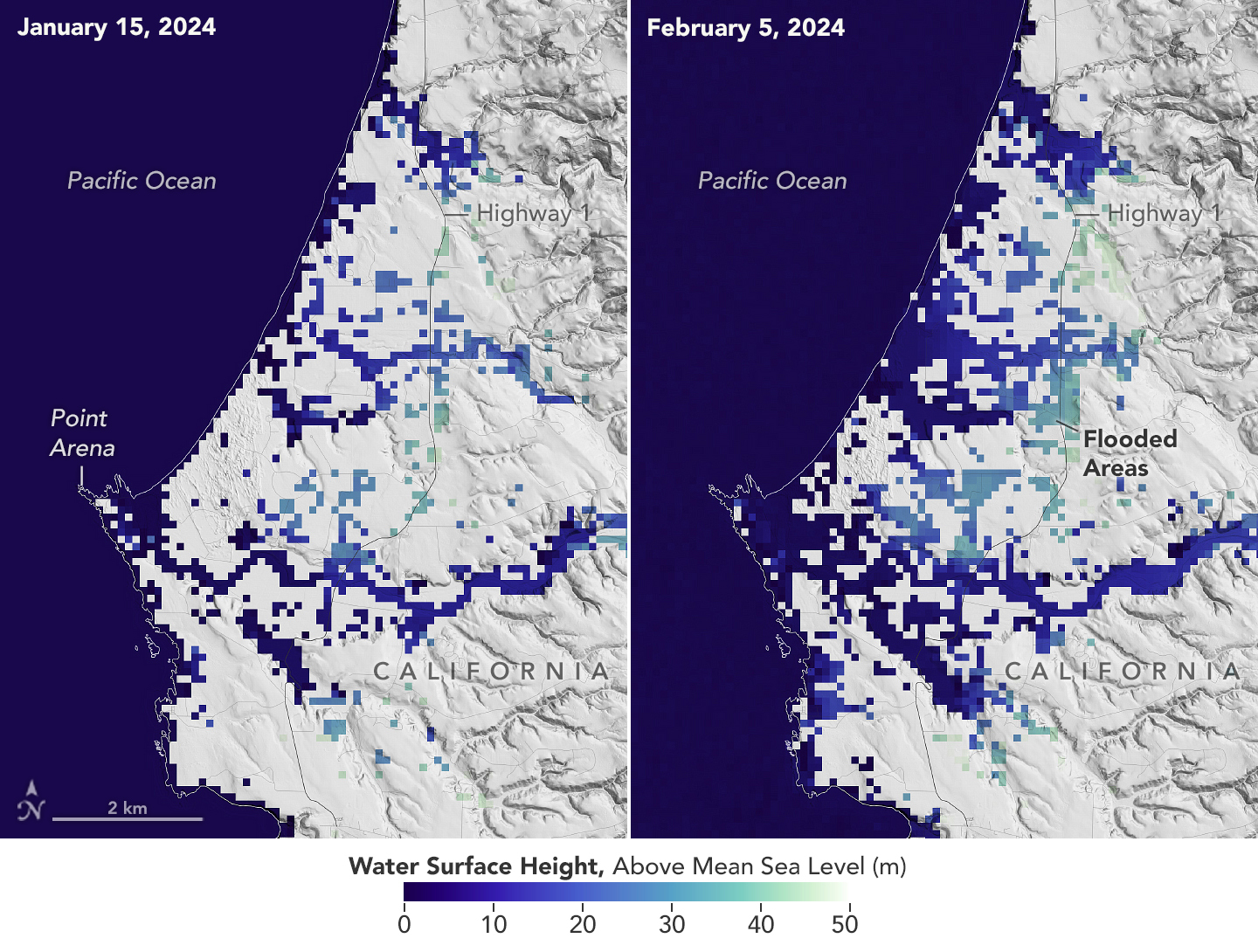
SWOT Satellite Catches Coastal Flooding During California Storms
4 min read Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater) This image shows SWOT satellite data for water surface height in part of Mendocino County, Northern California, on Jan. 15, before several atmospheric rivers arrived, and on Feb. 4, after the first storms. Light blue and green indicate the highest water levels relative to mean sea level. (Inland water heights include the underlying ground elevation.) NASA/JPL-Caltech Operated by NASA and the French space agency, the Surface Water and Ocean Topography mission provides a new view of water on land,…
Read MoreSpaceX rocket launches pioneering methane-tracking satellite to orbit
A new satellite that will track climate-heating methane emissions from oil and gas companies around the world launched this week from California’s Vandenberg Space Force Base. The washing-machine-sized satellite, named MethaneSAT, lifted off Monday (March 4) atop a Falcon 9 rocket, one of 53 payloads on SpaceX’s Transporter-10 rideshare mission. MethaneSAT is designed to ultimately help policymakers independently verify industry reports by pinpointing hotspots of methane, the invisible but potent greenhouse gas, which traps much more heat in Earth’s atmosphere per molecule than carbon dioxide. MethaneSAT, the first satellite by…
Read MoreCan Volcanic Super Eruptions Lead to Major Cooling? Study Suggests No
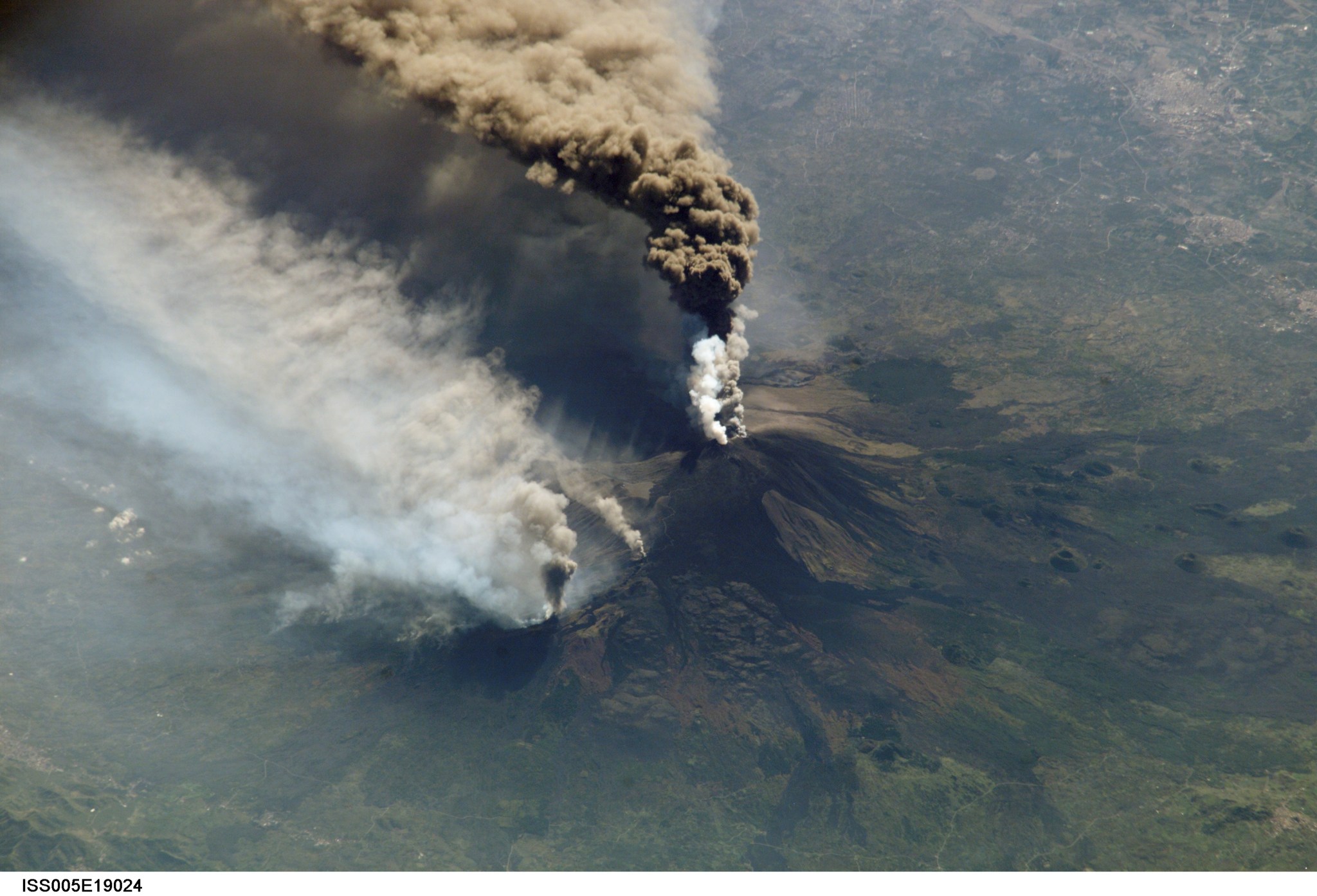
Some 74,000 years ago, the Toba volcano in Indonesia exploded with a force 1,000 times more powerful than the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. The mystery is what happened after that – namely, to what degree that extreme explosion might have cooled global temperatures. Crew aboard the International Space Station photographed the eruption of Mount Etna in Sicily in October 2002. Ashfall was reported more than 350 miles away. When it comes to explosive power, however, no eruption in modern times can compare with a super eruption – which…
Read MoreShanghai from Space
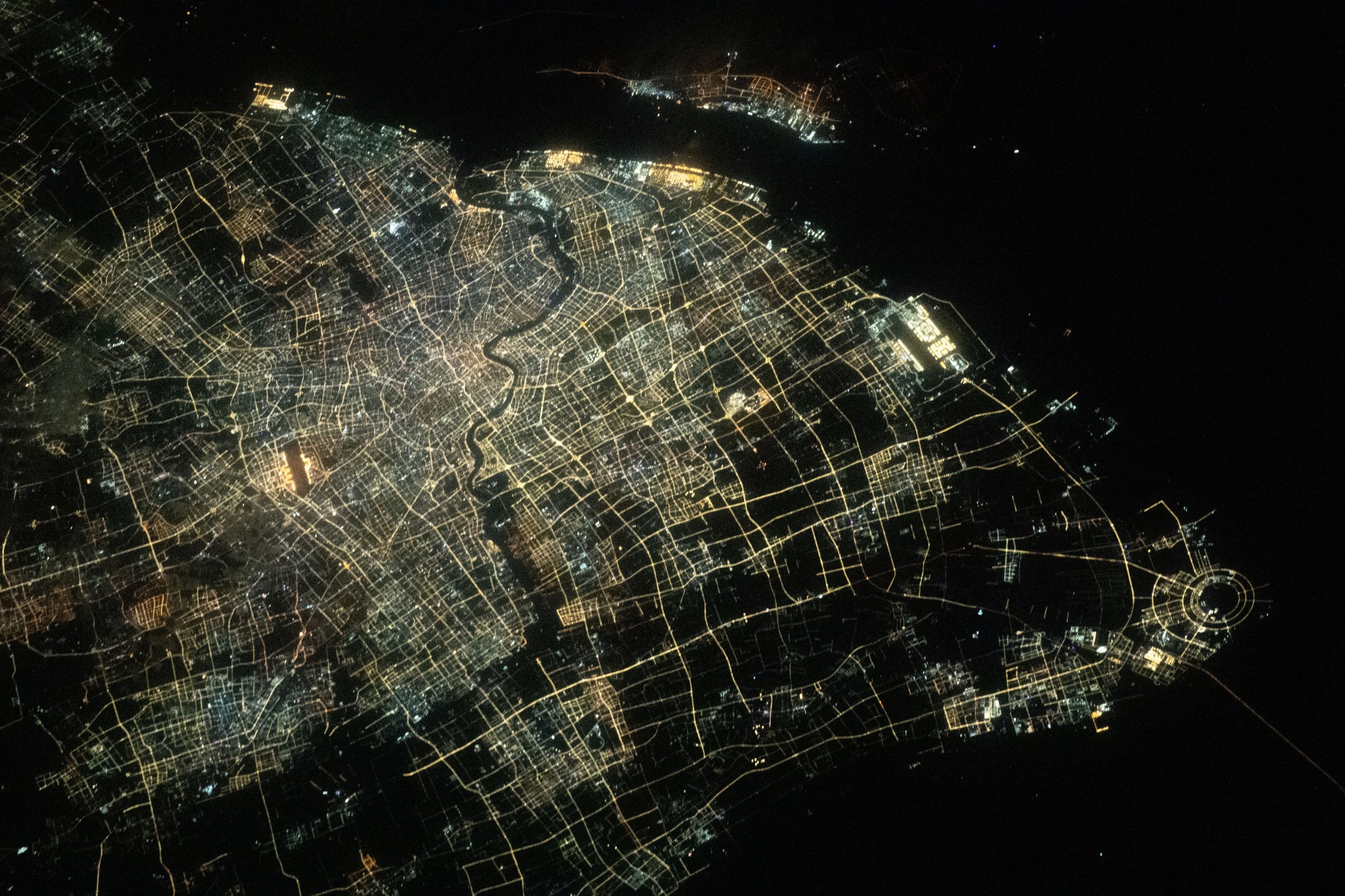
NASA/Jasmin Moghbeli While the International Space Station orbited 260 miles above the East China Sea, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli snapped this photo of Shanghai’s city lights and the Huangpu River flowing through downtown. Shanghai is the most populous city in China with a population of about 24.9 million. The space station serves as a unique platform for observing Earth with both hands-on and automated equipment. Station crew members have produced hundreds of thousands of images, recording phenomena such as storms in real time, observing natural events such as volcanic eruptions…
Read MoreWhat’s Made in a Thunderstorm and Faster Than Lightning? Gamma Rays!
3 min read What’s Made in a Thunderstorm and Faster Than Lightning? Gamma Rays! A flash of lightning. A roll of thunder. These are normal stormy sights and sounds. But sometimes, up above the clouds, stranger things happen. Our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope has spotted bursts of gamma rays – some of the highest-energy forms of light in the universe – coming from thunderstorms. Gamma rays are usually found coming from objects with crazy extreme physics like neutron stars and black holes. So why is Fermi seeing them come from thunderstorms? About a thousand times a…
Read MoreMajor ‘magnetic anomaly’ discovered deep below New Zealand’s Lake Rotorua
New maps have revealed a hidden hydrothermal system beneath a legendary lake in New Zealand, which serves as the setting for a famous Māori love story. Lake Rotorua sits at the heart of a massive ancient crater of a dormant volcano on New Zealand’s North Island. The lake has a storied history: it is where the daughter of an influential chief is said to have overcome forbidden love by swimming across the lake to be with a young warrior. The Rotorua area is also well known for hydrothermal activity, with…
Read MoreSpace mysteries: Why do Earth’s magnetic poles flip?
Earth, our rocky, watery oasis in the cosmos is the ideal place for life to flourish for a number of reasons. We sit at just the right distance from our home star for liquid water to exist on the planet’s surface. The gravitational pull of other large planets helps protect us from apocalyptic collisions with wandering meteorites. And the planet’s magnetic field encircles Earth with a protective barrier that shields us from charged particles hurtling through space. Earth’s magnetic field is generated by the complex flow of molten metallic material…
Read MoreGoodbye sun: What it’s like to experience the polar night along Norway’s rugged coastline
Anyone who has ventured to the far north or south during winter will have experienced the surreal phenomenon of the “polar night,” during which the sun doesn’t rise. Most people who have encountered the polar night will have done so in the Northern Hemisphere in either Norway, parts of Alaska, Canada, Greenland, Finland, Russia or Sweden. The only landmass in the Southern Hemisphere to welcome the polar night is Antarctica. Lucky for me, I got my first true taste of the polar night while on an Astronomy Voyage along…
Read MoreWhat would happen if Earth stopped spinning?
Even though Earth is always spinning, we can’t feel it, and you probably take it for granted. But what would happen if it stopped? If Earth suddenly stopped spinning, it would be catastrophic. Almost everyone and everything not attached to the planet would continue to move at the current speed of Earth’s rotation, around 1,000 mph (1,600 km/h) at its fastest, which is along the equator. Related: 10 dramatic discoveries about Earth from 20 “The momentum of all the material that’s normally rotating — the water, the air, all the…
Read More