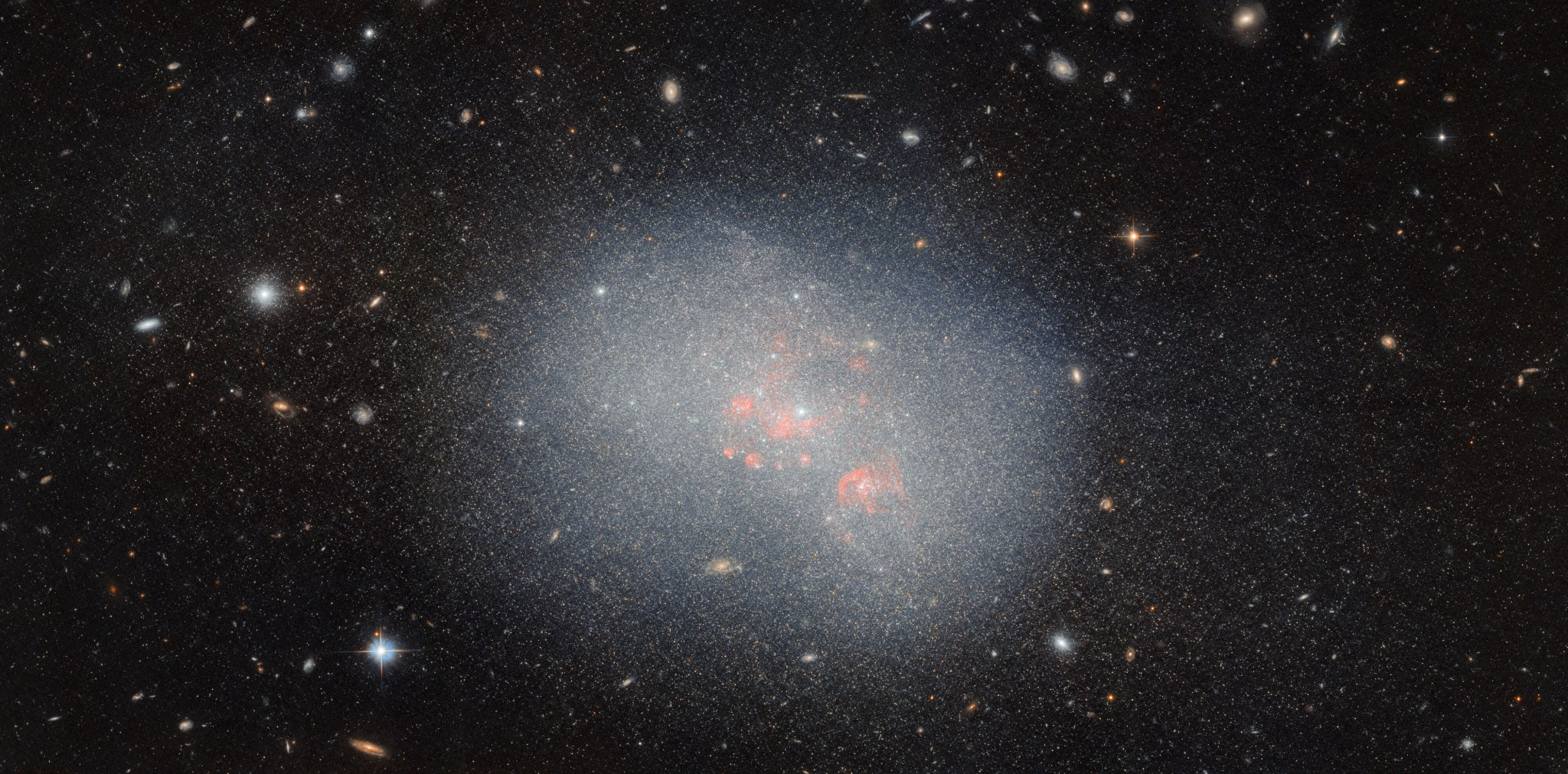
3 min read Hubble Studies a Potential Galactic Merger This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image captures the dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 5238. ESA/Hubble & NASA, F. Annibali This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features the dwarf irregular galaxy NGC 5238, located 14.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. Its unexciting, blob-like appearance seems to resemble an oversized star cluster more than a classic image of a galaxy. Its lackluster appearance belies its complicated structure, which is the subject of a great deal of research. As the image…
Read MoreTag: Galaxies
Vivid Portrait of Interacting Galaxies Marks Webb’s Second Anniversary
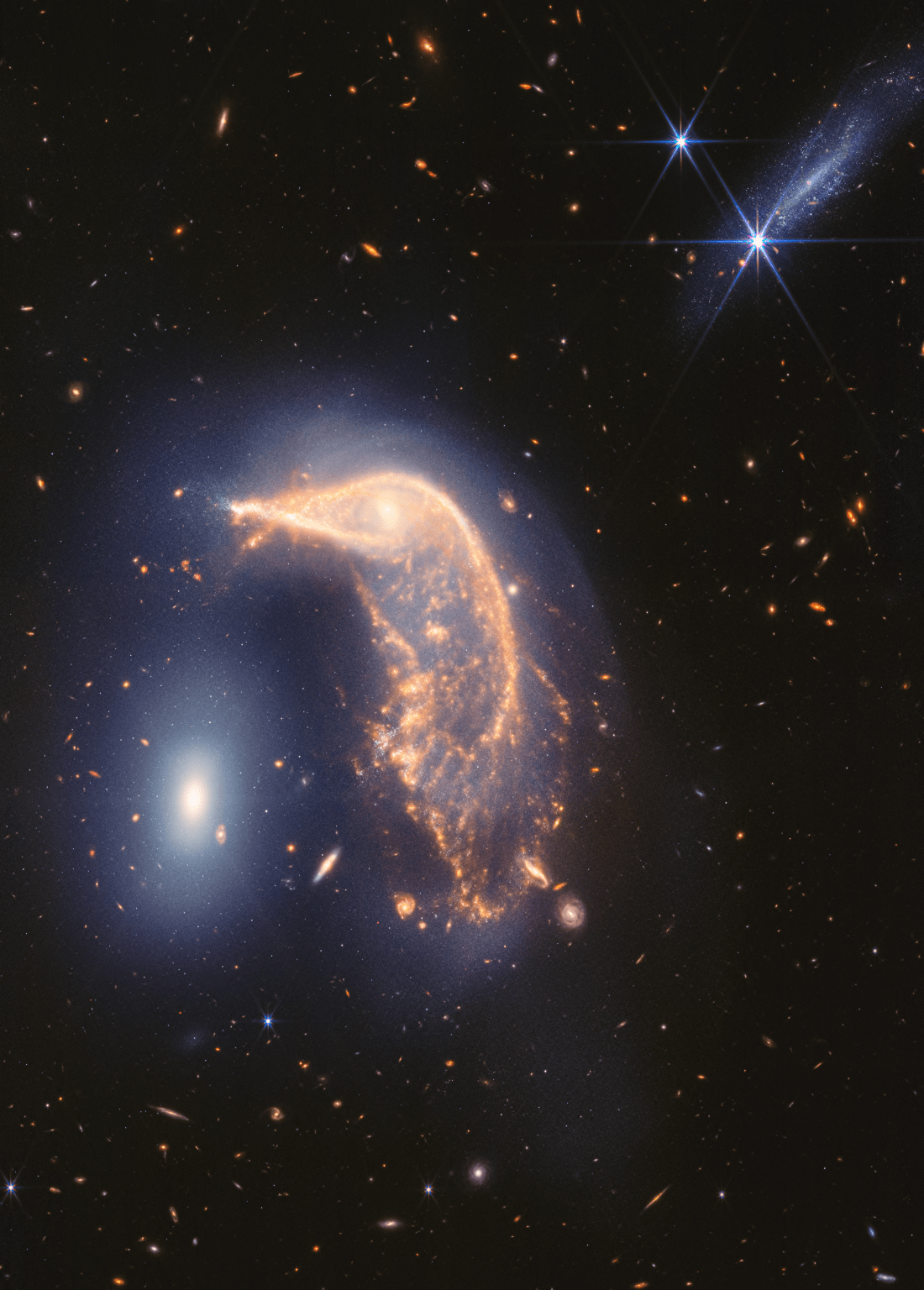
6 Min Read Vivid Portrait of Interacting Galaxies Marks Webb’s Second Anniversary Webb’s view of the interacting galaxies of Arp 142 that combines Webb’s NIRCam and MIRI instrument images. Full image below. Two for two! A duo of interacting galaxies commemorates the second science anniversary of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, which takes constant observations, including images and highly detailed data known as spectra. Its operations have led to a “parade” of discoveries by astronomers around the world. “Since President Biden and Vice President Harris unveiled the first image from…
Read MoreHubble Measures the Distance to a Supernova
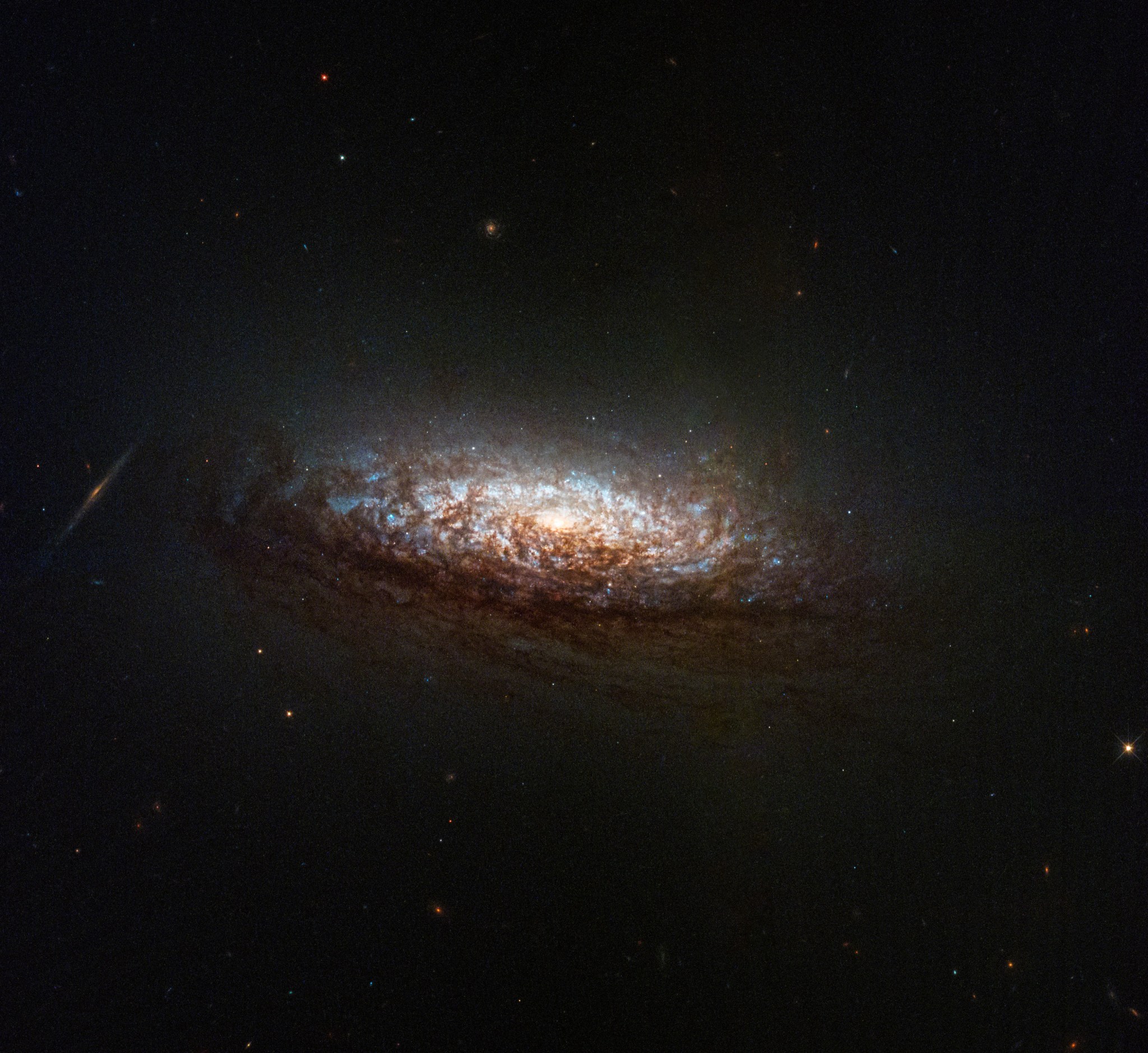
3 min read Hubble Measures the Distance to a Supernova This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image features the galaxy NGC 3810. ESA/Hubble & NASA, D. Sand, R. J. Foley Measuring the distance to truly remote objects like galaxies, quasars, and galaxy clusters is a crucial task in astrophysics, particularly when it comes to studying the early universe, but it’s a difficult one to complete. We can only measure the distances to a few nearby objects like the Sun, planets, and some nearby stars directly. Beyond that, astronomers need to use…
Read MoreTake a Summer Cosmic Road Trip With NASA’s Chandra and Webb
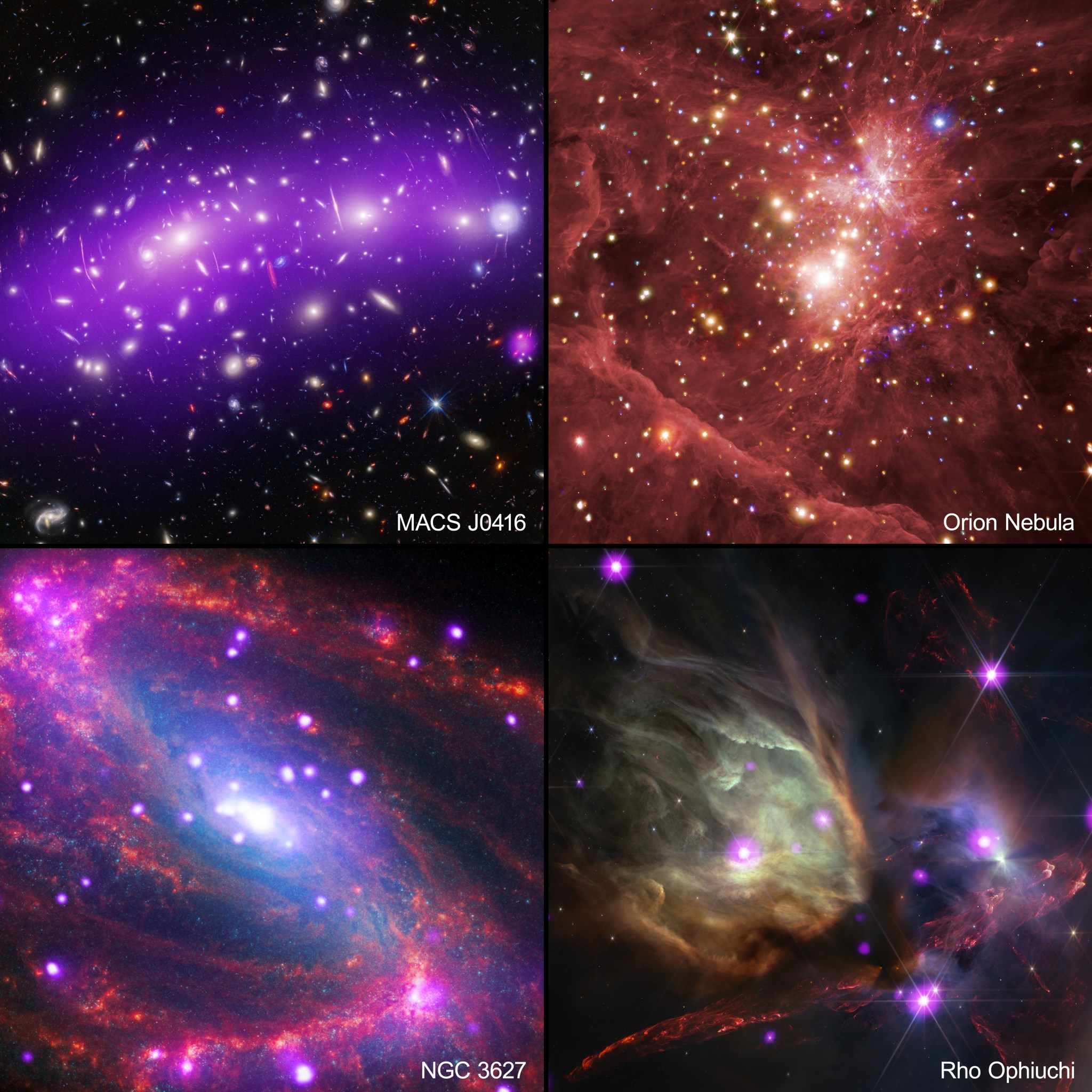
Cosmic Road Trip: four distinct composite images from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the James Webb Space Telescope, presented in a two-by-two grid, Rho Ophiuchi at lower right, the heart of the Orion Nebula at upper right, the galaxy NGC 3627 at lower left and the galaxy cluster MACS J0416. X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO; Optical/Infrared: (Hubble) NASA/ESA/STScI; IR: (JWST) NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI It’s time to take a cosmic road trip using light as the highway and visit four stunning destinations across space. The vehicles for this space get-away are NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and…
Read MoreHubble Examines an Active Galaxy Near the Lion’s Heart
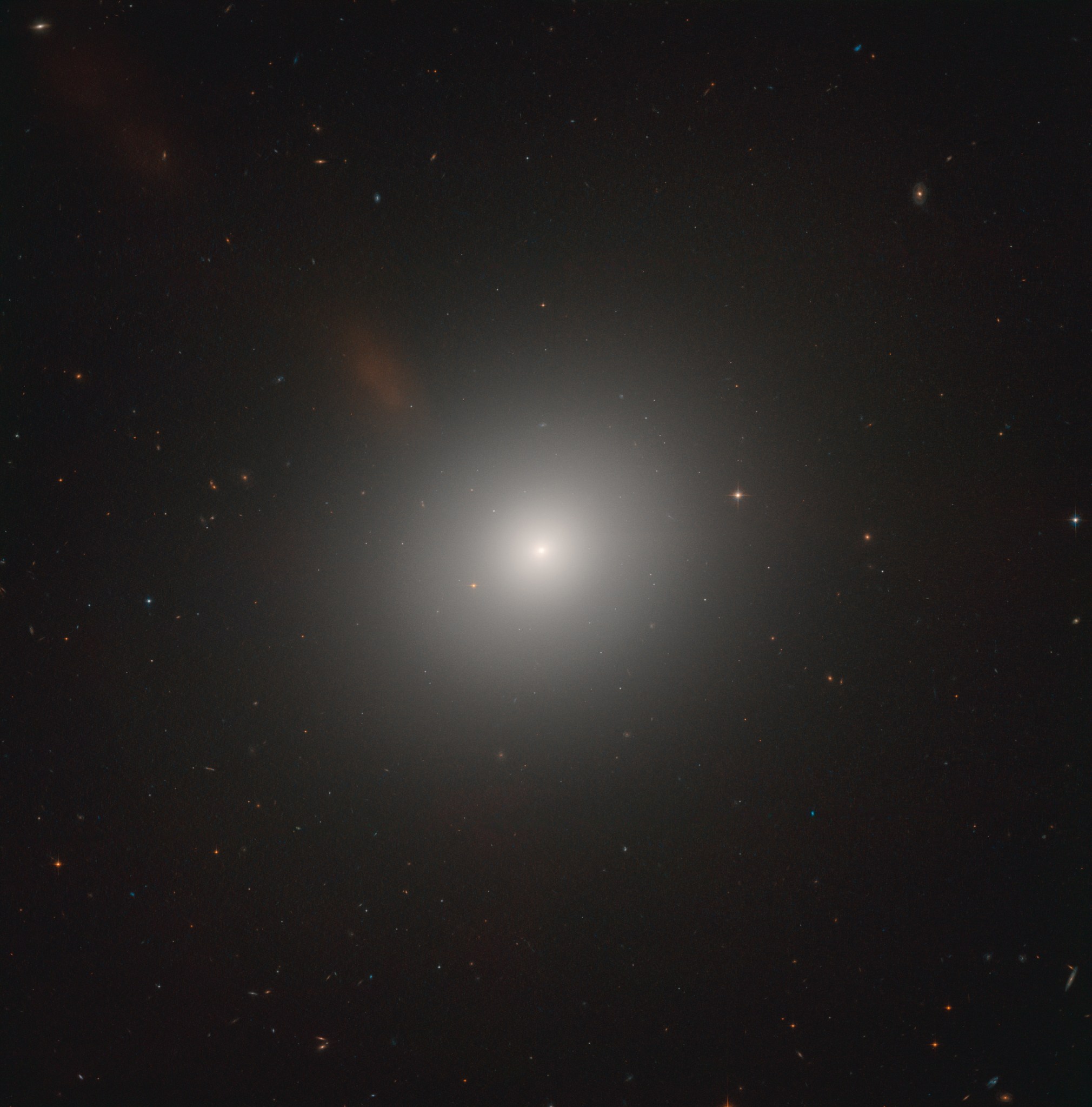
2 min read Hubble Examines an Active Galaxy Near the Lion’s Heart This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope features the elliptical galaxy Messier 105. ESA/Hubble & NASA, C. Sarazin et al. It might appear featureless and unexciting at first glance, but NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope observations of this elliptical galaxy — known as Messier 105 — show that the stars near the galaxy’s center are moving very rapidly. Astronomers have concluded that these stars are zooming around a supermassive black hole with an estimated mass of 200 million Suns! This black…
Read MoreNASA Releases Hubble Image Taken in New Pointing Mode
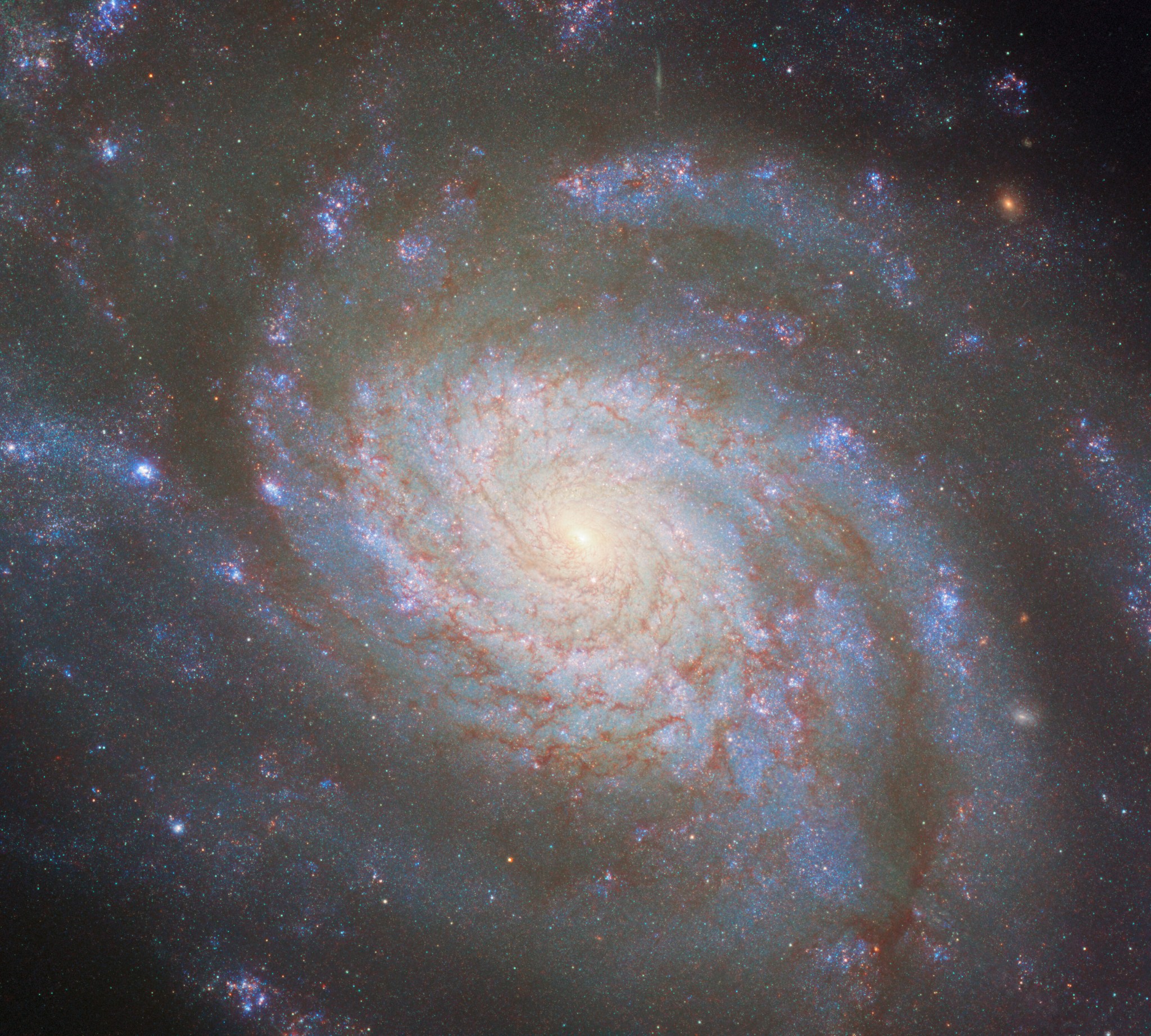
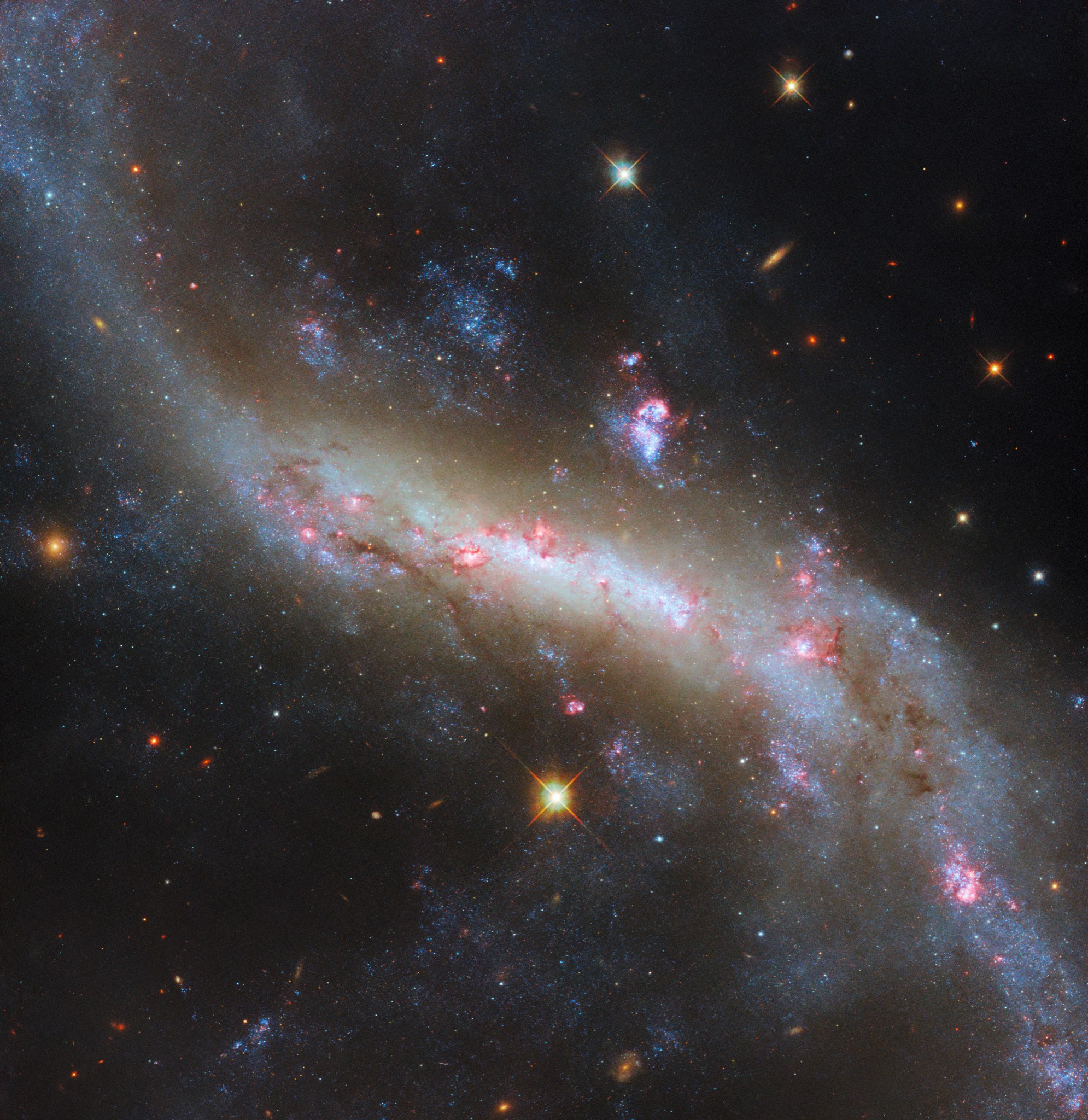
2 min read NASA Releases Hubble Image Taken in New Pointing Mode This NASA Hubble Space Telescope features the galaxy NGC 1546. NASA, ESA, STScI, David Thilker (JHU) NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has taken its first new images since changing to an alternate operating mode that uses one gyro. The spacecraft returned to science operations June 14 after being offline for several weeks due to an issue with one of its gyroscopes (gyros), which help control and orient the telescope. This new image features NGC 1546, a nearby galaxy in…
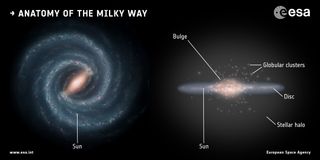
Read MoreThe Milky Way’s last major act of galactic cannibalism was surprisingly recent
New findings from the Gaia space telescope indicate the Milky Way may have cannibalized a small galaxy not too long ago, cosmically speaking. In fact, the last major collision between our galaxy and another seems to have occurred billions of years later than previously suspected. The Milky Way has been long understood to have grown via a series of violent collisions, which see smaller galaxies ripped apart by the immense gravitational influence of our solar system’s spiral home. These collisions distribute stars from the devoured galaxy across the halo that…
Read MoreHubble Views the Lights of a Galactic Bar
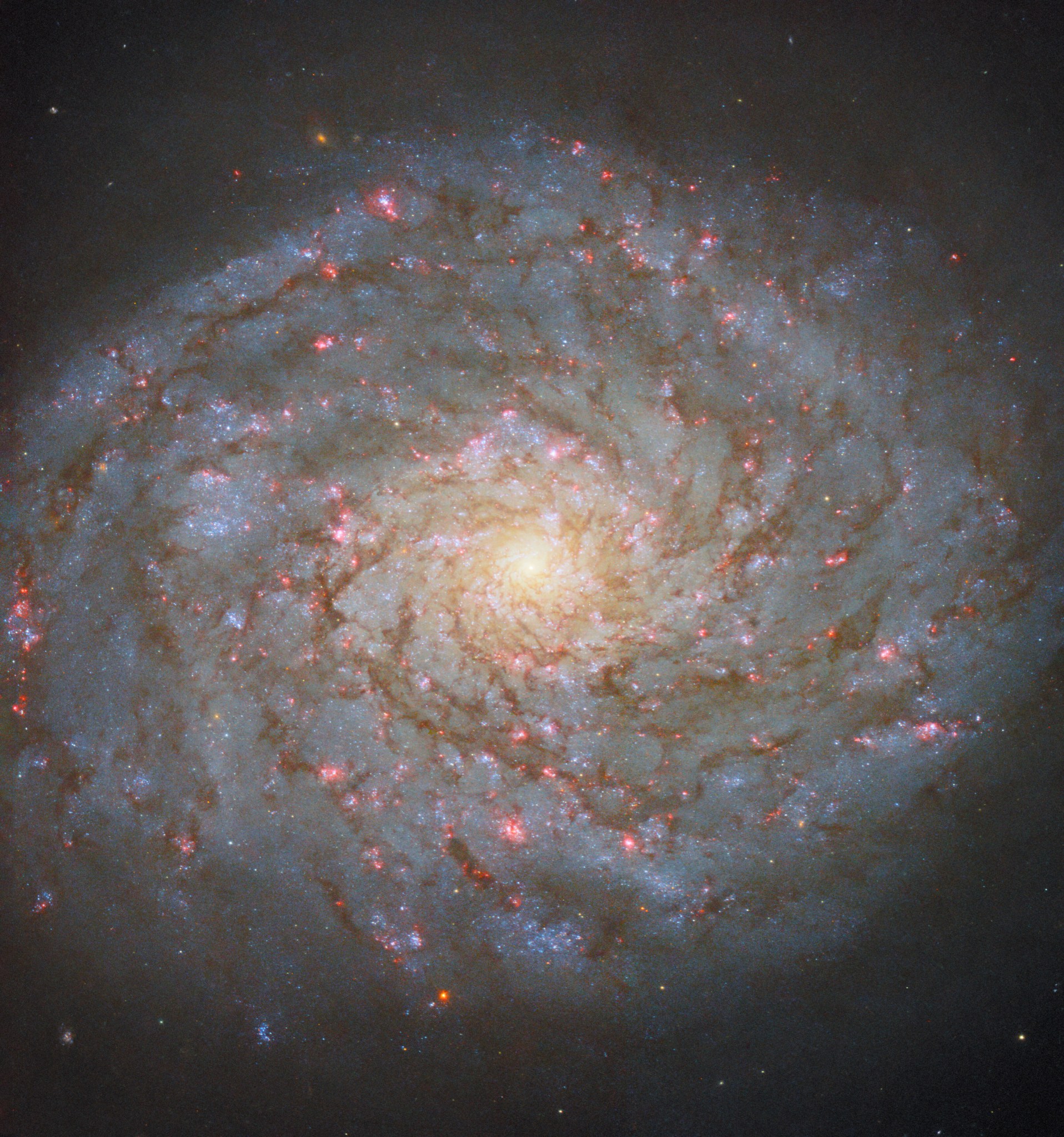
2 min read Hubble Views the Lights of a Galactic Bar This Hubble Space Telescope image reveals details in the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4731. ESA/Hubble & NASA, D. Thilker This new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows the broad and sweeping spiral galaxy NGC 4731. It lies in the constellation Virgo and is located 43 million light-years from Earth. This highly detailed image uses data collected from six different filters. The abundance of color illustrates the galaxy’s billowing clouds of gas, dark dust bands, bright pink star-forming…
Read MoreHubble Captures a Bright Spiral in the Queen’s Hair
2 min read Hubble Captures a Bright Spiral in the Queen’s Hair This Hubble Space Telescope image showcases the bright spiral galaxy NGC 4689. ESA/Hubble & NASA, D. Thilker, J. Lee, and the PHANGS-HST Team This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows the jewel-bright spiral galaxy NGC 4689, which lies 54 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Coma Berenices. This constellation has the distinction of being the only one of the 88 constellations officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) as one named after the historical figure, Queen…
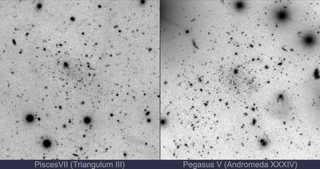
Read MoreAmateur astronomer finds 5 fascinating new galaxies — and they’re now named after him
An amateur astronomer from Italy has discovered five new dwarf galaxies around a distant spiral galaxy — a spiral that’s one of the largest galaxies in the sky over Earth. His name is Giuseppe Donatiello, and those five dwarf galaxies are now named Donatiello V, Donatiello VI, Donatiello VII, Donatiello VIII, and Donatiello IX (Do V, Do VI, Do VII, Do VIII, and Do IX). “Out of eleven discoveries, nine galaxies bear my name. To my knowledge, I am the first and only amateur astronomer to have galaxies named after them,”…
Read More