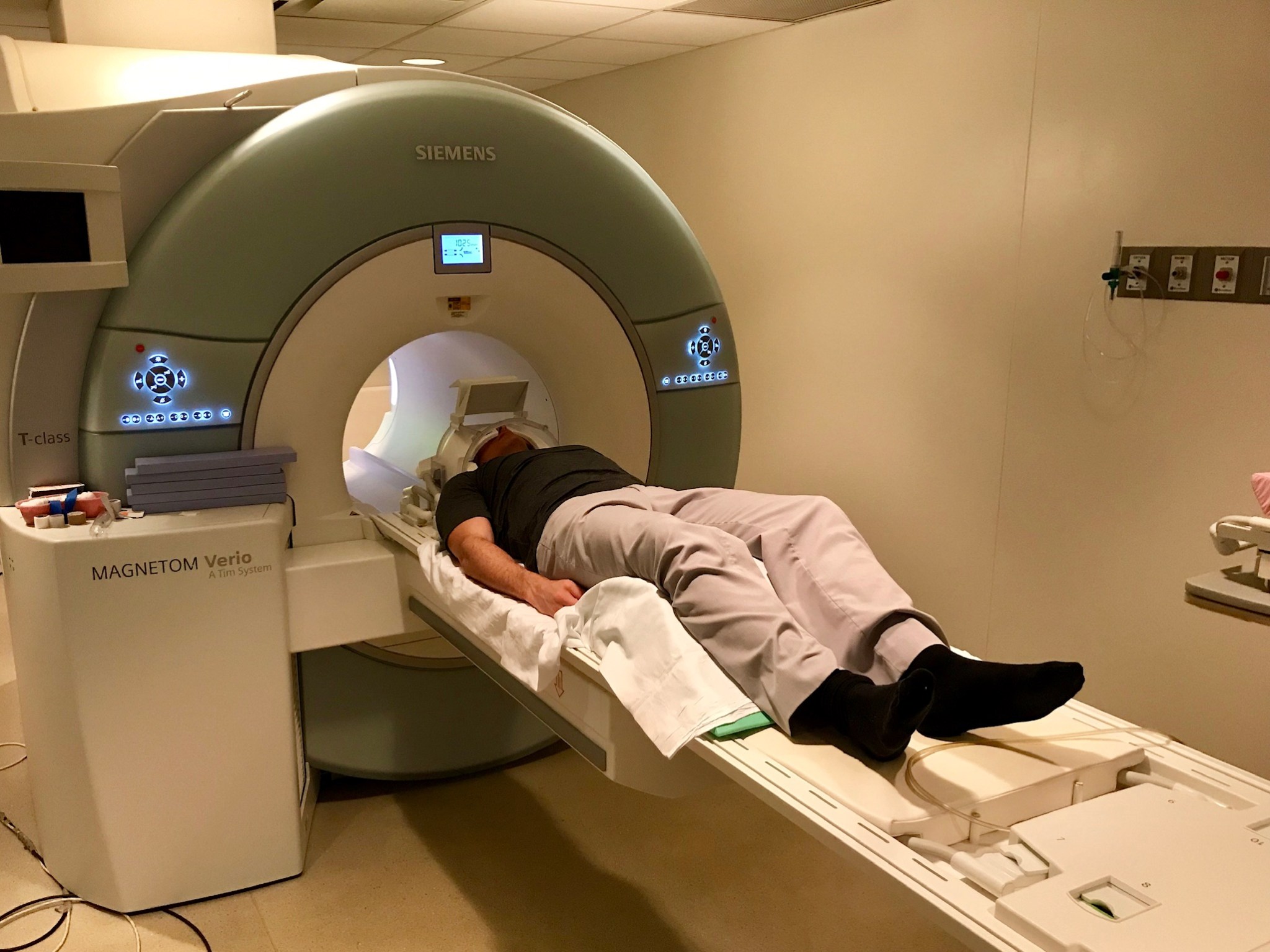
Challenges to measuring space-induced brain changes CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut David Saint-Jacques undergoes an MRI for Wayfinding. CSA Researchers found that an upward shift in the brain during spaceflight makes it hard to distinguish different types of tissue, causing errors in determining changes in brain volume. Previous studies have interpreted these changes as evidence of adaptation to space. This finding suggests that unique methods are needed to analyze astronaut brain structure. Wayfinding, a CSA (Canadian Space Agency) investigation, looked at how the brain adapts to space and readapts after…
Read MoreTag: ISS Research
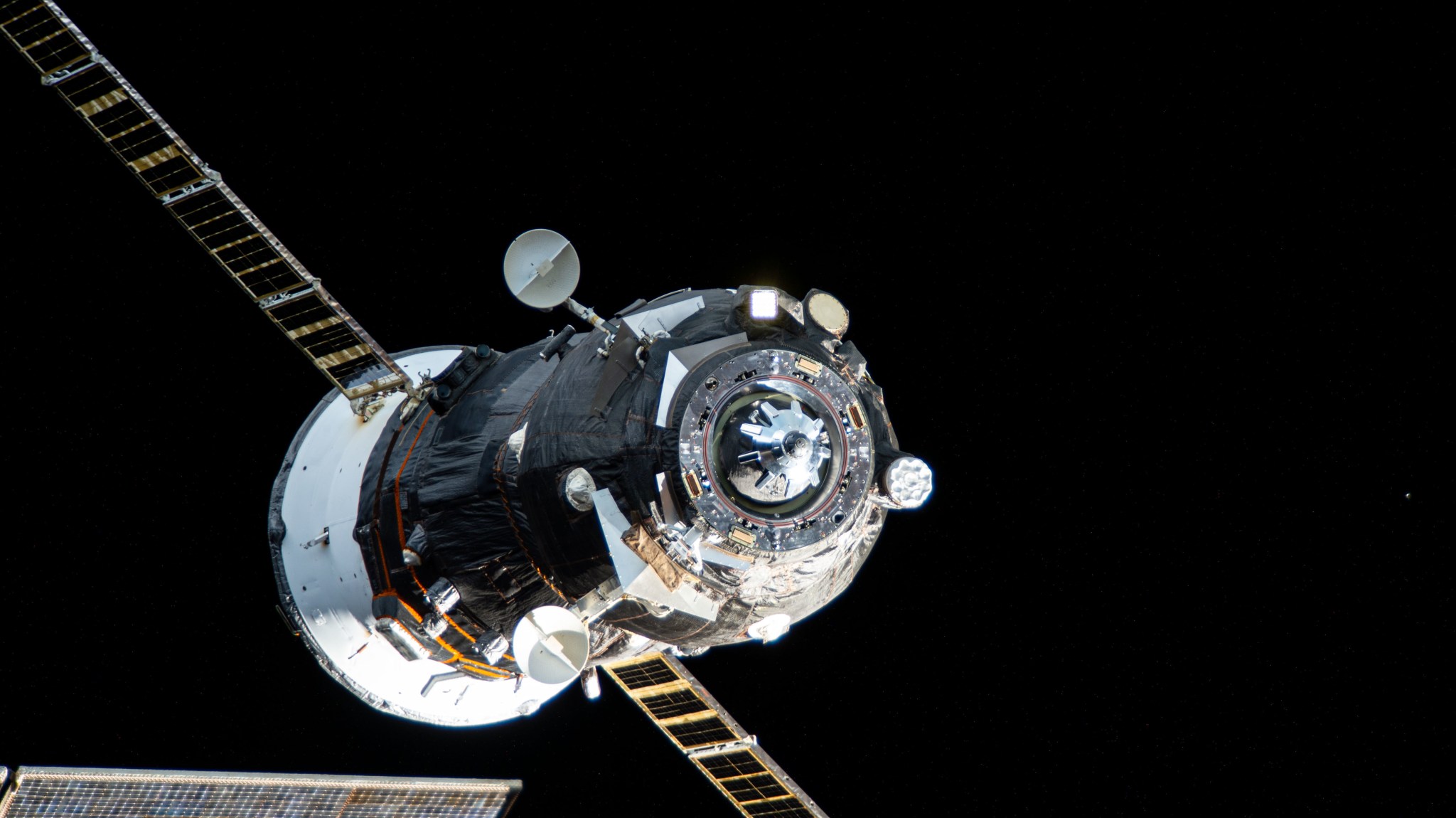
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 Scientific Mission on Space Station Concludes
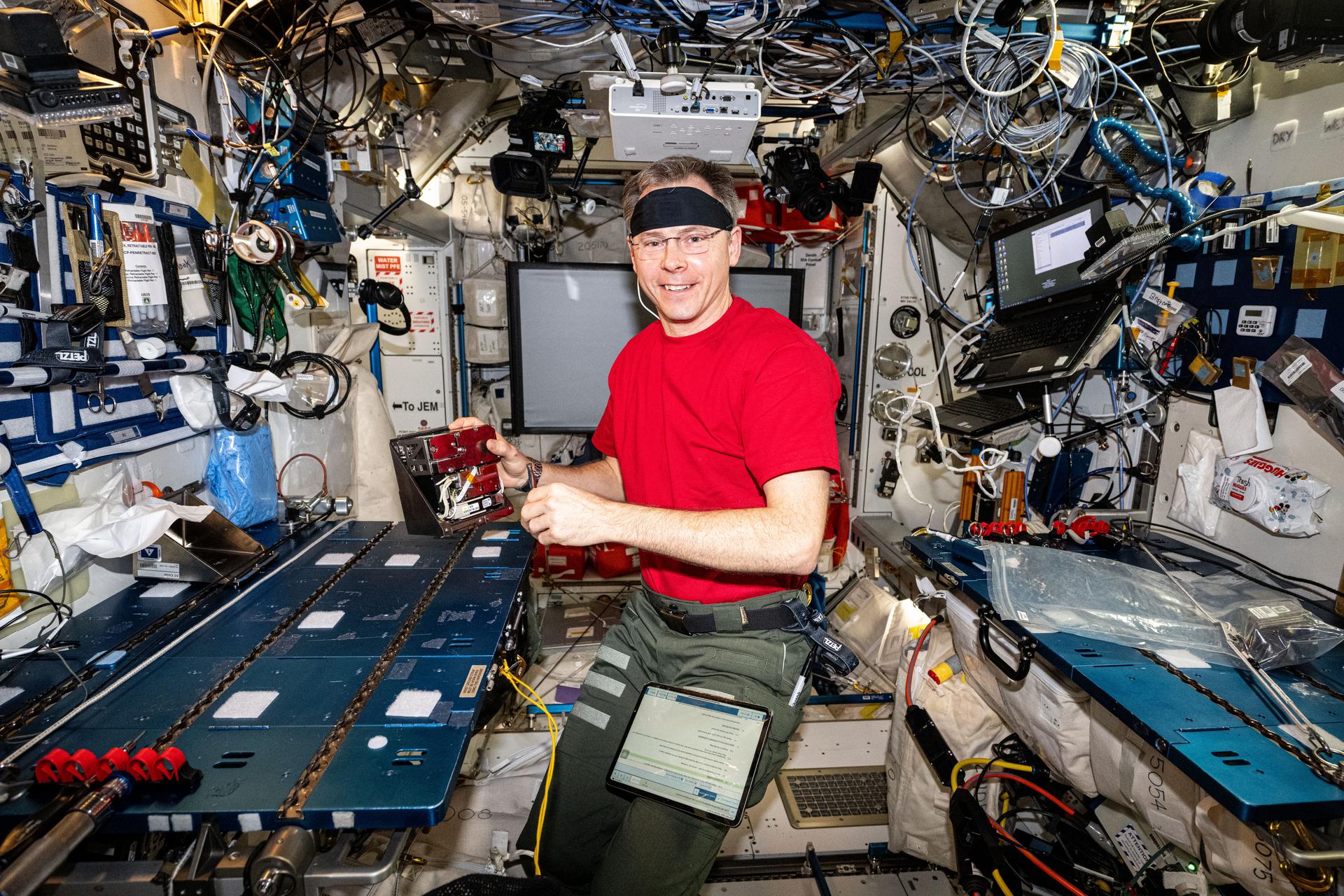
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission with agency astronauts Nick Hague, Butch Wilmore, and Suni Williams, and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov is preparing to return to Earth following their science mission aboard the International Space Station. Hague, Williams, and Wilmore completed more than 900 hours of research between over 150 unique scientific experiments and technology demonstrations during their stay aboard the orbiting laboratory. Here’s a look at some scientific milestones accomplished during their journey: Mighty microalgae NASA astronaut Nick Hague processes samples for Arthrospira C, an investigation from ESA (European Space Agency)…
Read MoreNASA Sets Coverage for Agency’s SpaceX Crew-10 Launch, Docking
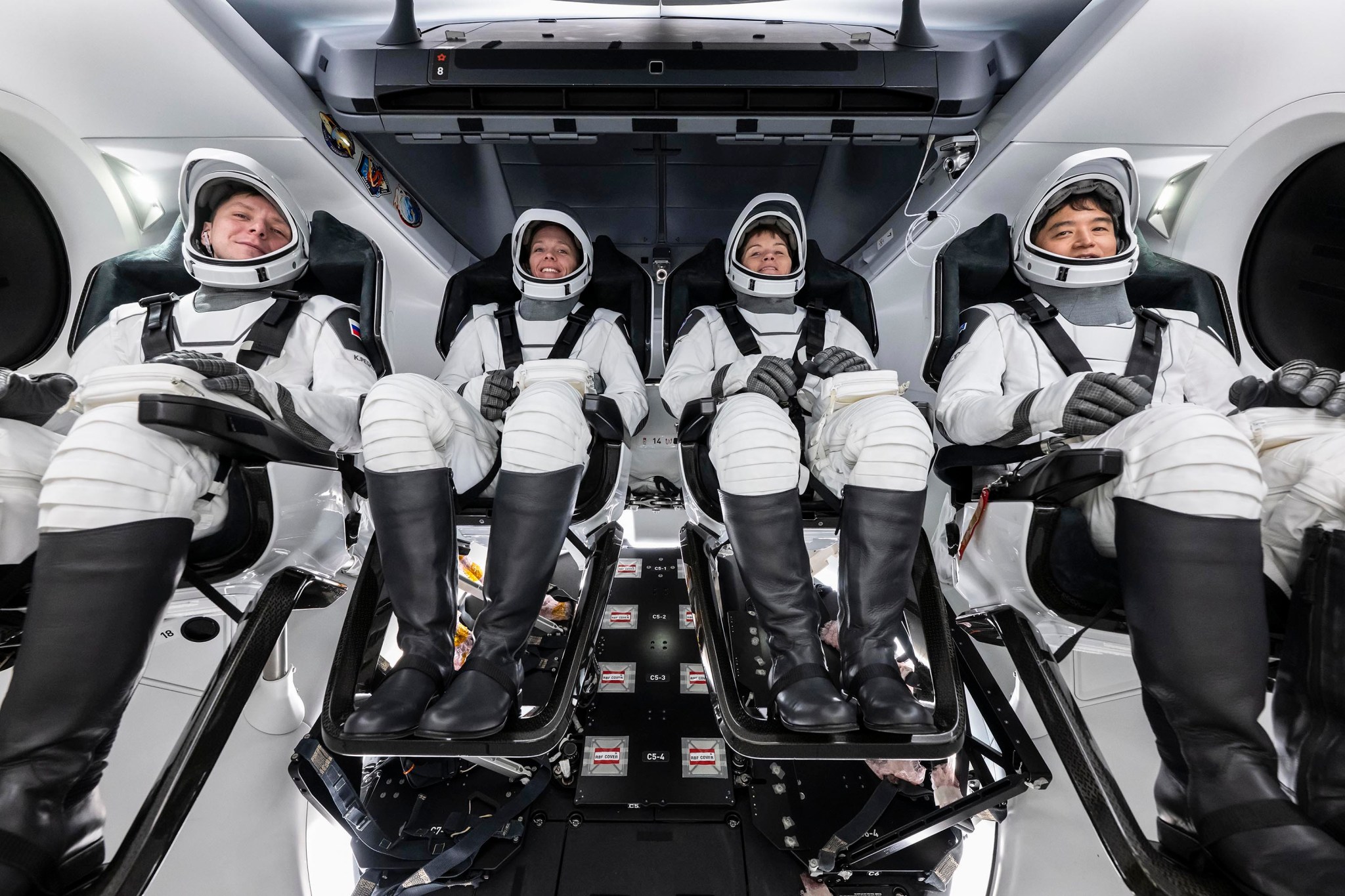
The crew of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission pictured during an equipment test at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Credit: SpaceX Editor’s Note: This advisory was updated March 5, 2025, to correct that media may ask questions by phone only during the mission overview teleconference. NASA will provide coverage of the upcoming prelaunch and launch activities for the agency’s SpaceX Crew-10 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff is targeted for 7:48 p.m. EDT, Wednesday, March 12, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The…
Read MoreStation Science Top News: Feb. 27, 2025
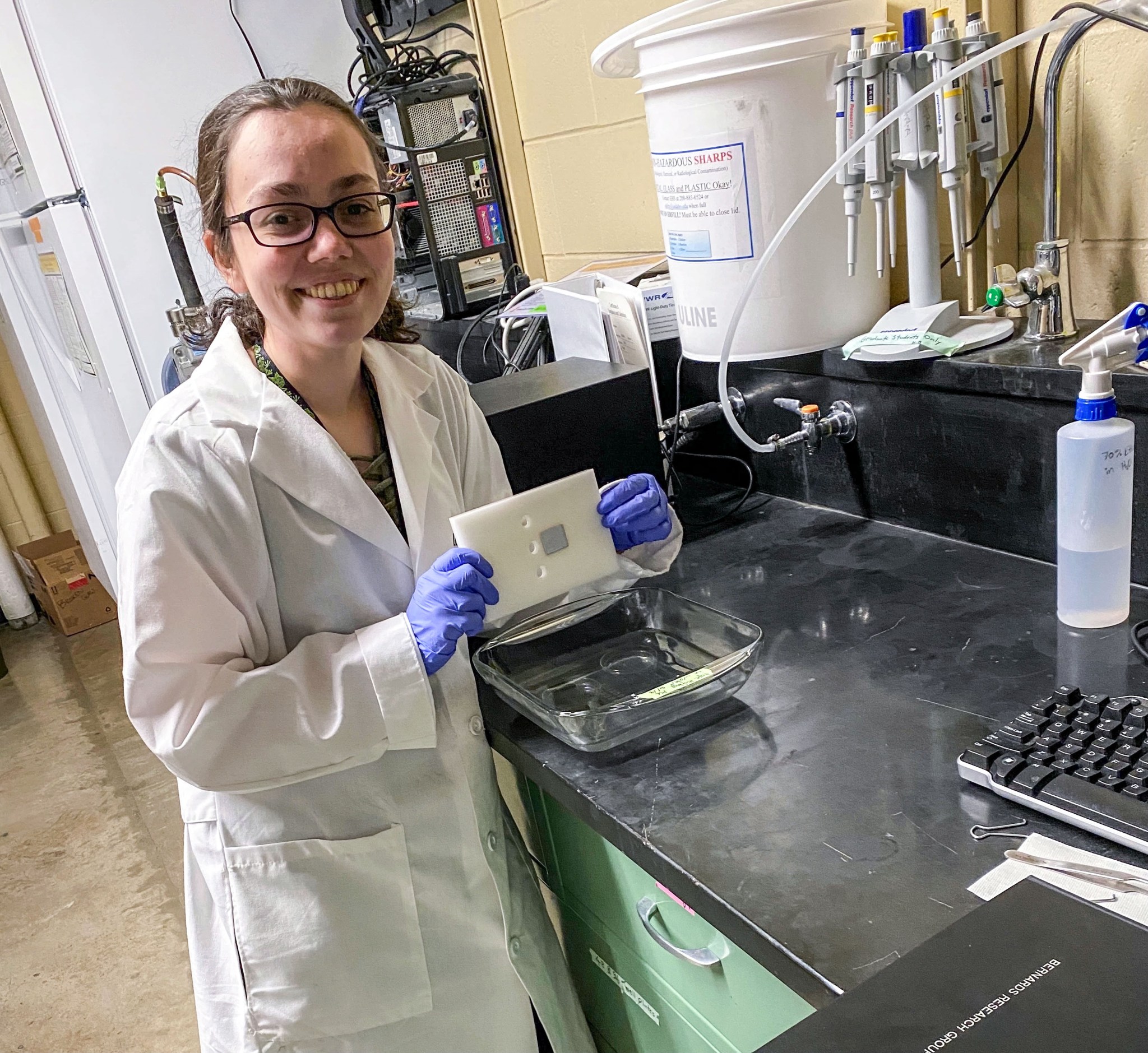
Preventing biofilm formation in space Ashley Keeley, University of Idaho, holds an anti-bacterial coating sample. University of Idaho Student Payload Opportunity with Citizen Science Team Two anti-microbial coatings reduced formation of biofilms in microgravity and have potential for use in space. Controlling biofilms could help protect human health and prevent corrosion and degradation of equipment on future long-duration space missions. Biofilms, communities of microorganisms that attach to a surface, can damage mechanical systems and present a risk of disease transmission. Bacteria Resistant Polymers in Space examined how microgravity affects polymer…
Read MoreScience in Orbit: Results Published on Space Station Research in 2024
4 Min Read Science in Orbit: Results Published on Space Station Research in 2024 NASA and its international partners have hosted research experiments and fostered collaboration aboard the International Space Station for over 25 years. More than 4,000 investigations have been conducted, resulting in over 4,400 research publications with 361 in 2024 alone. Space station research continues to advance technology on Earth and prepare for future space exploration missions. Below is a selection of scientific results that were published over the past year. For more space station research achievements and…
Read MoreNASA to Provide Coverage of Progress 91 Launch, Space Station Docking
The unpiloted Roscosmos Progress spacecraft pictured on Aug. 13, 2024, from the International Space Station. Credit: NASA NASA will provide live launch and docking coverage of a Roscosmos cargo spacecraft delivering approximately three tons of food, fuel, and supplies for the crew aboard the International Space Station. The unpiloted Roscosmos Progress 91 spacecraft is scheduled to launch at 4:24 p.m. EST, Thursday, Feb. 27 (2:24 a.m. Baikonur time, Friday, Feb. 28), on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Live launch coverage will begin at 4 p.m. on…
Read MoreStation Science Top News: Feb. 21, 2025
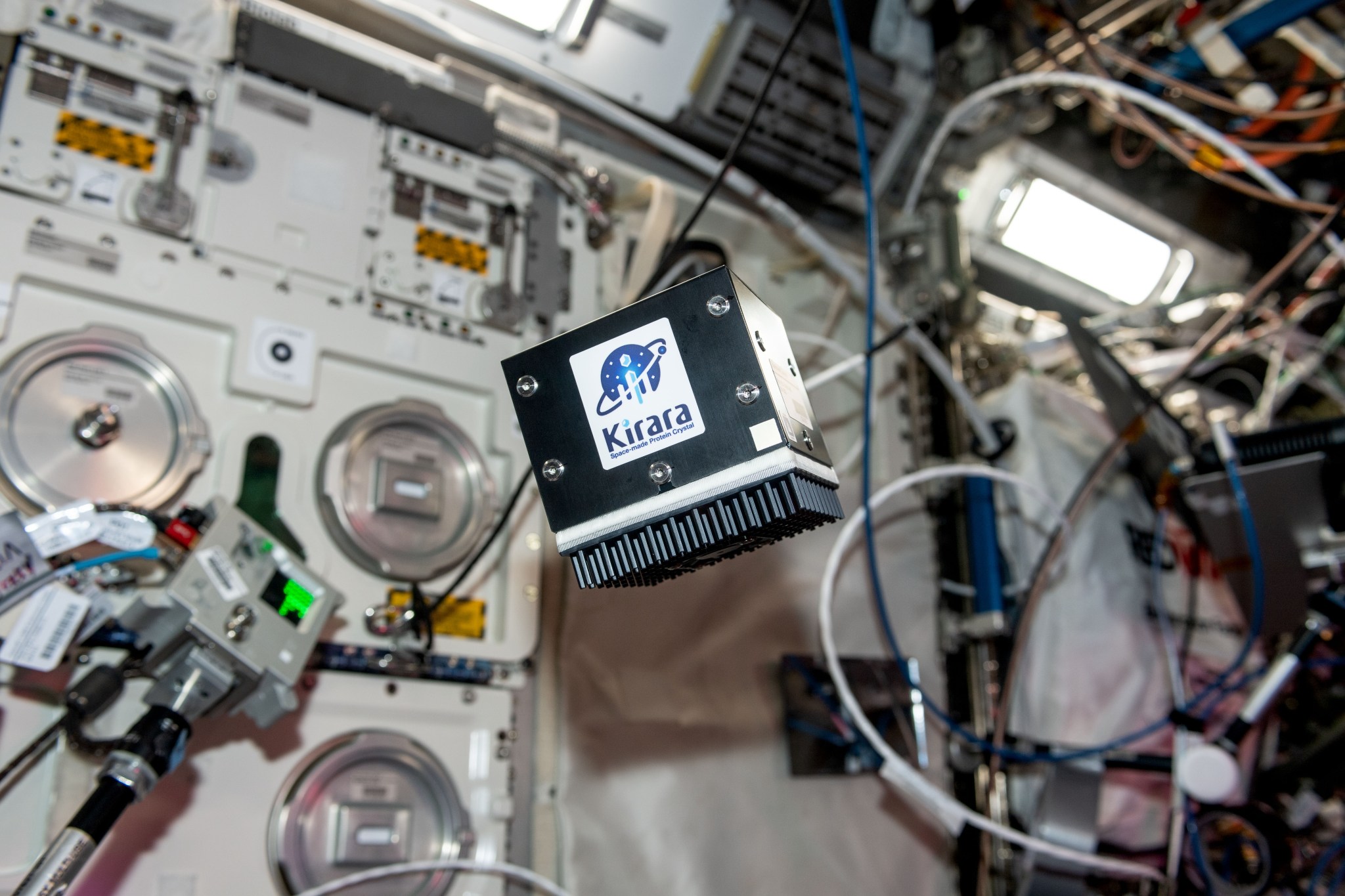
Improving space-based pharmaceutical research View of the Ice Cubes experiment #6 (Kirara) floating in the Columbus European Laboratory module aboard the International Space Station. UAE (United Arab Emirates)/Sultan Alneyadi Researchers found differences in the stability and degradation of the anti-Covid drug Remdesivir in space and on Earth on its first research flight, but not on a second. This highlights the need for more standardized procedures for pharmaceutical research in space. Long-term stability of drugs is critical for future space missions. Because multiple characteristics of spaceflight could influence chemical stability, the…
Read MoreNASA Sends Experiment to Space to Study Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
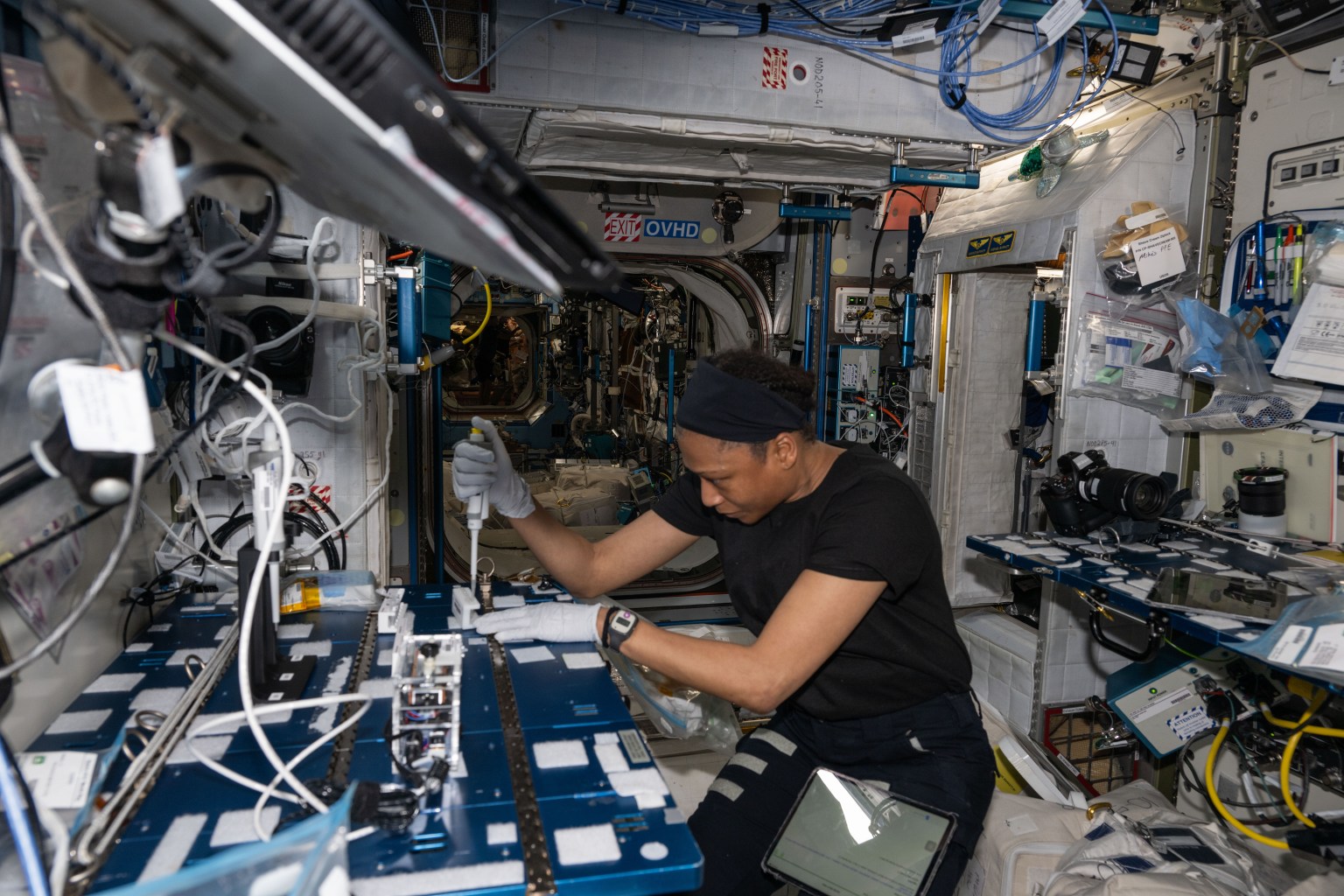
5 min read Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater) Astronaut Jeanette Epps extracts DNA samples from bacteria colonies for genomic analysis aboard the International Space Station’s Harmony module. NASA In an effort to learn more about astronaut health and the effects of space on the human body, NASA is conducting a new experiment aboard the International Space Station to speed up the detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, thus improving the health safety not only of astronauts but patients back on Earth. Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria can be difficult…
Read More2024 Annual Highlights of Results from the International Space Station Science
The 2024 Annual Highlights of Results from the International Space Station is now available. This new edition contains updated bibliometric analyses, a list of all the publications documented in fiscal year 2024, and synopses of the most recent and recognized scientific findings from investigations conducted on the space station. These investigations are sponsored by NASA and all international partners – CSA (Canadian Space Agency), ESA (European Space Agency), JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and the State Space Corporation Roscosmos (Roscosmos) – for the advancement of science, technology, and education. Dr. Dmitry Oleynikov…
Read MoreHeart Health
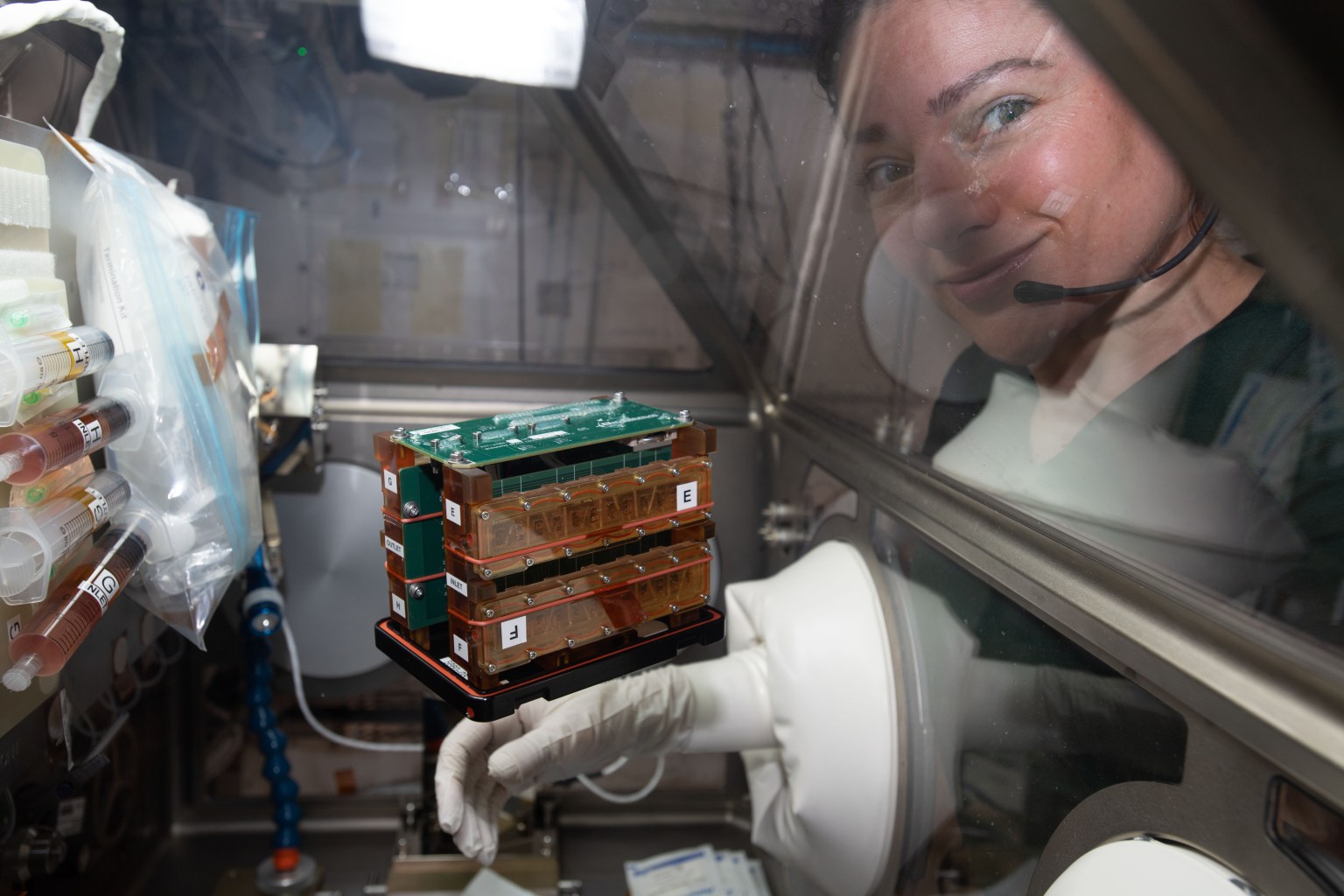
4 Min Read Heart Health Jessica Meir conducts cardiac research in the space station’s Life Sciences Glovebox. Credits: NASA Science in Space: February 2025 February was first proclaimed as American Heart Month in 1964. Since then, its 28 (or 29) days have served as an opportunity to encourage people to focus on their cardiovascular health. The International Space Station serves as a platform for a variety of ongoing research on human health, including how different body systems adapt to weightlessness. This research includes assessing cardiovascular health in astronauts during and…
Read More