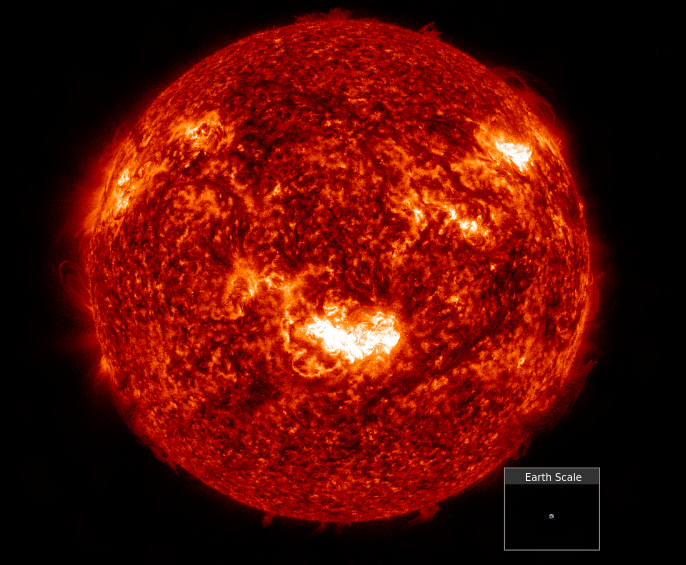
6 min read What NASA Is Learning from the Biggest Geomagnetic Storm in 20 Years One year on, NASA scientists are still making huge discoveries about the largest geomagnetic storm to hit Earth in two decades, the Gannon storm. The findings are helping us better understand and prepare for the ways in which the Sun’s activity can affect us. On May 10, 2024, the first G5 or “severe” geomagnetic storm in over two decades hit Earth. The event did not cause any catastrophic damages, but it did produce surprising effects…
Read MoreTag: NASA Centers & Facilities
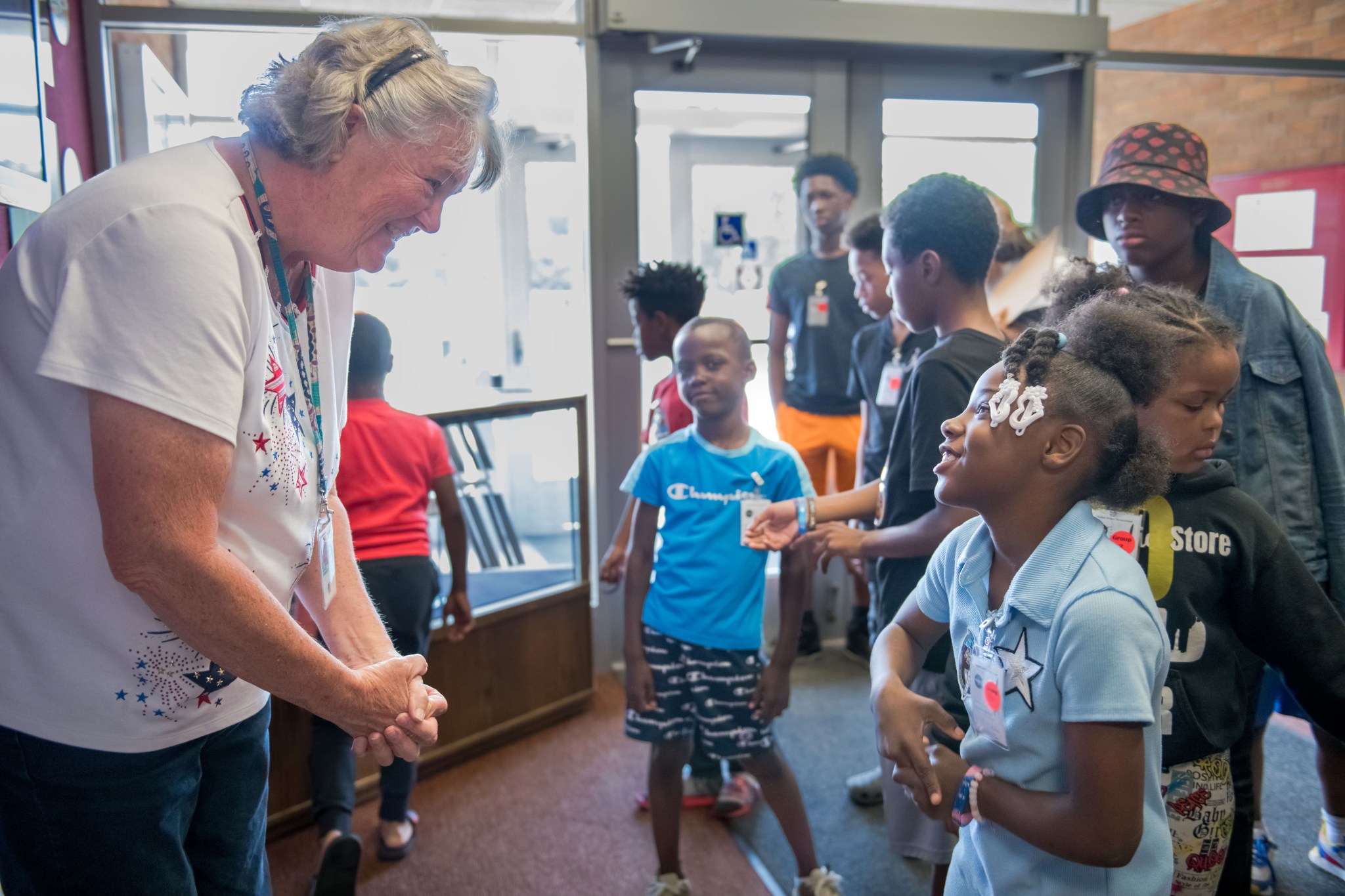
NASA Invites Local Middle Schoolers to Explore Agency STEM Careers
Students take a tour of the Glenn International Space Station Payload Operations Center at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, where researchers operate International Space Station experiments, during 4-H Day on June 14, 2024. Credit: NASA/Jef Janis Ohio middle school students will step into the shoes of real-world NASA professionals for a day of career exploration and hands-on activities at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. Nearly 200 students are slated to participate in TECH Day at NASA Glenn on May 1, from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. Media are…
Read MoreNASA’s Curiosity Rover Detects Largest Organic Molecules Found on Mars
Researchers analyzing pulverized rock onboard NASA’s Curiosity rover have found the largest organic compounds on the Red Planet to date. The finding, published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests prebiotic chemistry may have advanced further on Mars than previously observed. Scientists probed an existing rock sample inside Curiosity’s Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) mini-lab and found the molecules decane, undecane, and dodecane. These compounds, which are made up of 10, 11, and 12 carbons, respectively, are thought to be the fragments of fatty acids that…
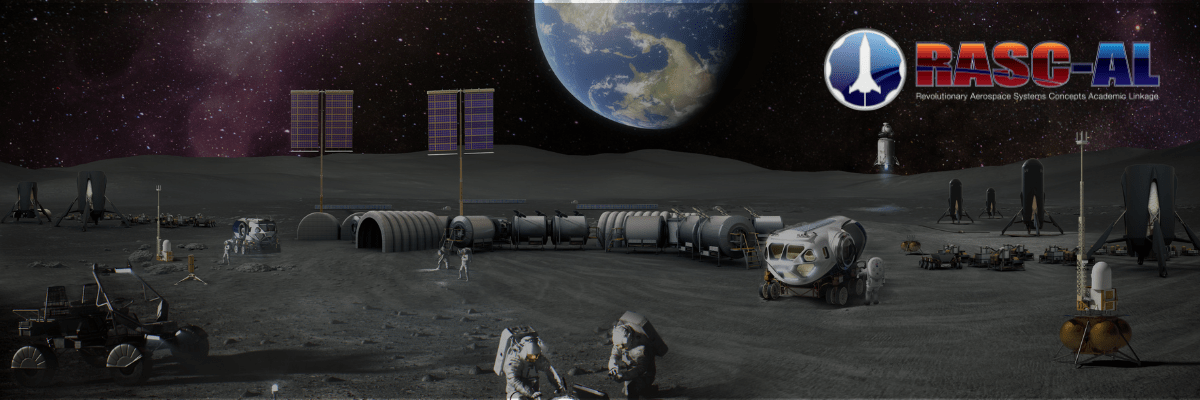
Read MoreNASA Selects 14 Finalist Teams for the 2025 RASC-AL Competition
This year’s RASC-AL competition invited undergraduate and graduate students from across the nation to develop new, innovative concepts to improve our ability to operate on the Moon, Mars, and beyond.ASA NASA Fourteen university teams have been selected as finalists for NASA’s 2025 Revolutionary Aerospace Systems – Academic Linkage (RASC-AL) Competition. This year’s competition invited undergraduate and graduate students from across the nation to develop new, innovative concepts to improve our ability to operate on the Moon, Mars, and beyond. Finalists will present their proposed concepts to a panel of NASA…
Read MoreTexas High School Aerospace Scholars: A Launchpad for Future Innovators
NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement at Johnson Space Center offers Texas high school students a unique gateway to the world of space exploration through the High School Aerospace Scholars (HAS) program. This initiative gives juniors hands-on experience, working on projects that range from designing spacecraft to planning Mars missions. Nearly 30 participants who have been hired by NASA in the past five years are HAS alumni. Their stories highlight the program’s impact on students—inspiring innovation, fostering collaboration, unlocking their potential as they move forward into STEM careers. Discover how the…
Read MoreStation Science Top News: March 7, 2025
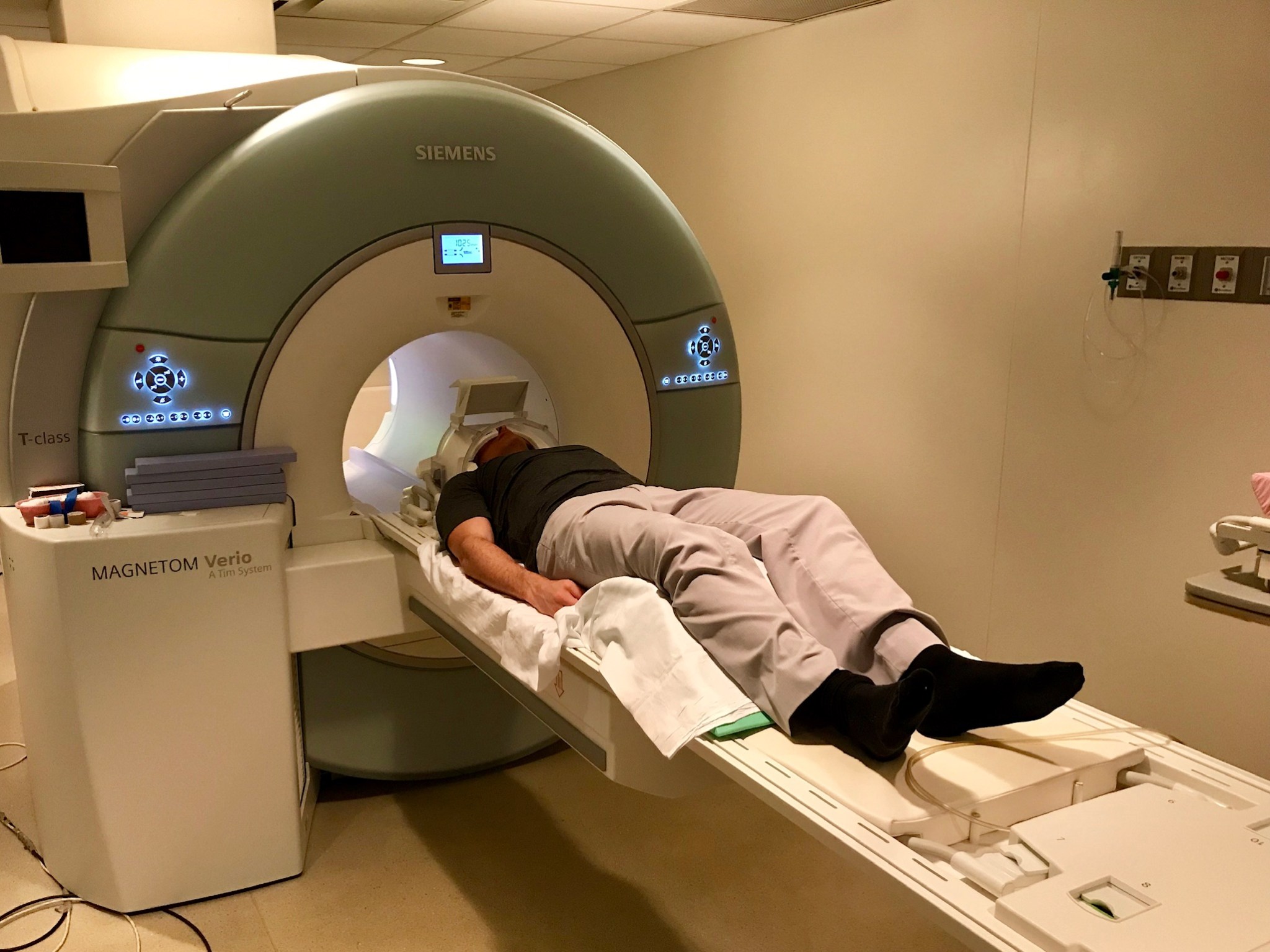
Challenges to measuring space-induced brain changes CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut David Saint-Jacques undergoes an MRI for Wayfinding. CSA Researchers found that an upward shift in the brain during spaceflight makes it hard to distinguish different types of tissue, causing errors in determining changes in brain volume. Previous studies have interpreted these changes as evidence of adaptation to space. This finding suggests that unique methods are needed to analyze astronaut brain structure. Wayfinding, a CSA (Canadian Space Agency) investigation, looked at how the brain adapts to space and readapts after…
Read MoreNASA Earns Best Place to Work in Government for 13th Consecutive Year
NASA’s Worm logo is displayed in front of the agency’s headquarters in Washington. Credit: NASA For the 13th straight year, NASA has earned the title of Best Place to Work in the Federal Government – large agency – from the Partnership for Public Service. The ranking reflects employee satisfaction and workplace elements across the agency while executing NASA’s mission to explore the unknown and discover new knowledge for the benefit of humanity. “NASA’s greatest asset has always been its people – those who rise to the challenge of leading in…
Read MoreStation Nation: Meet Chris Wade, Visiting Vehicle Integration Manager for SpaceX Vehicles
Chris Wade is a visiting vehicle integration manager for SpaceX vehicles in the International Space Station Transportation Integration Office. He plays a key role in ensuring that all vehicle requirements are on track to support SpaceX missions to the space station. Chris also manages a team of real-time mission support personnel who follow launch, docking, undocking, and splashdown operations. Read on to learn about his career with NASA and more! Where are you from? I am from Clarksdale, Mississippi. Tell us about your role at NASA. I manage horizontal integration…
Read MoreStation Science Top News: Feb. 27, 2025
Preventing biofilm formation in space Ashley Keeley, University of Idaho, holds an anti-bacterial coating sample. University of Idaho Student Payload Opportunity with Citizen Science Team Two anti-microbial coatings reduced formation of biofilms in microgravity and have potential for use in space. Controlling biofilms could help protect human health and prevent corrosion and degradation of equipment on future long-duration space missions. Biofilms, communities of microorganisms that attach to a surface, can damage mechanical systems and present a risk of disease transmission. Bacteria Resistant Polymers in Space examined how microgravity affects polymer…
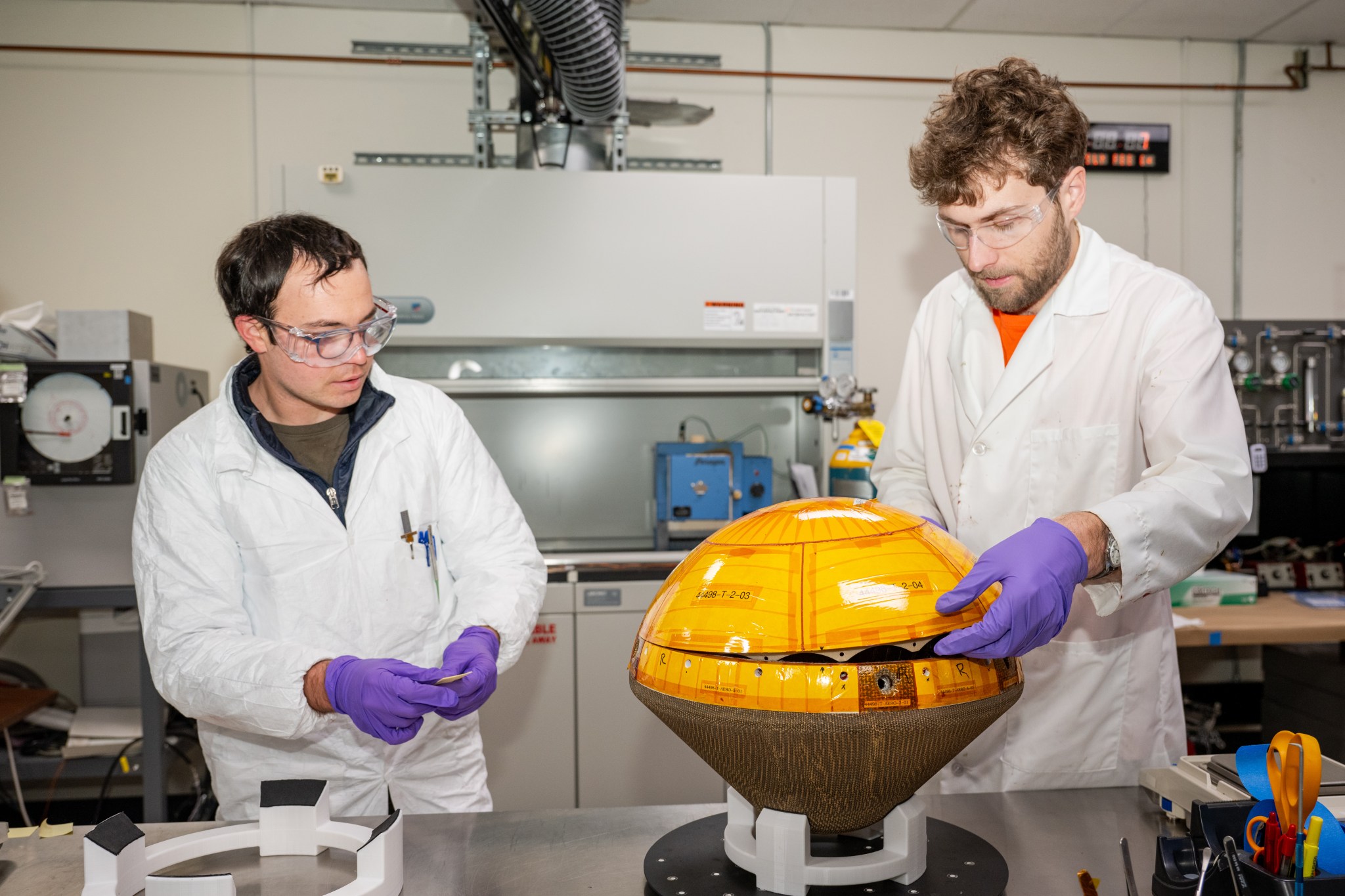
Read MoreNASA Installs Heat Shield on First Private Spacecraft Bound for Venus
NASA/Brandon Torres Navarrete Engineers at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley, Bohdan Wesely, right, and Eli Hiss, left, complete a fit check of the two halves of a space capsule that will study the clouds of Venus for signs of life. Led by Rocket Lab of Long Beach, California, and their partners at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, Rocket Lab’s Venus mission will be the first private mission to the planet. NASA’s role is to help the commercial space endeavor succeed by providing expertise in thermal protection…
Read More