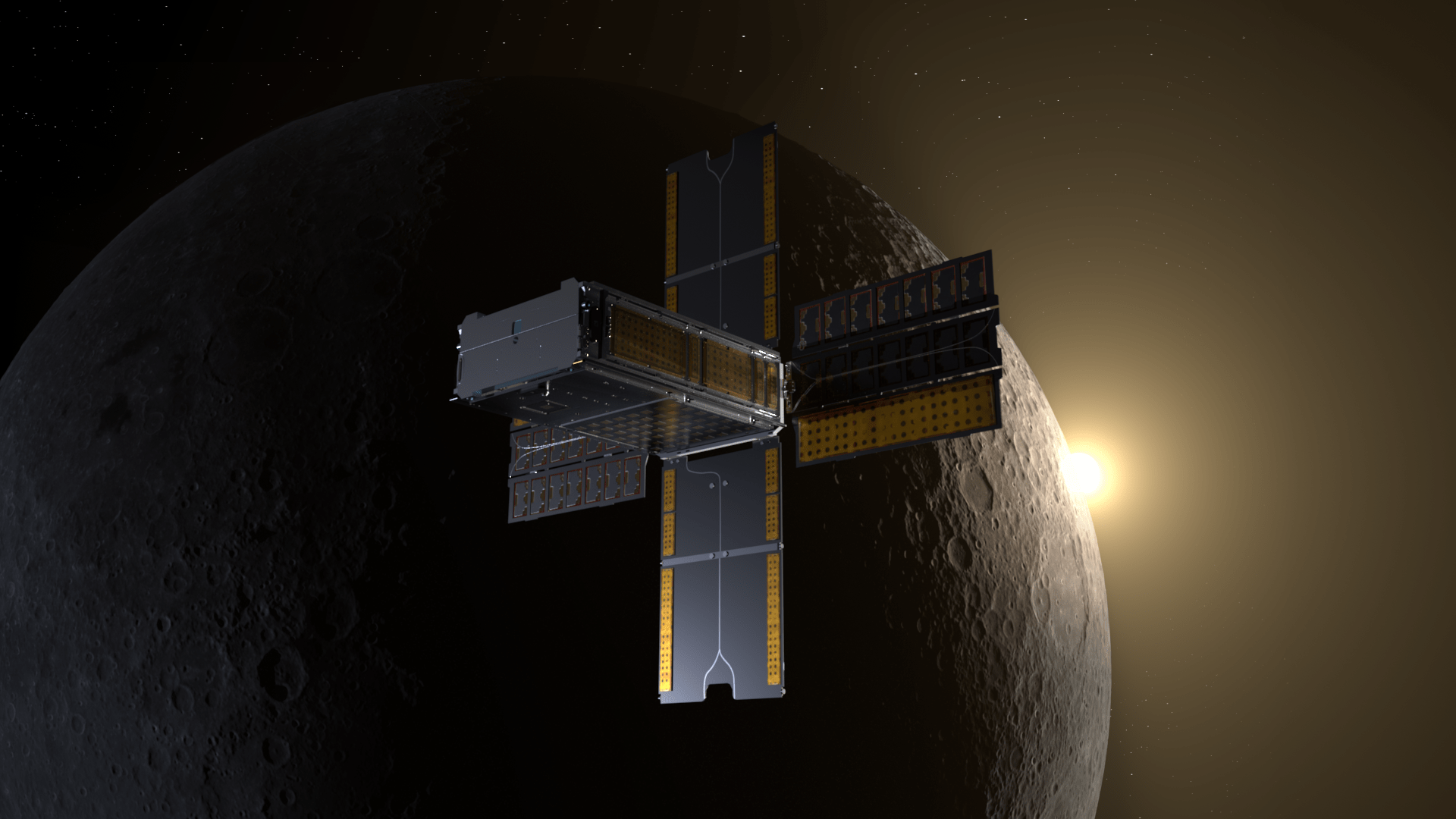
llustration of BioSentinel’s spacecraft flying past the Moon. NASA/Daniel Rutter Editor’s Note: This article was updated Nov. 20, 2024 shortly after BioSentinel’s mission marked two years of operation in deep space. Astronauts live in a pretty extreme environment aboard the International Space Station. Orbiting about 250 miles above the Earth in the weightlessness of microgravity, they rely on commercial cargo missions about every two months to deliver new supplies and experiments. And yet, this place is relatively protected in terms of space radiation. The Earth’s magnetic field shields space station crew from much of the…
Read MoreTag: Science Instruments
Station Science Top News: Oct. 18, 2024
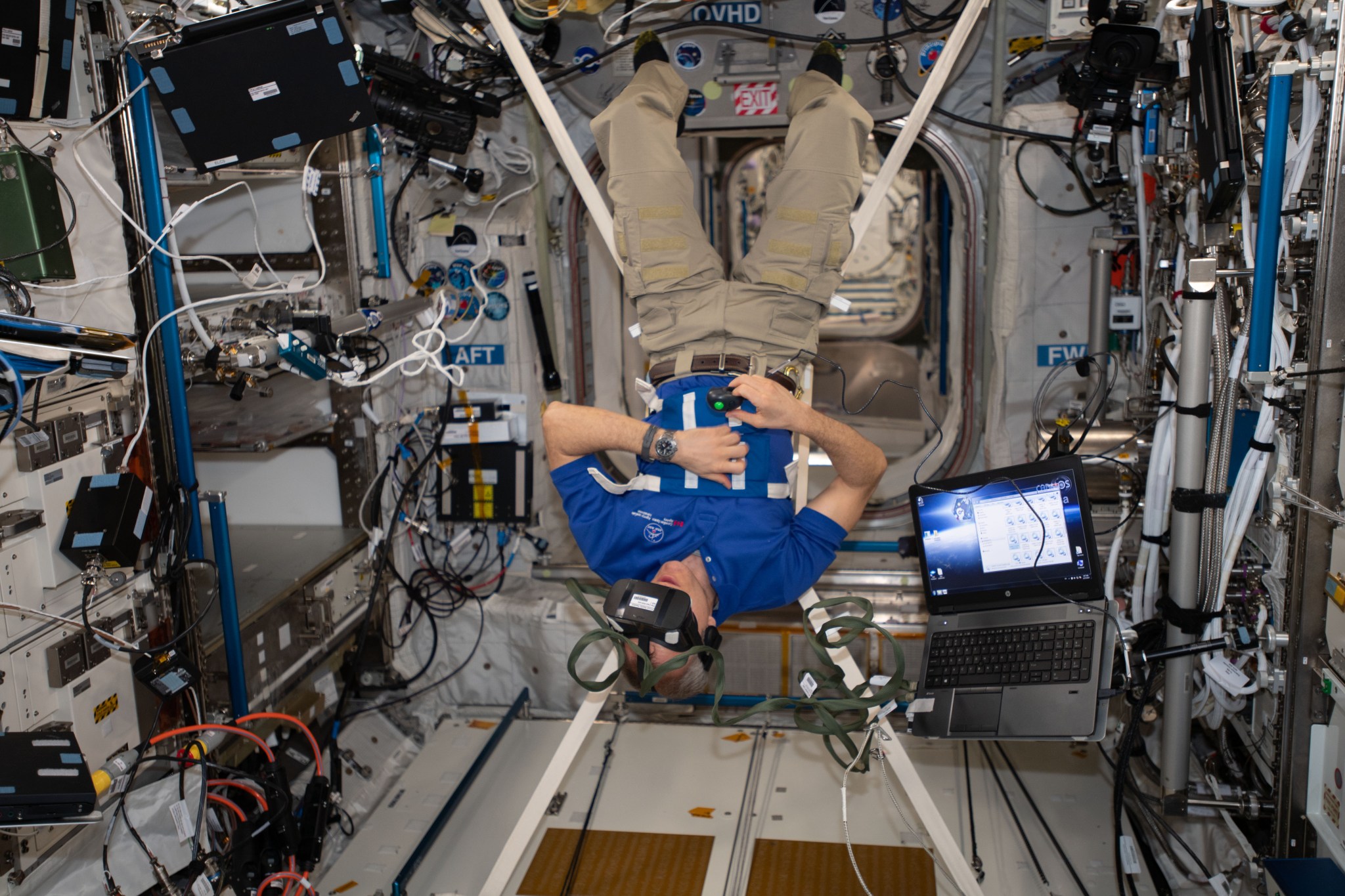
Microgravity had no immediate effect on a person’s ability to perceive the height of an object, indicating that astronauts can safely perform tasks that rely on accurate and precise height judgments soon after arrival in space. We use the height and width of objects around us to complete tasks such as reaching for objects and deciding whether we can fit through an opening. VECTION, an investigation from the Canadian Space Agency, examined the effect of microgravity on an astronaut’s visual perception and how that ability may adapt during flight or upon return to…
Read More