3 min read Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater) How do we do research in zero gravity? Actually when astronauts do experiments on the International Space Station, for instance, to environment on organisms, that environment is actually technically called microgravity. That is, things feel weightless, but we’re still under the influence of Earth’s gravity. Now, the very microgravity that we’re trying to study up there can make experiments actually really kind of difficult for a bunch of different reasons. First of all, stuff floats. So losing things in…
Read MoreTag: Science & Research
Andrea Harrington’s Vision Paves the Way for Lunar Missions
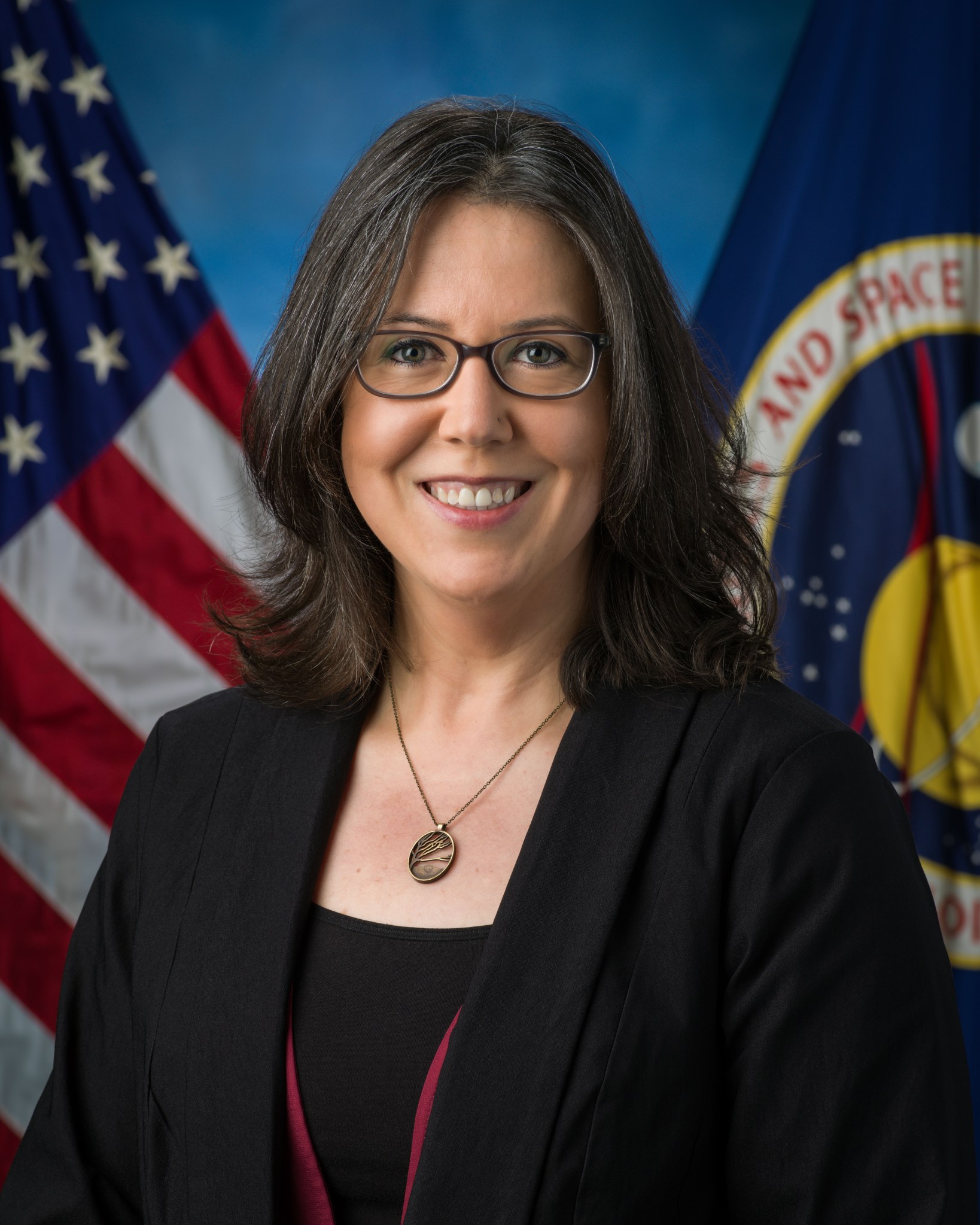
When future astronauts set foot on Mars, they will stand on decades of scientific groundwork laid by people like Andrea Harrington. As NASA’s sample return curation integration lead, Harrington is helping shape the future of planetary exploration and paving the way for interplanetary discovery. Official portrait of Andrea Harrington. NASA/Josh Valcarcel Harrington works in NASA’s Astromaterials Research and Exploration Sciences Division, or ARES, at Johnson Space Center in Houston, where she integrates curation, science, engineering, and planetary protection strategies into the design and operation of new laboratory facilities and sample…
Read MoreWhat NASA Is Learning from the Biggest Geomagnetic Storm in 20 Years
6 min read What NASA Is Learning from the Biggest Geomagnetic Storm in 20 Years One year on, NASA scientists are still making huge discoveries about the largest geomagnetic storm to hit Earth in two decades, the Gannon storm. The findings are helping us better understand and prepare for the ways in which the Sun’s activity can affect us. On May 10, 2024, the first G5 or “severe” geomagnetic storm in over two decades hit Earth. The event did not cause any catastrophic damages, but it did produce surprising effects…
Read MoreNASA’s NICER Maps Debris From Recurring Cosmic Crashes
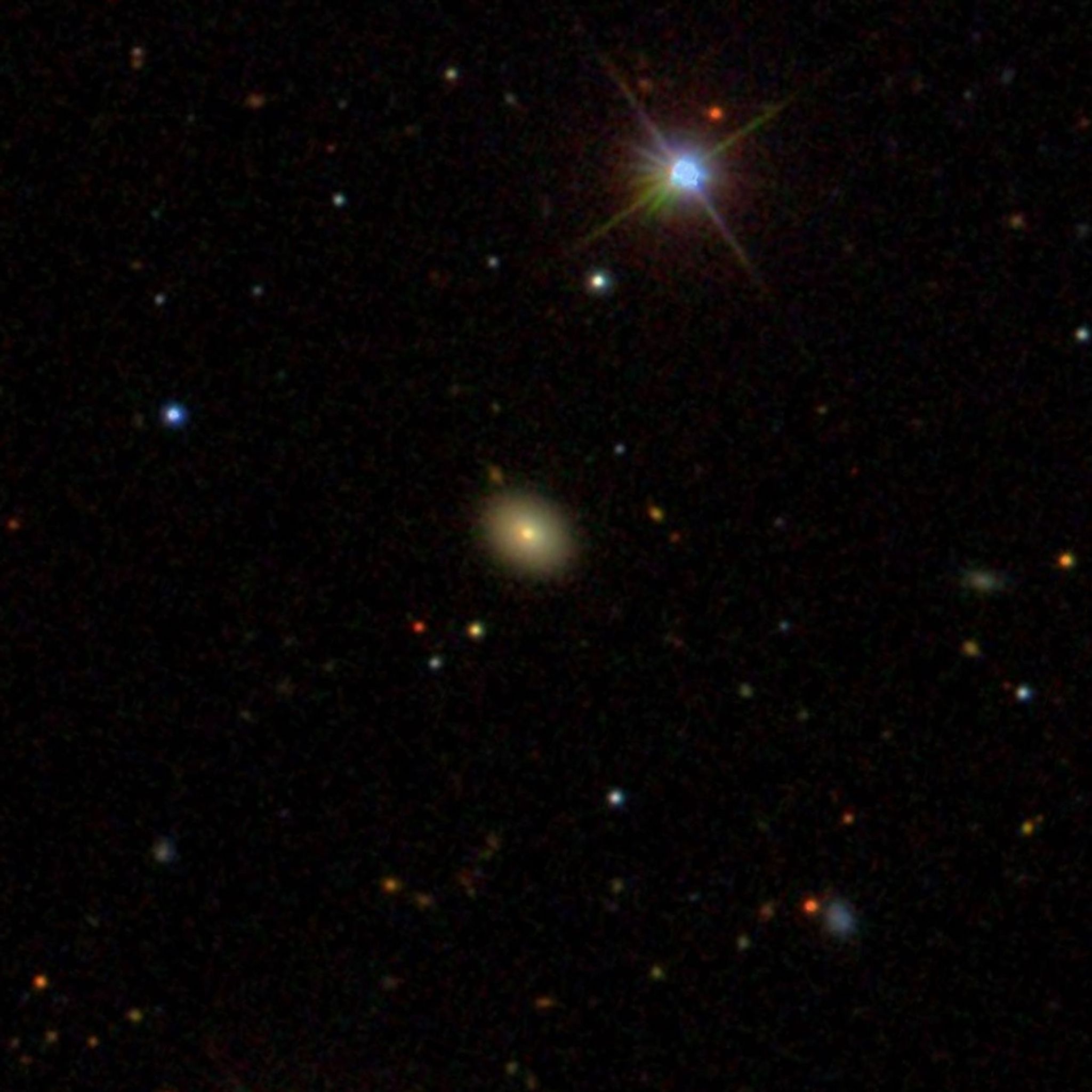
5 min read NASA’s NICER Maps Debris From Recurring Cosmic Crashes Lee esta nota de prensa en español aquí. For the first time, astronomers have probed the physical environment of repeating X-ray outbursts near monster black holes thanks to data from NASA’s NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) and other missions. Scientists have only recently encountered this class of X-ray flares, called QPEs, or quasi-periodic eruptions. A system astronomers have nicknamed Ansky is the eighth QPE source discovered, and it produces the most energetic outbursts seen to date. Ansky also…
Read MoreNASA Harvests Lettuce for Space Station Study
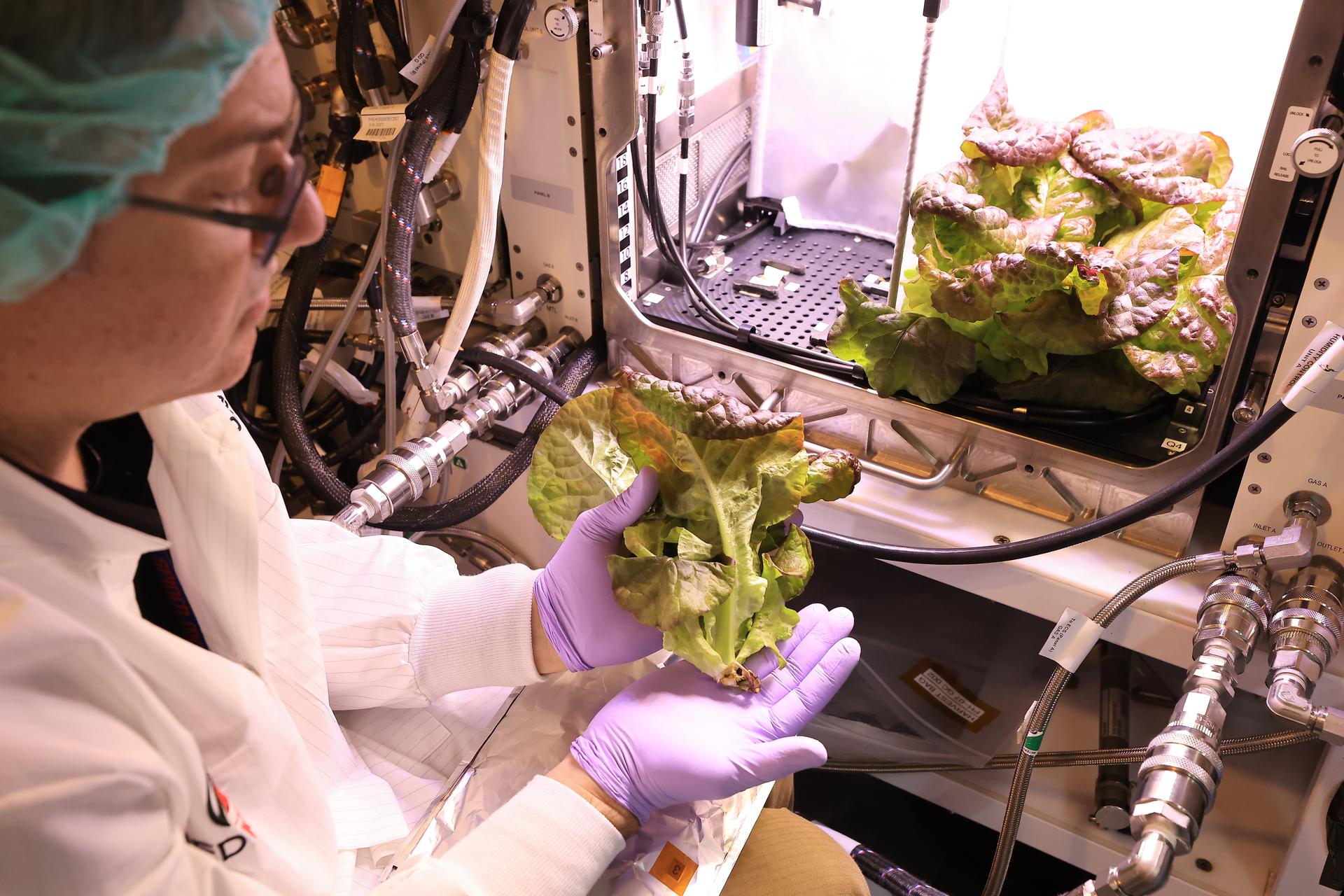
Inside a laboratory in the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a payload implementation team member harvests ‘Outredgeous’ romaine lettuce growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat ground unit on Thursday, April 24, 2025. The harvest is part of the ground control work supporting Plant Habitat-07, which launched to the International Space Station aboard NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission. The experiment focuses on studying how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions affect plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome in microgravity. Research like this…
Read MoreNICER Status Updates
April 17, 2025 Following Repair, NASA’s NICER Improves Daytime Measurements A NASA X-ray telescope on the International Space Station called NICER, or Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer, has regained additional daytime observation capabilities thanks to repairs completed during a spacewalk and a reconfiguration of its detectors. In May 2023, NICER developed a light leak in which unwanted sunlight began entering the instrument. Photos taken from inside the space station revealed several small areas of damage to the telescope’s thin thermal shields, which block sunlight while allowing X-rays through to the…
Read MoreAtomic Clock and Plant DNA Research Launching Aboard NASA’s SpaceX CRS-32 Mission
NASA’s SpaceX 32nd commercial resupply services mission, scheduled to lift off from the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in April, is heading to the International Space Station with experiments that include research on whether plant DNA responses in space correlate to human aging and disease, and measuring the precise effects of gravity on time. Discover more details about the two experiments’ potential impacts on space exploration and how they can enhance life on Earth: “Second Guessing” Time in Space As outlined in Einstein’s general theory of relativity, how we experience the…
Read MoreWhy Do We Grow Plants in Space?
1 min read Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater) Why do we grow plants in space? Plants are such versatile organisms that they can fulfill many roles in our exploration of space. Plants provide us with food, with oxygen, they can recycle water and waste, and they can even provide us with psychological benefits. So all these functions will help NASA in fulfilling our goal of trying to create a sustainable environment for human presence in space. But there are also other benefits. We can investigate how plants…
Read MoreNASA Measures Moonlight to Improve Earth Observations
The airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) instrument is moved across the hangar floor by robotic engineer Alexander McCafferty-Leroux ,from right to left, co-investigator Dr. John Woodward, NIST astronomer Dr. Susana Deustua, air-LUSI chief system engineer Dr. Kathleen “Kat” Scanlon, and members of the ER-2 ground crew at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, in March 2025. NASA/Genaro Vavuris Flying high above the clouds and moon-gazing may sound like a scene from a timeless romance, but NASA did just that in the name of Earth science research. In March…
Read MoreNASA’s Curiosity Rover Detects Largest Organic Molecules Found on Mars
Researchers analyzing pulverized rock onboard NASA’s Curiosity rover have found the largest organic compounds on the Red Planet to date. The finding, published Monday in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests prebiotic chemistry may have advanced further on Mars than previously observed. Scientists probed an existing rock sample inside Curiosity’s Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) mini-lab and found the molecules decane, undecane, and dodecane. These compounds, which are made up of 10, 11, and 12 carbons, respectively, are thought to be the fragments of fatty acids that…
Read More