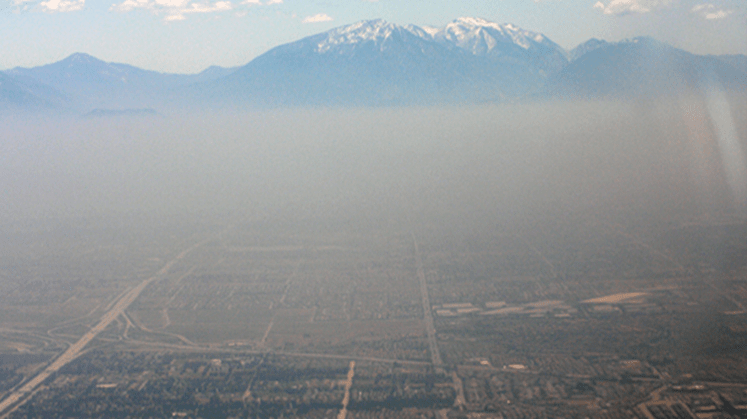
Smog over a deep mountain valley. Credit: NOAA NASA, on behalf of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), has selected BAE Systems (formerly known as Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corporation) of Boulder, Colorado, to develop an instrument to monitor air quality and provide information about the impact of air pollutants on Earth for NOAA’s Geostationary Extended Observations (GeoXO) satellite program. This cost-plus-award-fee contract is valued at approximately $365 million. It includes the development of one flight instrument as well as options for additional units. The anticipated period of performance…
Read MoreTag: Science & Research
New NASA Strategy Envisions Sustainable Future for Space Operations
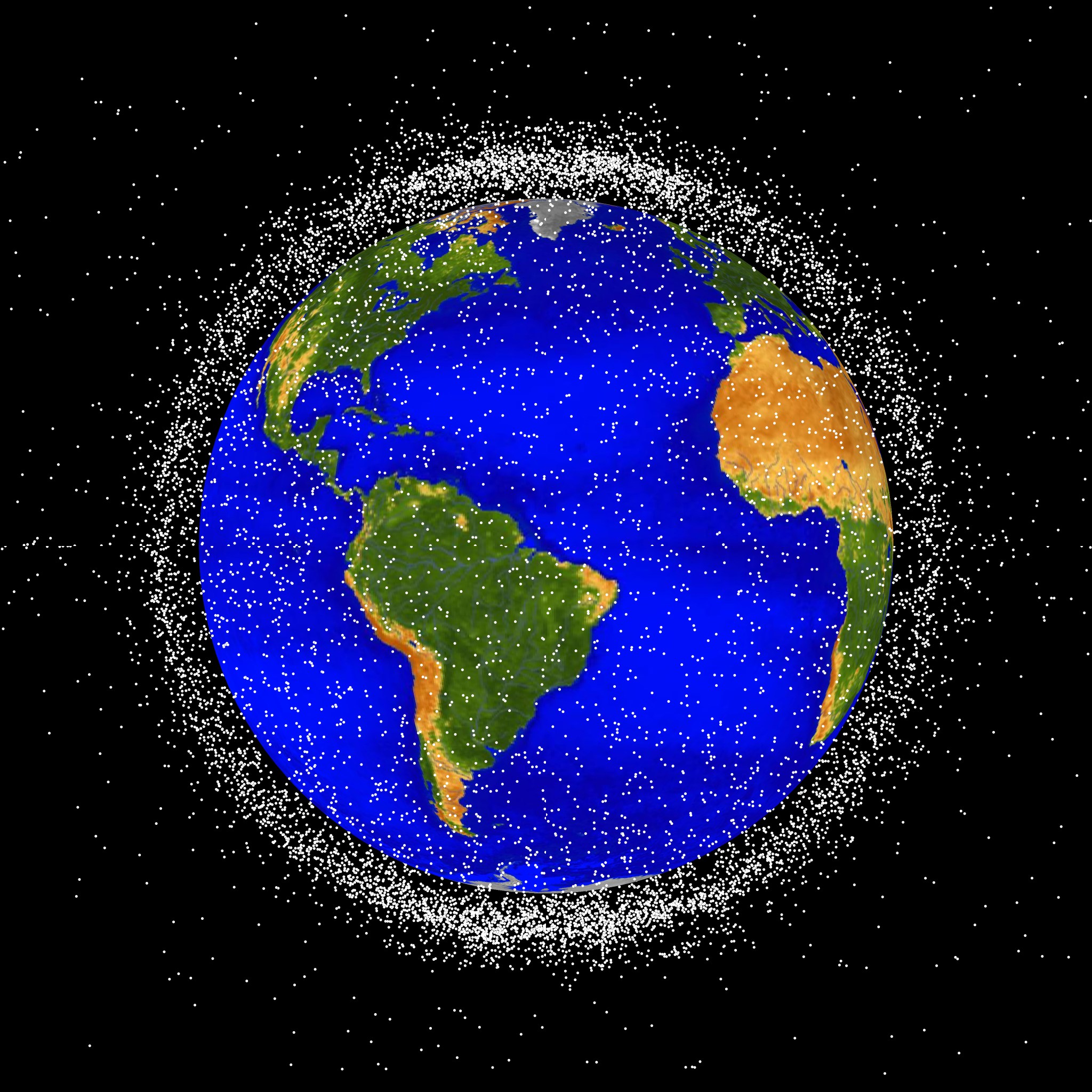
Low Earth orbit, the focus of volume one of NASA’s Space Sustainability Strategy, is the most concentrated area for orbital debris. This computer-generated image showcases objects that are currently being tracked. Credits: NASA ODPO To address a rapidly changing space operating environment and ensure its preservation for generations to come, NASA released the first part of its integrated Space Sustainability Strategy, on Tuesday advancing the agency’s role as a global leader on this crucial issue. “The release of this strategy marks true progress for NASA on space sustainability,” said NASA…
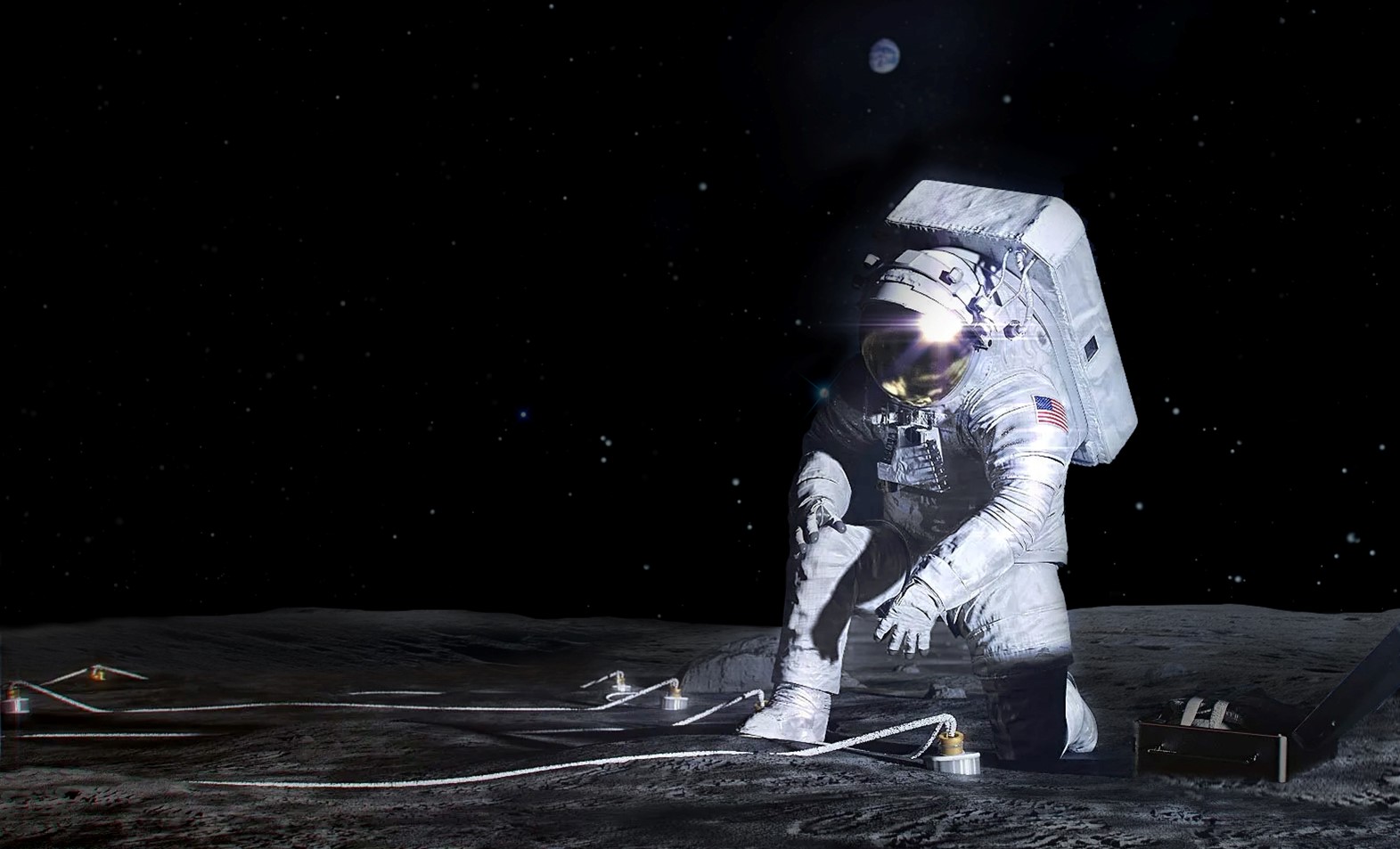
Read MoreNASA Selects First Lunar Instruments for Artemis Astronaut Deployment
Artist’s concept of an Artemis astronaut deploying an instrument on the lunar surface. Credits: NASA NASA has chosen the first science instruments designed for astronauts to deploy on the surface of the Moon during Artemis III. Once installed near the lunar South Pole, the three instruments will collect valuable scientific data about the lunar environment, the lunar interior, and how to sustain a long-duration human presence on the Moon, which will help prepare NASA to send astronauts to Mars. “Artemis marks a bold new era of exploration, where human presence…
Read MoreNASA to Launch Sounding Rockets into Moon’s Shadow During Solar Eclipse
5 min read NASA to Launch Sounding Rockets into Moon’s Shadow During Solar Eclipse NASA will launch three sounding rockets during the total solar eclipse on April 8, 2024, to study how Earth’s upper atmosphere is affected when sunlight momentarily dims over a portion of the planet. The Atmospheric Perturbations around Eclipse Path (APEP) sounding rockets will launch from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia to study the disturbances in the ionosphere created when the Moon eclipses the Sun. The sounding rockets had been previously launched and successfully recovered from…
Read MoreInternational Space Station welcomes biological and physical science experiments
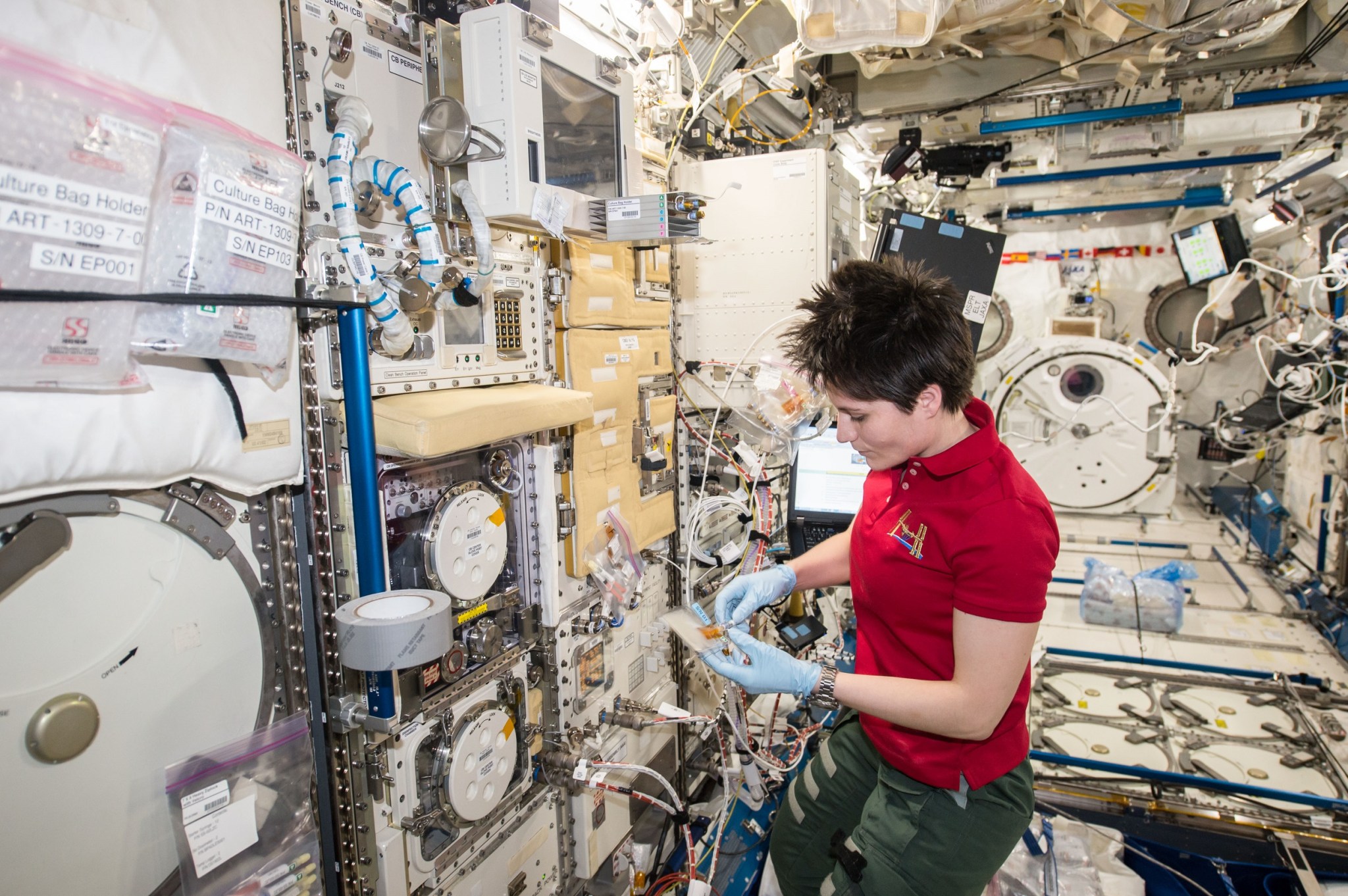
3 min read International Space Station welcomes biological and physical science experiments NASA is sending several biological and physical sciences experiments and equipment aboard SpaceX’s 30th commercial resupply services mission. Studying biological and physical phenomena under extreme conditions allows researchers to advance the fundamental scientific knowledge required to go farther and stay longer in space, while also benefitting life on Earth. Not only can these experiments provide pioneering scientific discovery – they enable sustainable deep space exploration and support transformative engineering. The commercial resupply launch took place Thursday, March 21,…
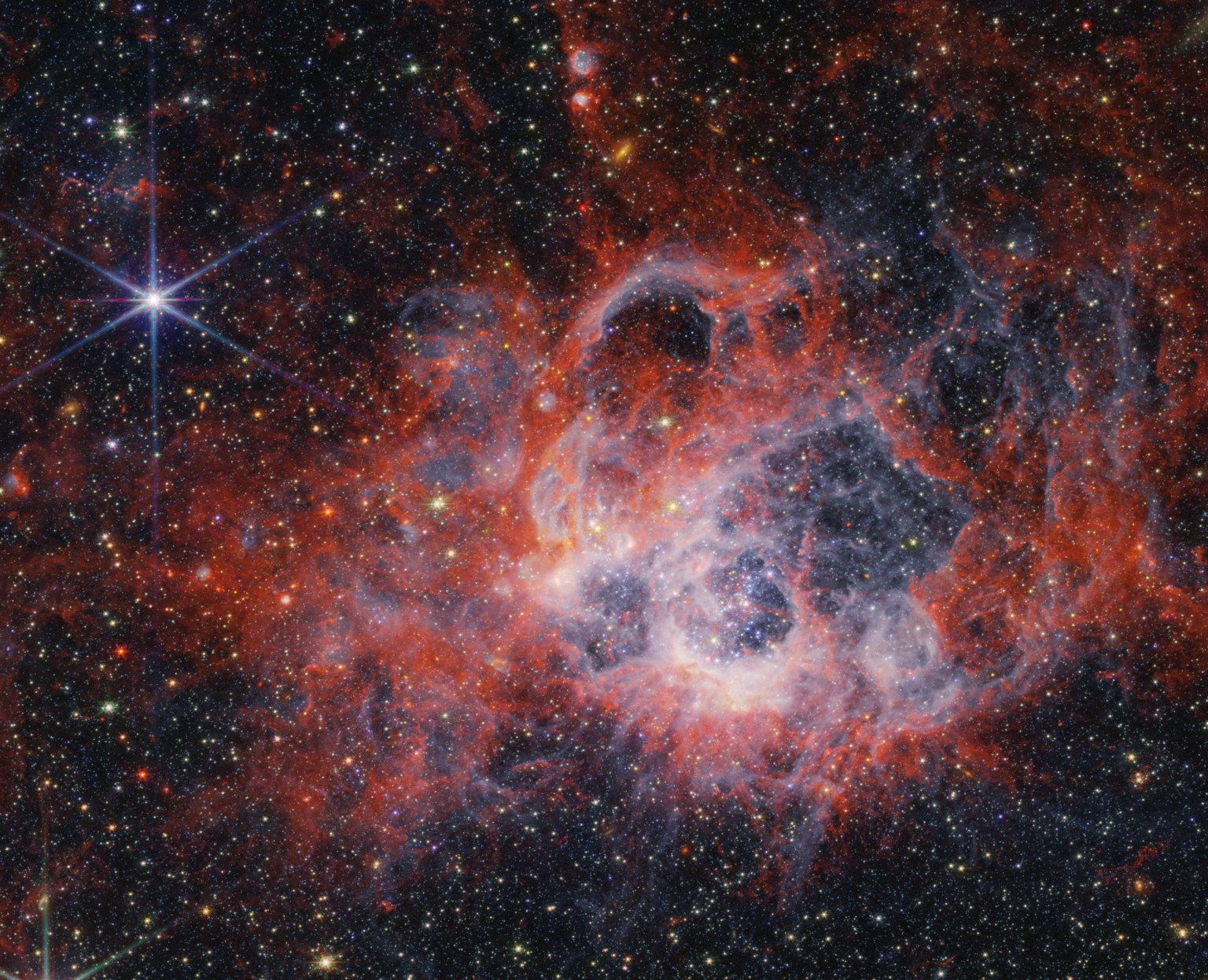
Read MorePeering Into the Tendrils of NGC 604 with NASA’s Webb
4 Min Read Peering Into the Tendrils of NGC 604 with NASA’s Webb Star-forming region NGC 604. Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI The formation of stars and the chaotic environments they inhabit is one of the most well-studied, but also mystery-shrouded, areas of cosmic investigation. The intricacies of these processes are now being unveiled like never before by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Two new images from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) and MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) showcase star-forming region NGC 604, located in the Triangulum galaxy (M33), 2.73 million light-years away…
Read MoreNight-Shining Cloud Mission Ends; Yields High Science Results for NASA
5 min read Night-Shining Cloud Mission Ends; Yields High Science Results for NASA NASA’s Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere (AIM) mission, seen in this visualization, contributed to NASA’s understanding of the region that borders between Earth’s atmosphere and space. NASA After 16 years studying Earth’s highest clouds for the benefit of humanity – polar mesospheric clouds – from its orbit some 350 miles above the ground, NASA’s Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, or AIM, mission has come to an end. Initially slated for a two-year mission, AIM was…
Read MoreInternational Space Station Welcomes Trio of Experiments Focused on Enhancing Life Beyond Earth
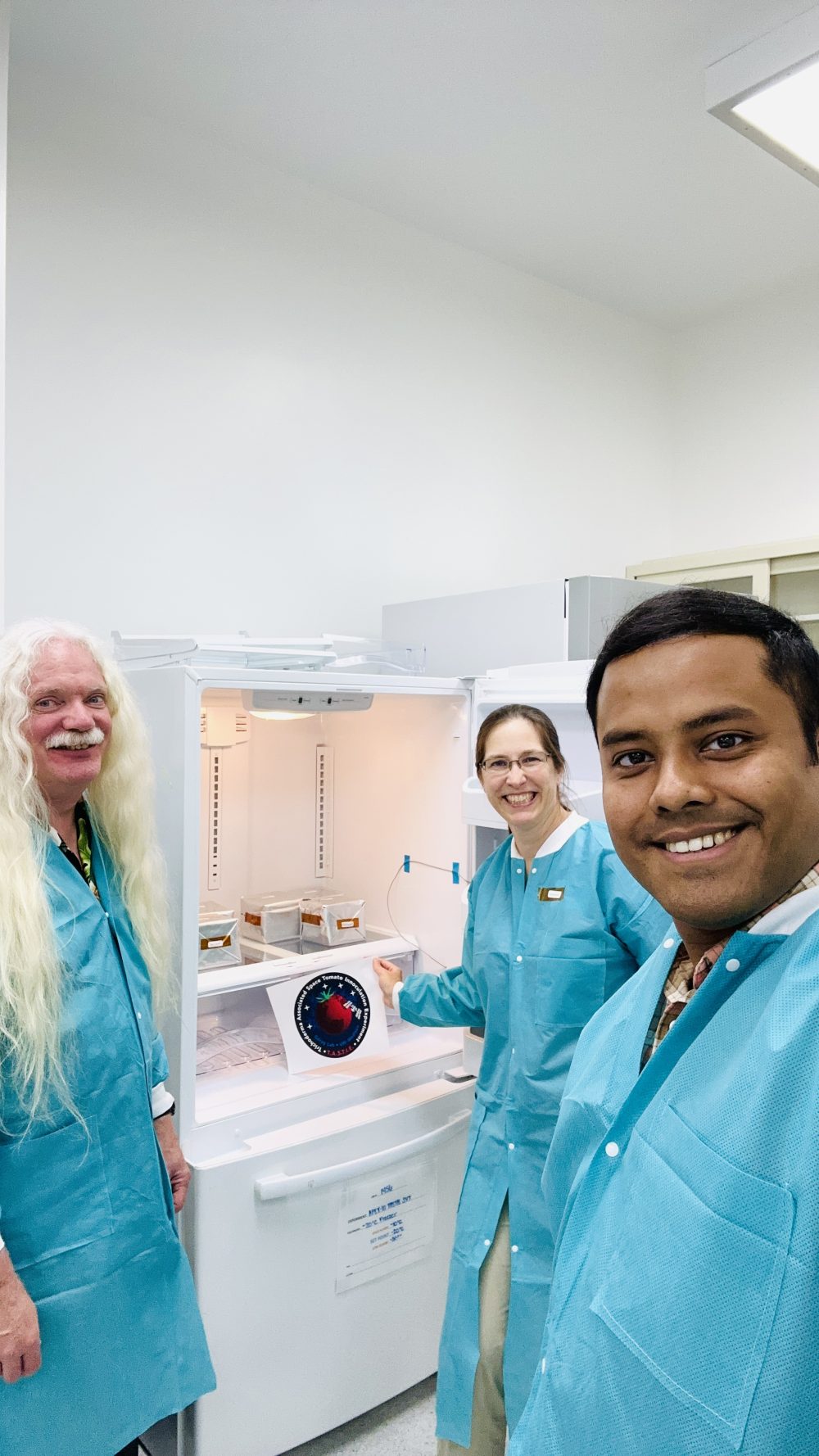
3 min read International Space Station Welcomes Trio of Experiments Focused on Enhancing Life Beyond Earth NASA’s Biological and Physical Sciences Division is sending three physical sciences and space biology experiments and equipment to the International Space Station aboard Northrop Grumman’s 20th commercial resupply services mission. These experiments aim to pioneer scientific discovery, enable sustainable deep space exploration, and support transformative engineering. The launch is scheduled to take place no earlier than Tuesday, January 30, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Using Microbes to Improve Plant Growth in…
Read MoreStation Science 101: Epigenetics Research in Space
A growing body of research suggests a link between epigenetic mechanisms and a wide variety of illnesses and behaviors, including cancer, cardiovascular and autoimmune illnesses, and cognitive dysfunction. Epigenetics also plays a role in the changes humans and other living things experience in space. This phenomenon has become part of studies in a wide variety of fields, including microgravity research conducted aboard the International Space Station. So just what is epigenetics? According to a paper from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, it includes any process that alters gene…
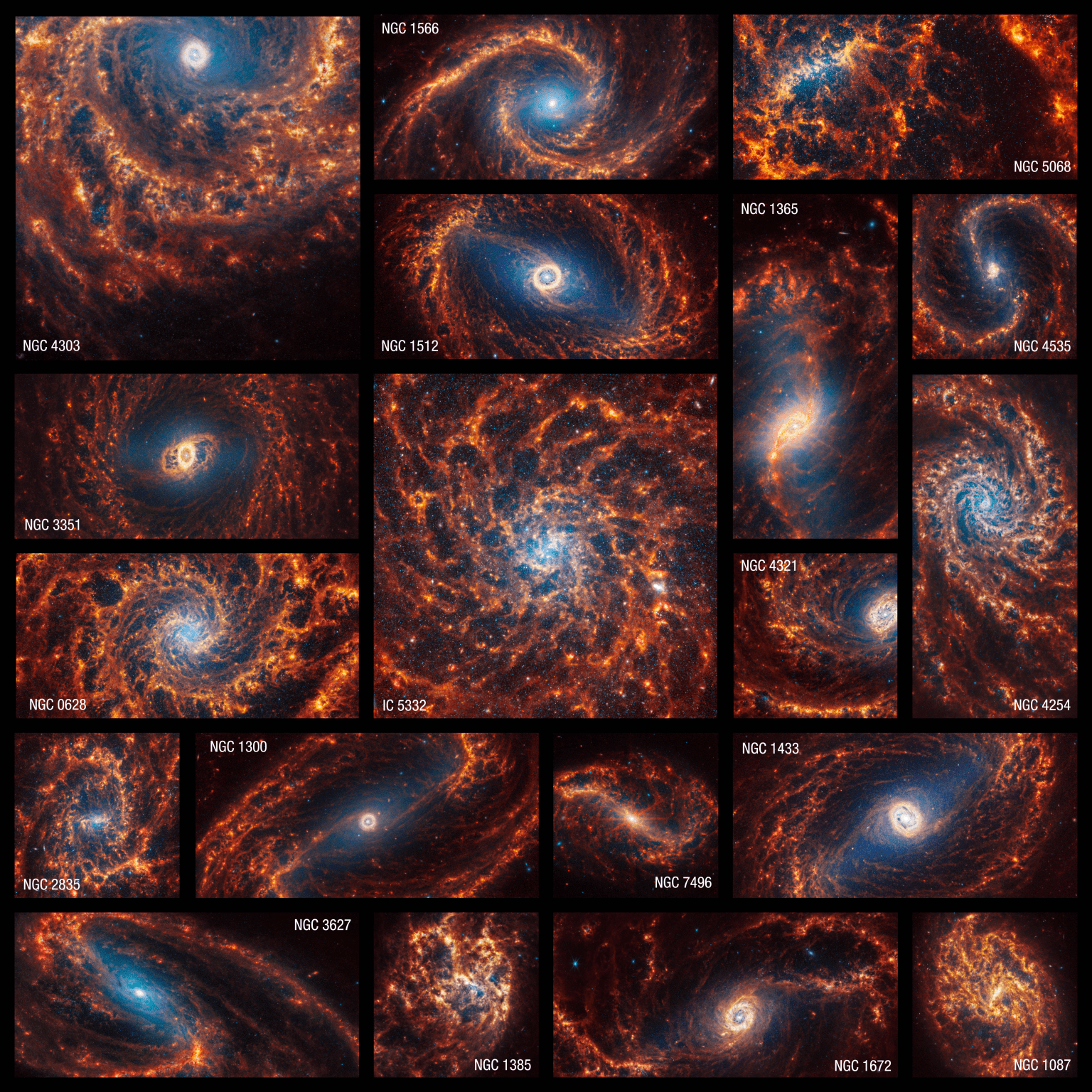
Read MoreNASA’s Webb Depicts Staggering Structure in 19 Nearby Spiral Galaxies
6 Min Read NASA’s Webb Depicts Staggering Structure in 19 Nearby Spiral Galaxies Webb’s set of 19 PHANGS images of face-on spiral galaxies. Credits: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Janice Lee (STScI), Thomas Williams (Oxford), and the PHANGS team It’s oh-so-easy to be absolutely mesmerized by these spiral galaxies. Follow their clearly defined arms, which are brimming with stars, to their centers, where there may be old star clusters and – sometimes – active supermassive black holes. Only NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope can deliver highly detailed scenes of nearby galaxies…
Read More