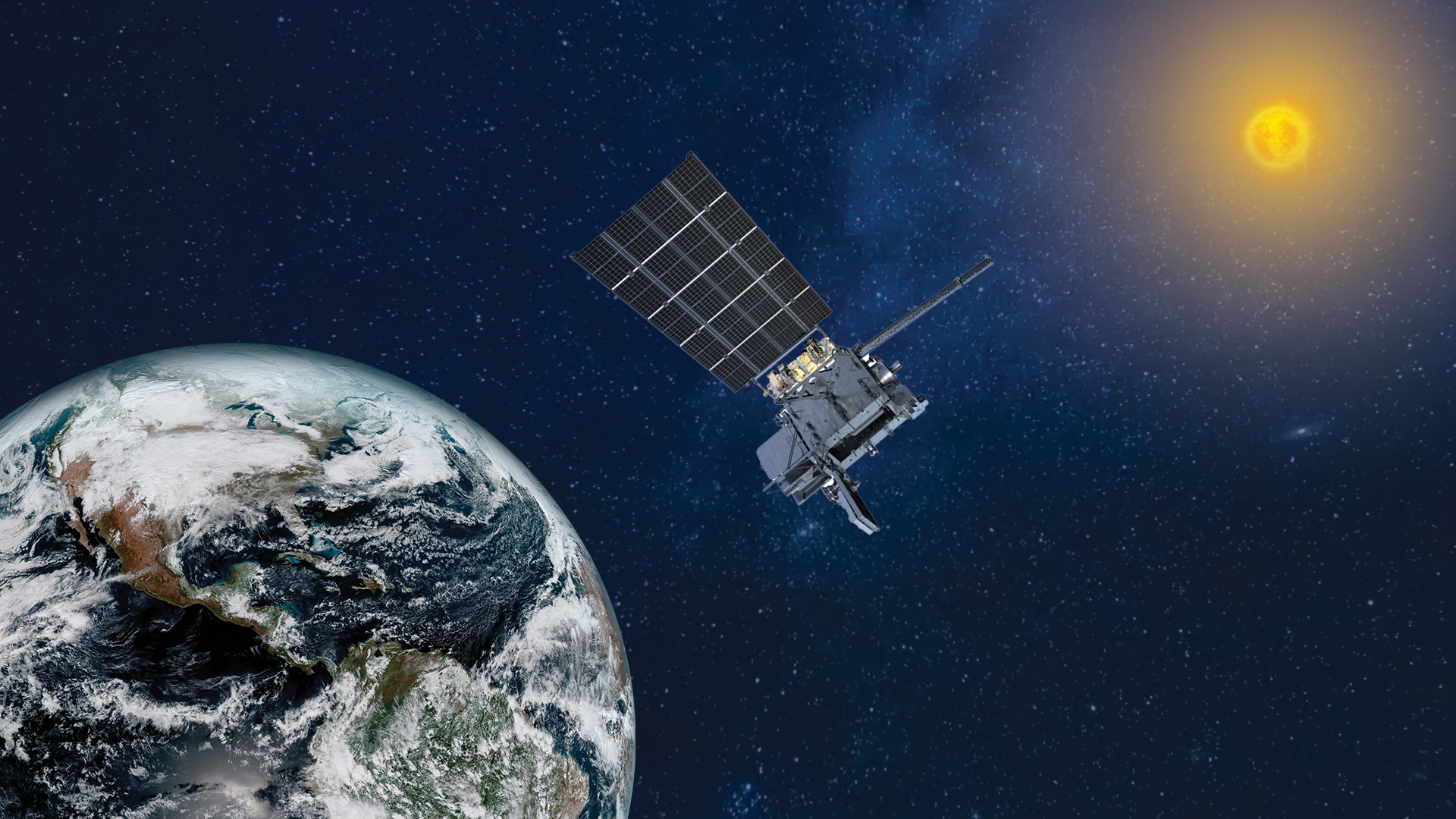
The final satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R weather satellite series has a new place in orbit … and a new name. The GOES-19 weather satellite, which launched into orbit in June 2024, has officially taken the place of its predecessor GOES-16 to watch over the Western Hemisphere from its perch 22,236 miles (35,785 kilometers) above us. To mark the milestone, the satellite has the new name of GOES East to serve as the dominant geostationary satellite in the fleet, NOAA officials said in a statement. “With GOES-19 now in operation, NOAA…
Read MoreTag: Solar System
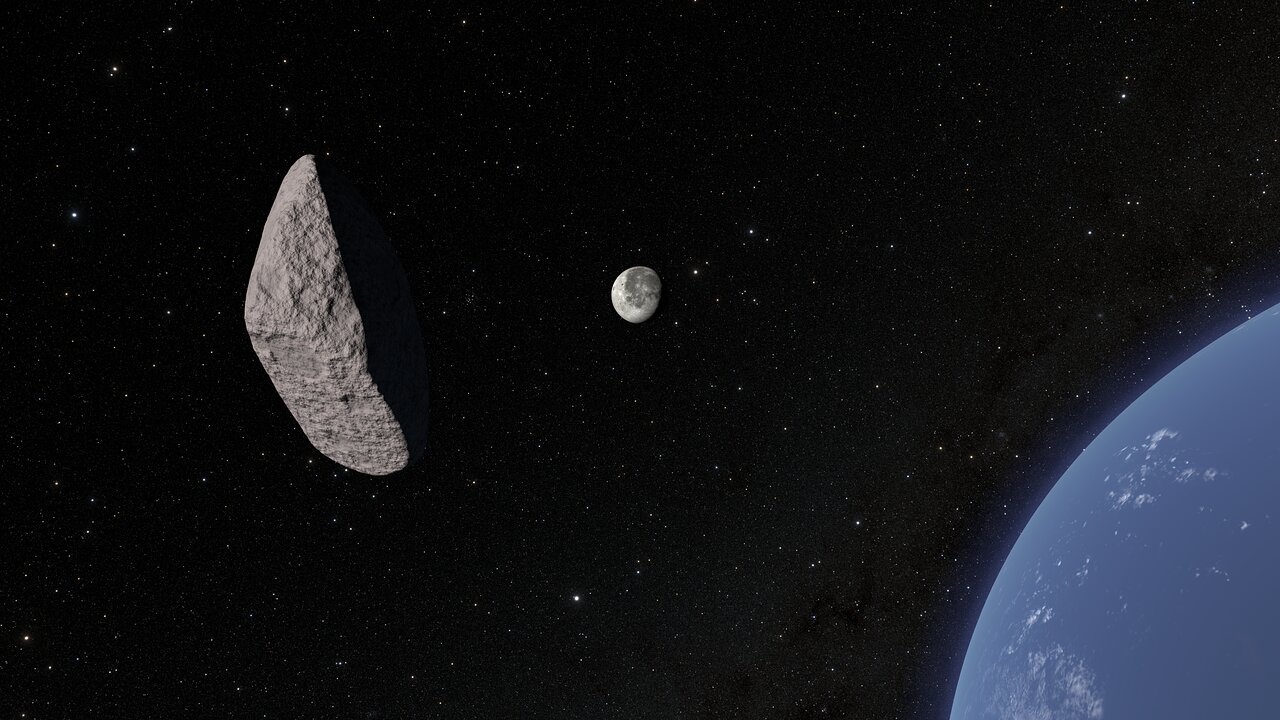
We now know the shape of notorious asteroid 2024 YR4 that dominated headlines recently — it’s probably ‘suburban,’ too
The asteroid 2024 YR4 — the one that caused a stir earlier this year due to its potential collision course with Earth — has a surprising tale to tell. A new study reports that this space rock likely hails from the central region of the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter — a cosmic “suburb” scientists don’t typically associate with asteroids that cross paths with our planet. Shortly after its discovery late last year, astronomers calculated that 2024 YR4 had a 1.3% chance (1-in-83) of impacting Earth in December…
Read MoreA day on Uranus is actually longer than we thought, Hubble Telescope reveals
Uranus just got a little more time on its hands. A fresh analysis of a decade’s worth of Hubble Space Telescope observations shows Uranus takes 17 hours, 14 minutes and 52 seconds to complete a full rotation — that’s 28 seconds longer than the estimate provided by NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft nearly four decades ago. In January 1986, Voyager 2 became the first — and so far the only — spacecraft to explore Uranus, and with its data, astronomers pegged the ice giant’s rotation period at 17 hours, 14 minutes…
Read MoreNorth America is ‘dripping’ down into Earth’s mantle, scientists discover
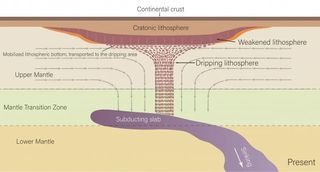
An ancient slab of Earth’s crust buried deep beneath the Midwest is sucking huge swatches of present-day’s North American crust down into the mantle, researchers say. The slab’s pull has created giant “drips” that hang from the underside of the continent down to about 400 miles (640 kilometers) deep inside the mantle, according to a new study. These drips are located beneath an area spanning from Michigan to Nebraska and Alabama, but their presence appears to be impacting the entire continent. The dripping area looks like a large funnel, with…
Read MoreEarth’s sea ice hits all-time low, NASA satellites reveal
New research from NASA and the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) in Colorado measured Arctic sea ice cover on March 22, during what should’ve been its annual peak. In conclusion, the agency reported seeing 5.53 million square miles (14.33 million square kilometers) of sea ice — for context, that’s the lowest Arctic winter sea ice levels have ever been. To make matters worse, NASA scientists also discovered that, this year, summer ice in the Antarctic retreated to 764,000 square miles (1.98 million square kilometers) as of March 1,…
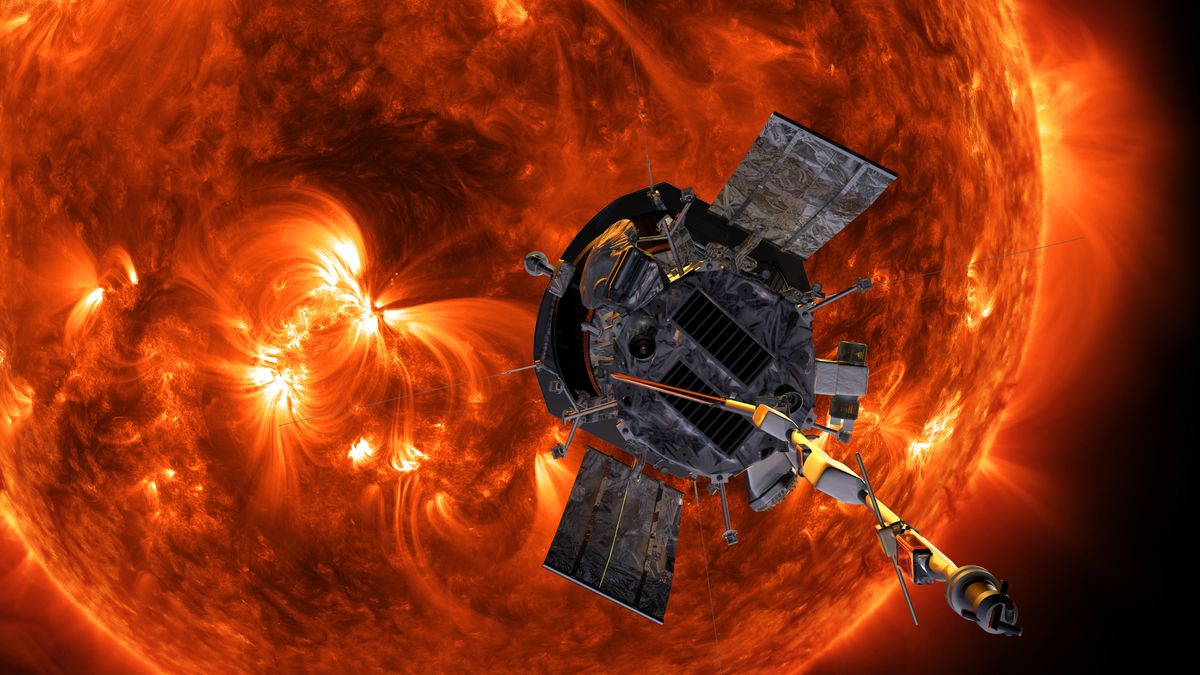
Read MoreNASA’s daredevil solar spacecraft survives 2nd close flyby of our sun
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe has successfully completed its second close flyby of the sun, the space agency announced earlier this week. The car-sized spacecraft swooped within 8 million miles (6.1 million kilometers) of the sun‘s surface at a whopping 430,000 miles per hour (692,000 kilometers per hour), matching the historic record it set during its encounter on Christmas Eve last year. During this approach, which occurred on Saturday (March 22), the Parker Solar Probe once again operated autonomously, with its four science instruments programmed to collect science data about solar…
Read MoreWatch the sun set over the moon in epic video from private Blue Ghost lunar lander
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander made the most of its last few hours of life on the moon. The solar-powered Blue Ghost shut down on Sunday evening (March 16), shortly after the sun set over its lunar locale. The lander watched our star’s descent and disappearance over the cratered horizon, capturing the oncoming, killing darkness in a poignant video that Firefly shared with the world today (March 18). “These are the first high-definition images taken of the sun going down and then going into darkness at the horizon [on…
Read MoreFarewell, Blue Ghost! Private moon lander goes dark to end record-breaking commercial lunar mission
The historic mission of Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander is over. The solar-powered Blue Ghost went dark on Sunday evening (March 16) after the sun set on its lunar locale, bringing an end to a highly successful two weeks of surface operations on the moon. “We battle-tested every system on the lander and simulated every mission scenario we could think of to get to this point,” Blue Ghost Chief Engineer Will Coogan said in a Firefly statement today (March 17) that announced the end of the mission. “But what…
Read MoreThe 1st private mission to Venus comes together ahead of possible 2026 launch (photos)
Engineers at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley report progress in installing a heat shield on the first private spacecraft targeted for Venus. Rocket Lab of Long Beach, California, is leading the effort, along with their partners at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. NASA’s Heatshield for Extreme Entry Environment Technology (HEEET) was invented at the NASA Ames center. NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology program, part of the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, supported the development of the heat shield for Rocket Lab’s Venus mission. You…
Read MoreWorld’s largest iceberg runs aground in South Atlantic after 1,200-mile journey (satellite photos)
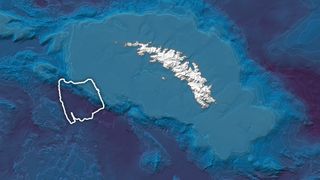
Earth’s largest iceberg has run aground off the coast of South Georgia Island, a common rendezvous spot for large icebergs, new satellite images show. Measuring 1,240 square miles (3,460 square kilometers), the Antarctic iceberg A-23A has come to a grinding halt after a long and winding journey across the Scotia Sea, also known as “iceberg alley.” Satellite images taken at the beginning of March show the iceberg parked on a shallow underwater shelf off the coast of South Georgia Island, which is a British overseas territory in the South Atlantic…
Read More