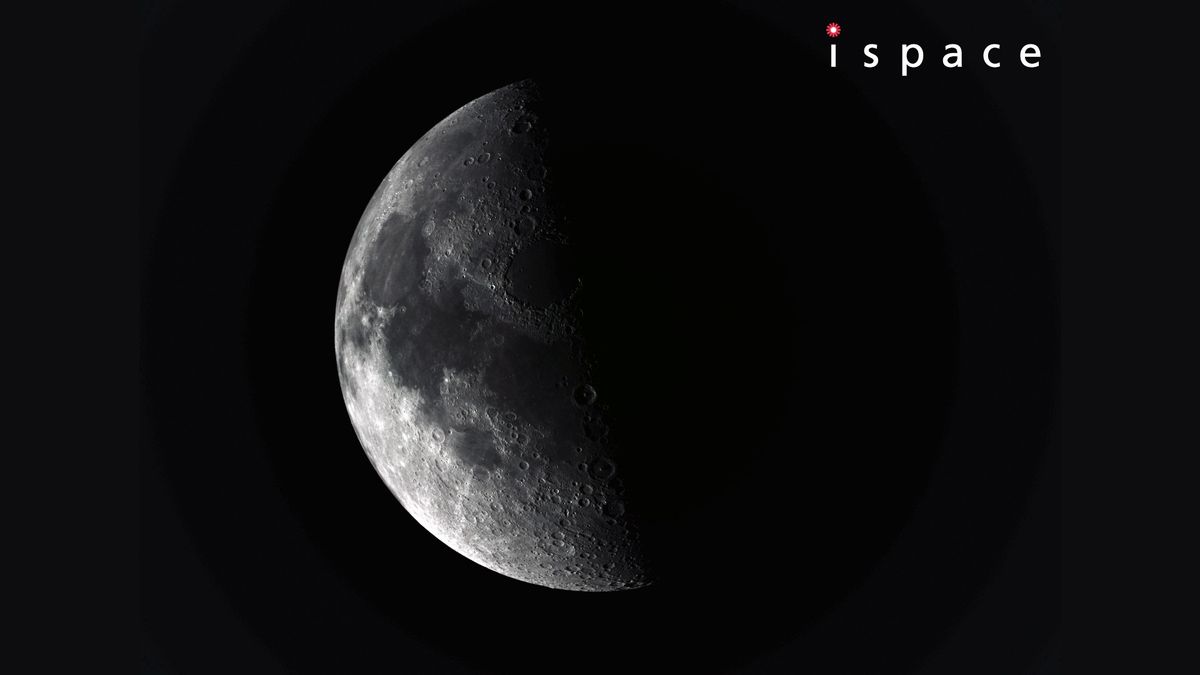
The private Resilience lunar lander just got its first up-close look at the moon. Resilience, which was built by Japanese company ispace, aced a flyby of the moon on Friday evening (Feb. 14), coming within a mere 5,220 miles (8,400 kilometers) of Earth’s nearest neighbor. The lander memorialized the milestone with a photo, snapping a nice shot of the battered lunar surface from a distance of 8,972 miles (14,439 km). The close encounter was “a historic first of its type for a Japanese private, commercial lunar lander,” according to ispace.…
Read MoreTag: Solar System
‘City-killer’ asteroid 2024 YR4 could hit the moon instead of us, scientists say
An asteroid that’s big enough to wipe out a city has a 1-in-43 chance of hitting our planet in the year 2032. But according to new calculations, there’s an even smaller chance that it might crash into the moon instead. On Feb. 7, NASA scientists increased the likelihood of asteroid 2024 YR4 colliding with Earth on Dec. 22, 2032, nearly doubling the odds from 1.2% to 2.3%. The potentially hazardous asteroid measures an estimated 180 feet (55 meters) across — about as wide as Walt Disney World’s Cinderella Castle is…
Read MoreContinent-size blobs in Earth’s mantle are a billion years old, ancient crystals reveal
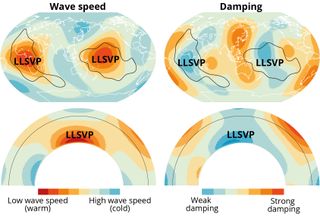
Continent-size islands deep inside Earth’s mantle could be more than a billion years old, a new study finds. Known as large low-seismic-velocity provinces (LLSVPs), these blobs are both hotter and older than nearby areas of the mantle. The findings, published Jan. 22 in the journal Nature, shed light on Earth’s deep interior and could help explain how the mantle moves over time. Scientists have known about these LLSVPs for a few decades. The two giant blobs — one beneath the Pacific Ocean and one beneath Africa — lie at the…
Read MoreWhat the asteroid with a 1-in-48 chance of hitting Earth in 2032 looks like (images)
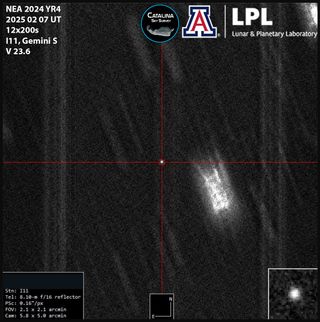
It might not look like much in this image, but this is the asteroid that has made a major news impact in 2025. That’s because this space rock, designated asteroid 2024 YR4, has a 1-in-48 chance of impacting Earth in 2032. For obvious reasons, astronomers are desperate to learn as much as they can about 2024 YR4, estimated to be as large as 177 feet wide (54 meters wide). That’s around as wide as Cinderella’s Castle in Walt Disney World Florida is tall. The image featured here was captured on…
Read MoreTiny plasma jets on the sun drive the elusive solar wind, Europe’s Solar Orbiter reveals
Solar scientists have found tiny, short-lived jets of energy on our sun to be the primary drivers of the solar wind, marking a step toward decoding our star’s elusive behavior and, eventually, refining predictions of its storms. The “solar wind” refers to pockets of energetic particles blasted out from the sun. These particles are occasionally directed toward Earth, like last summer when a rare cluster of such storms rained on our planet and sparked breathtaking auroras across the globe — likely the strongest auroras we’ve seen in centuries. The solar…
Read More‘Marsquakes’ may solve 50-year-old mystery about the Red Planet
Recordings of Martian earthquakes, or “marsquakes,” collected by a robot on the Red Planet may have finally solved a 50-year-old mystery: why one half of Mars is so drastically different from the other. Since the 1970s, researchers have known that Mars is split into two main areas. The northern lowlands cover around two-thirds of the planet’s northern hemisphere, while the southern highlands cover the rest of the planet and have an average elevation roughly 3 miles (5 kilometers) higher than that of the northern lowlands. Mars’ crust, which sits on…
Read MoreA year in isolation: 366-day mock moon mission wraps up in Russia
On Nov. 14, 2024, the Institute of Biomedical Problems (IBMP) of the Russian Academy of Sciences marked the successful completion of SIRIUS-23, a year-long biomedical isolation experiment simulating the conditions of deep-space travel and lunar surface operations. For 366 days, a crew of six analog astronauts lived and worked in a sealed environment, a meticulously controlled Earth-based stand-in for interplanetary missions of the future. The SIRIUS (Scientific International Research in Unique terrestrial Station) project, launched in collaboration with NASA’s Human Research Program and the IBMP in 2017, had previously conducted…
Read MoreMars was hot then cold then hot again. Could life have really survived there?
New research suggests that temperatures on ancient Mars may have fluctuated between hot and cold periods through a relatively short period during its lifetime of billions of years. But these hot and cold spells may have been detrimental to life if it existed on the Red Planet. Mars may be a dry and arid planet today, but scientists know that Earth’s neighbor was much wetter and much more like our planet in its ancient past. These new findings from a team of researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School…
Read MoreSatellites watch world’s largest iceberg on crash course with Antarctic penguin island (photo/video)
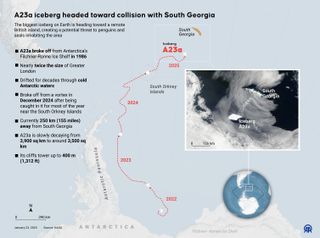
The world’s largest iceberg, A23a, is drifting toward South Georgia Island, a remote and ecologically vital wildlife haven. This massive block of ice, about the size of Rhode Island, poses a significant threat to the delicate ecosystem of the island, home to penguins and seals. Satellite images, including recent data captured by NOAA’s GOES East satellite on Jan. 22, 2025, are closely monitoring the iceberg’s slow journey through the Southern Ocean, where it could soon reach the shallow waters surrounding South Georgia. Breaking free Iceberg A23a has been a concern…
Read MoreEarth is bombarded with rocks from space — but who gets to keep these ultimate antiques?
Every day, about 48.5 tons of space rock hurtle towards Earth. Meteorites that fall into the ocean are never recovered. But the ones that crash on land can spark debates about legal ownership. Globally, meteorite hunting has become a lucrative business, with chunks of alien rock traded online and shipped between countries. Meteorites hold the key to the mysteries of the universe, but increasingly, significant scientific finds are being lost to private collectors. Last year, New Zealand formally recorded an apple-sized meteorite weighing 810g. It fell on Department of Conservation…
Read More