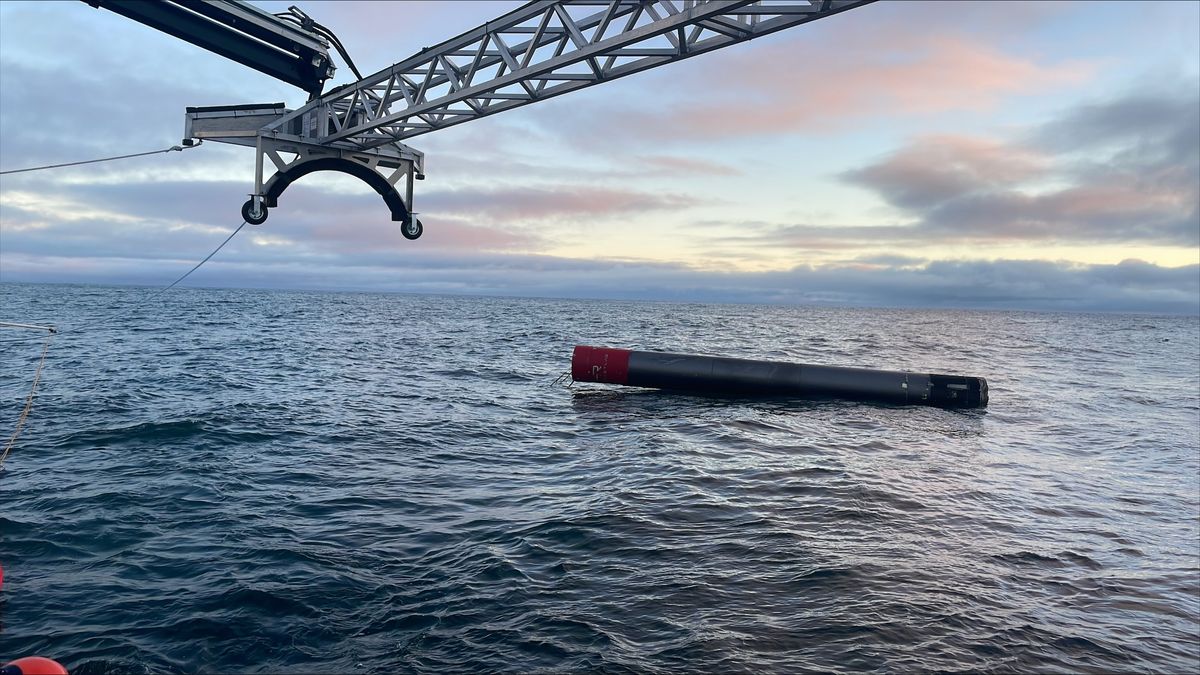
Researchers are developing a new, military-grade “quantum laser” that can cut through fog and operate across long distances. The U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has awarded a $1 million grant to scientists building a prototype “quantum photonic-dimer laser” that uses quantum entanglement to “glue” light particles together and generate a highly concentrated laser beam. Lasers play a crucial role in military operations and are used in everything from satellite communications and targeting technology to mapping and tracking systems like lidar (light detection and ranging). Conventional lasers work by…
Read MoreTag: Tech
DARPA unveils 6 new designs for uncrewed vertical-takeoff military aircraft, eyes 2026 test flights
The U.S. military could soon have new uncrewed aircraft that carry weapons and take off and land vertically. The vehicles could undergo test flights as early as 2026. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) has announced it is moving into a new testing phase for proposed experimental aircraft in which designs will be assessed for risk and analyzed for efficiency. The Advanced Aircraft Infrastructure-less Launch And Recovery (ANCILLARY) program will field designs for new, uncrewed aerial systems (UAS) carrying weapons. Specifically, the project aims to deliver X-planes capable of…
Read MoreUS economy to benefit from NASA investment in 3D-printable superalloy
NASA has invested in an innovative superalloy as part of its Technology Transfer Program, a program that allows technology built for missions to be utilized for other commercial purposes. The superalloy is known as GRX-810 and consists of a 3D-printable, high-temperature material that has the potential to make airplane equipment and spacecraft parts more heavy duty. Items built with this material will be able to withstand a wide range of severe conditions, including intense temperatures, both in the air and in space. As of now, the superalloy is licensed to…
Read MoreNASA-funded pulsed plasma rocket concept aims to send astronauts to Mars in 2 months
An innovative rocket system could revolutionize future deep space missions to Mars, reducing travel time to the Red Planet to just a few months. The goal of landing humans on Mars has presented a myriad of challenges, including the need to quickly transport large payloads to and from the distant planet, which, depending on the positions of Earth and Mars, would take almost two years for a round trip using current propulsion technology. The Pulsed Plasma Rocket (PPR), under development by Howe Industries, is a propulsion system designed to be…
Read MoreScientists could make blazing-fast 6G using curving light rays
The future of cellular data transfer could lie in “curving” light beams midair to deliver 6G wireless networks with blazing-fast speeds — bypassing the need for line of sight between transmitter and receivers. In a new study published March 30 in the journal Nature’s Communications Engineering, researchers explained how they developed a transmitter that can dynamically adjust the waves needed to support future 6G signals. The most advanced cellular communications standard is 5G. Expected to be thousands of times faster, 6G will begin rolling out in 2030, according to the…
Read MoreRocket Lab gearing up to refly Electron booster for 1st time
Rocket Lab is taking a big step toward its first-ever rocket reflight. On Jan. 31, one of the company’s Electron rockets launched four private satellites to Earth orbit. The vehicle’s first stage then came back down for a soft ocean splashdown, and Rocket Lab fished it out of the sea and hauled it back to shore for inspection and analysis. The company has recovered boosters in this manner multiple times in the past, gathering information about how to make Electron first stages reusable. But this particular booster will break new…
Read MoreBoom’s XB-1 test plane gets FAA green light for supersonic flight
Like Tom Cruise’s “Maverick” character in “Top Gun,” Boom Supersonic is feeling the need for speed. The Colorado company has received a first-of-its-kind approval from the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) to exceed Mach 1 during test flights of its XB-1 supersonic jet. These flights are slated to occur sometime this year within the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor in Mojave, California. The sleek, delta-shaped XB-1 took its maiden flight on March 22, 2024 from the Mojave Air & Space Port, and now it’s free to go supersonic at Boom’s California…
Read MoreNuclear fusion reactor in South Korea runs at 100 million degrees C for a record-breaking 48 seconds
South Korea’s “artificial sun” has set a new fusion record after superheating a plasma loop to 180 million degrees Fahrenheit (100 million degrees Celsius) for 48 seconds, scientists have announced. The Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) reactor broke the previous world record of 31 seconds, which was set by the same reactor in 2021.The breakthrough is a small but impressive step on the long road to a source of near-unlimited clean energy. Scientists have been trying to harness the power of nuclear fusion — the process by which stars…
Read More‘Them space drugs cooked real good:’ Varda Space just made an HIV medicine in Earth orbit
On Feb. 21, after some seven months in space, Varda Space Industries’ W-1 capsule successfully returned to Earth, carrying with it a unique payload: the HIV/AIDS medication ritonavir. Varda Space seeks to autonomously manufacture pharmaceuticals in microgravity, a strategy that could ultimately reduce the cost of life-saving drugs — and, according to a new preprint paper, the company is one step closer to achieving that goal. The W-1 mission sought to test the feasibility of making therapeutics in space, testing Varda’s hardware off Earth for the first time. During its time…
Read MoreKeep the lines of communication open by building your own infrared transmitter
(Image credit: Future) The idea of being in a remote location, unable to communicate with civilization, is foreign to most people. With cell phones, Wi-Fi, and radio readily available to us, we hardly think about how difficult it would be to communicate over long distances without them. But that could be a reality for members of the United States Space Force in the future. What do you do when your ability to communicate is hindered? In the second episode of the Space Force STEM Challenge, we show you how to…
Read More