Hubble Space Telescope Hubble Home Overview About Hubble The History of Hubble Hubble Timeline Why Have a Telescope in Space? Hubble by the Numbers At the Museum FAQs Impact & Benefits Hubble’s Impact & Benefits Science Impacts Cultural Impact Technology Benefits Impact on Human Spaceflight Astro Community Impacts Science Hubble Science Science Themes Science Highlights Science Behind Discoveries Hubble’s Partners in Science Universe Uncovered Explore the Night Sky Observatory Hubble Observatory Hubble Design Mission Operations Missions to Hubble Hubble vs Webb Team Hubble Team Career Aspirations Hubble Astronauts News Hubble…
Read MoreTag: The Universe
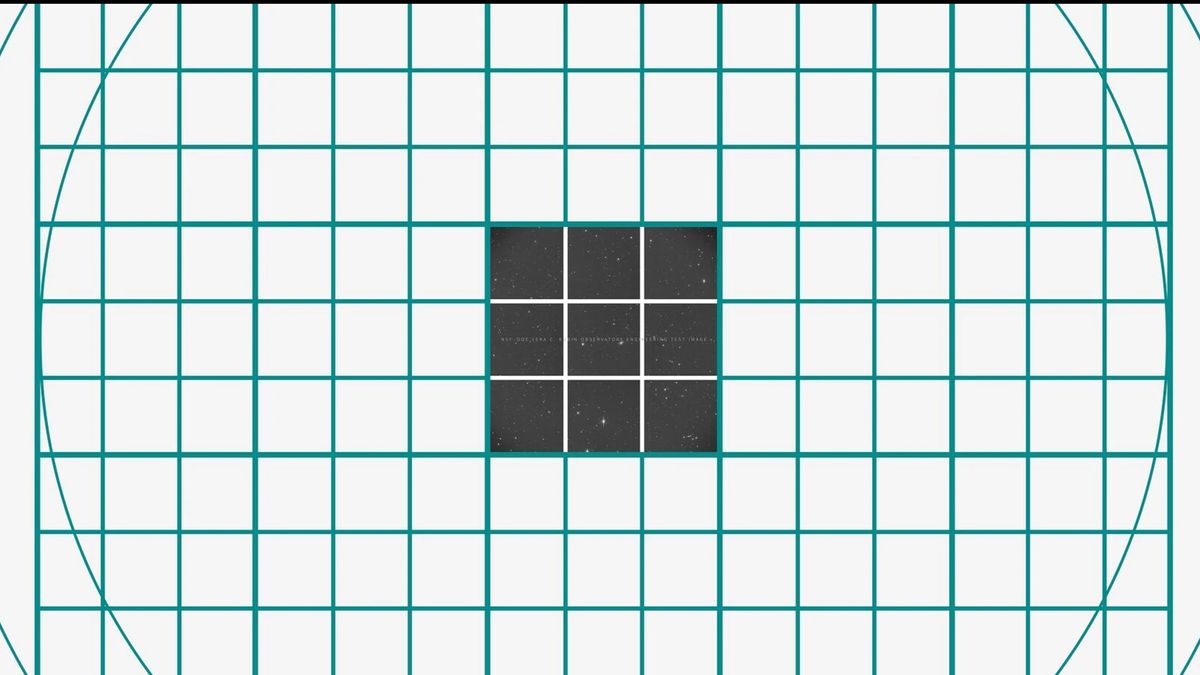
Rubin Observatory aces 1st image tests, gets ready to use world’s largest digital camera
NATIONAL HARBOR, Md. — A giant new telescope in Chile has opened its eyes for the first time — and while the view may not be impressive to some, its scientist parents are thrilled. The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, an 8.4-meter telescope built by the National Science Foundation and U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science, successfully passed a series of critical systems tests and even snapped early images of the sky with an engineering camera. The result? A clean bill of health and an early set of images that…
Read MoreNASA’s Webb Reveals Intricate Layers of Interstellar Dust, Gas
Webb Webb News Latest News Latest Images Blog (offsite) Awards X (offsite – login reqd) Instagram (offsite – login reqd) Facebook (offsite- login reqd) Youtube (offsite) Overview About Who is James Webb? Fact Sheet Impacts+Benefits FAQ Science Overview and Goals Early Universe Galaxies Over Time Star Lifecycle Other Worlds Observatory Overview Launch Orbit Mirrors Sunshield Instrument: NIRCam Instrument: MIRI Instrument: NIRSpec Instrument: FGS/NIRISS Optical Telescope Element Backplane Spacecraft Bus Instrument Module Multimedia About Webb Images Images Videos What is Webb Observing? 3d Webb in 3d Solar System Podcasts Webb Image…
Read MoreScientists turn 3 years’ worth of solar flares into audible sound (video)
If you’re more of an auditory learner than a visual one, this timelapse video is for you. (And, well, visual learners will probably love it, too!) The European Space Agency (ESA) has released an audio-visual representation of solar activity over the last three years, pulling data from its Solar Orbiter probe, which it runs with NASA. In the video, we see blue circles popping up across the surface of the sun — and audible tones paired with each of these circles. As time progresses toward the present day, the frequency…
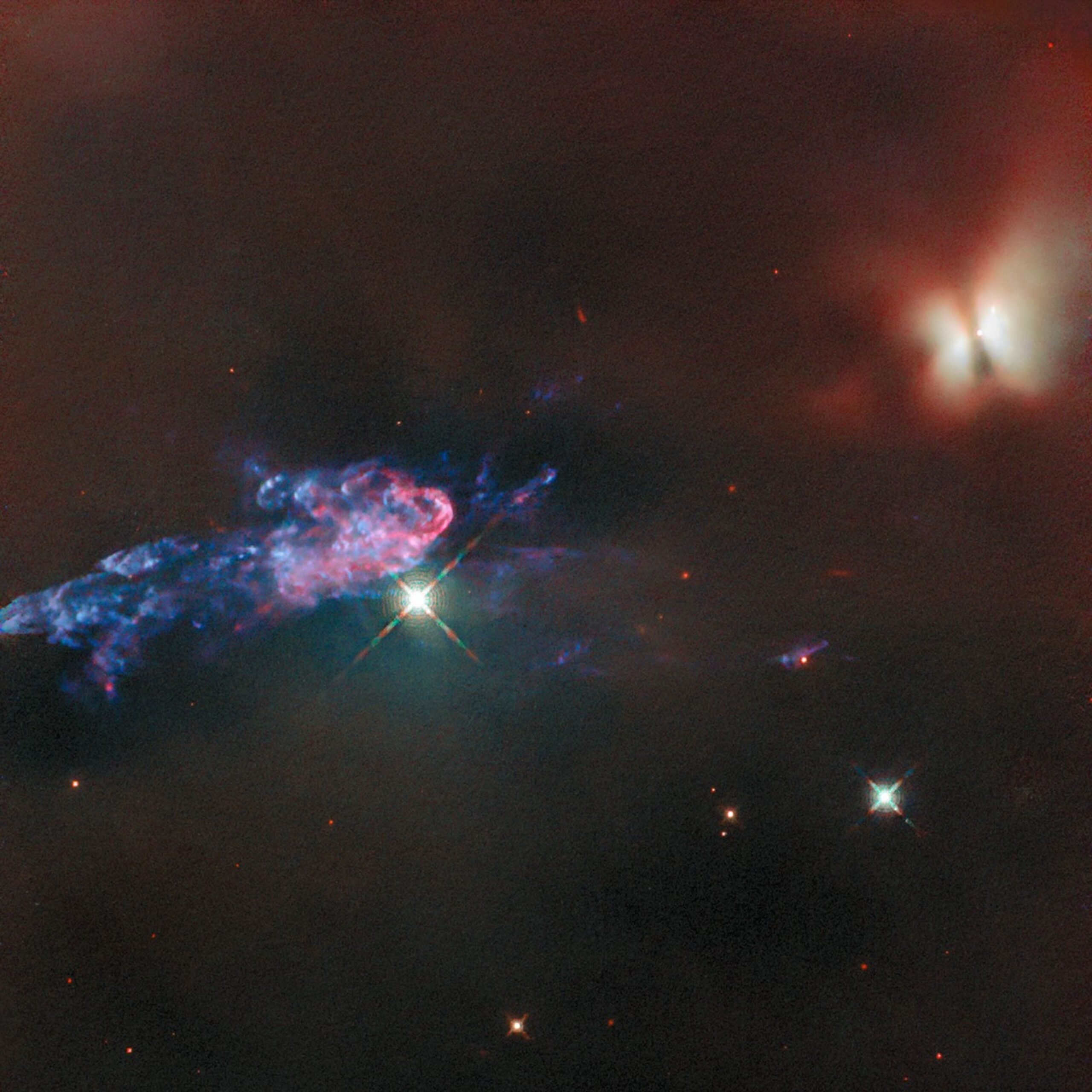
Read MoreAstronomers Catch Unprecedented Features at Brink of Active Black Hole
International teams of astronomers monitoring a supermassive black hole in the heart of a distant galaxy have detected features never seen before using data from NASA missions and other facilities. The features include the launch of a plasma jet moving at nearly one-third the speed of light and unusual, rapid X-ray fluctuations likely arising from near the very edge of the black hole. Radio images of 1ES 1927+654 reveal emerging structures that appear to be jets of plasma erupting from both sides of the galaxy’s central black hole following a…
Read MoreNASA Research To Be Featured at American Astronomical Society Meeting
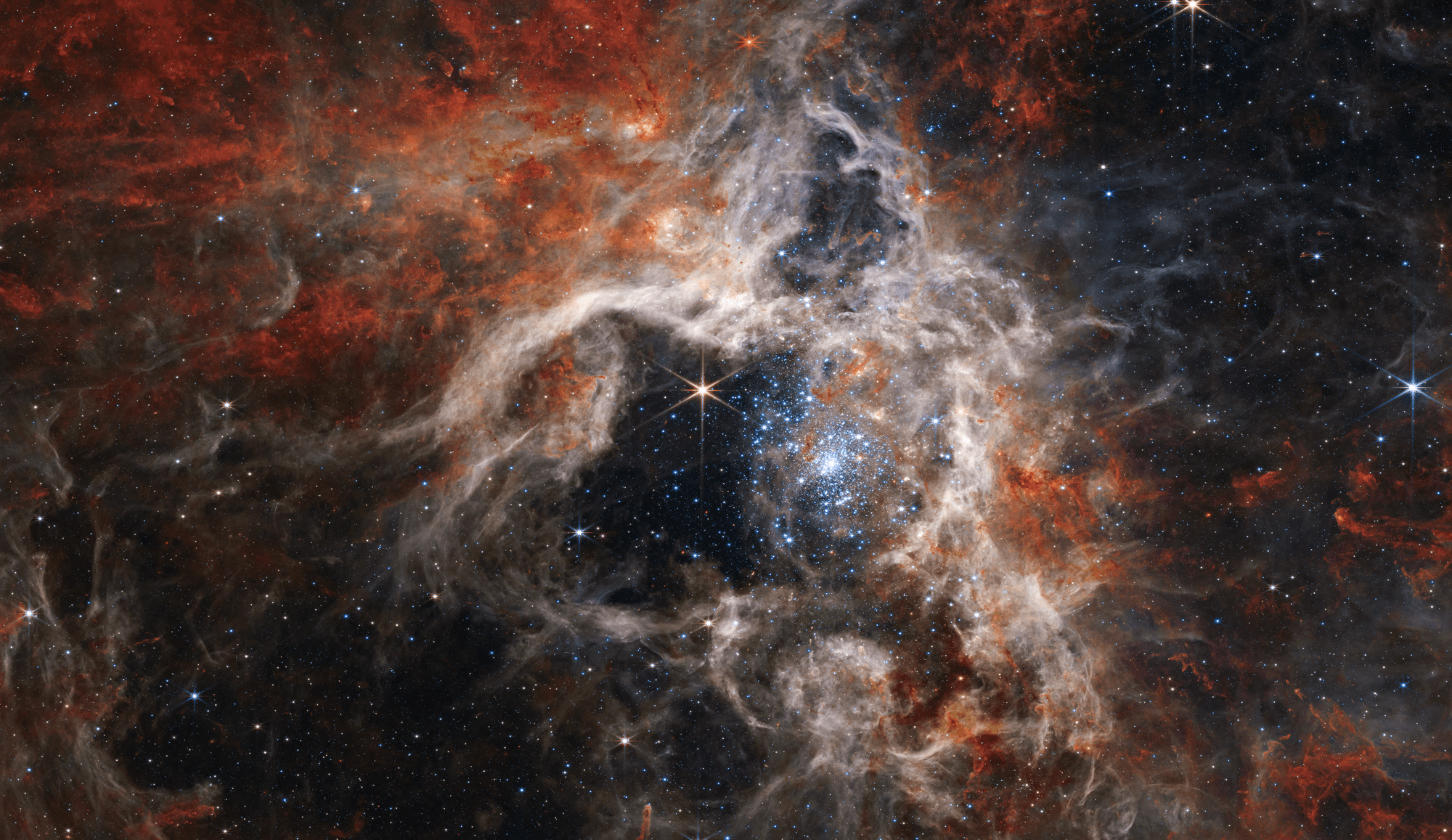
6 min read NASA Research To Be Featured at American Astronomical Society Meeting In this mosaic image stretching 340 light-years across, Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) displays the Tarantula Nebula star-forming region in a new light, including tens of thousands of never-before-seen young stars that were previously shrouded in cosmic dust. The most active region appears to sparkle with massive young stars, appearing pale blue. NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Webb ERO Production Team From new perspectives on the early universe to illuminating the extreme environment near a black hole, discoveries from…
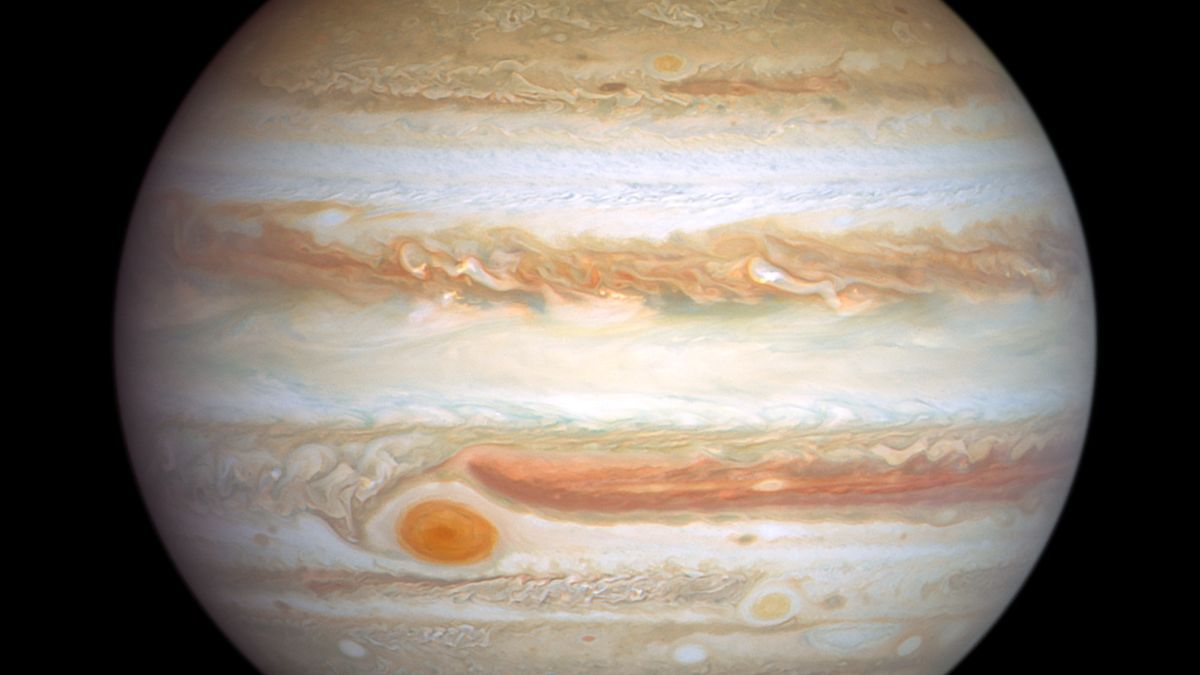
Read MoreAn amateur astronomer used an old technique to study Jupiter — and found something strange
Scientists and amateur astronomers have teamed up to upend a long-held assumption that Jupiter’s iconic swirling clouds are made of frozen ammonia — a pretty foundational revelation about the gas giant we thought we knew well. Using commercially available telescopes and spectral filters, an amateur astronomer named Steve Hill collected data to map the abundance of ammonia in Jupiter‘s atmosphere, but Hill ultimately found something that contradicted previous models of the gas giant’s atmospheric composition to begin with. “I was intrigued!” Patrick Irwin from the University of Oxford told Space.com.…
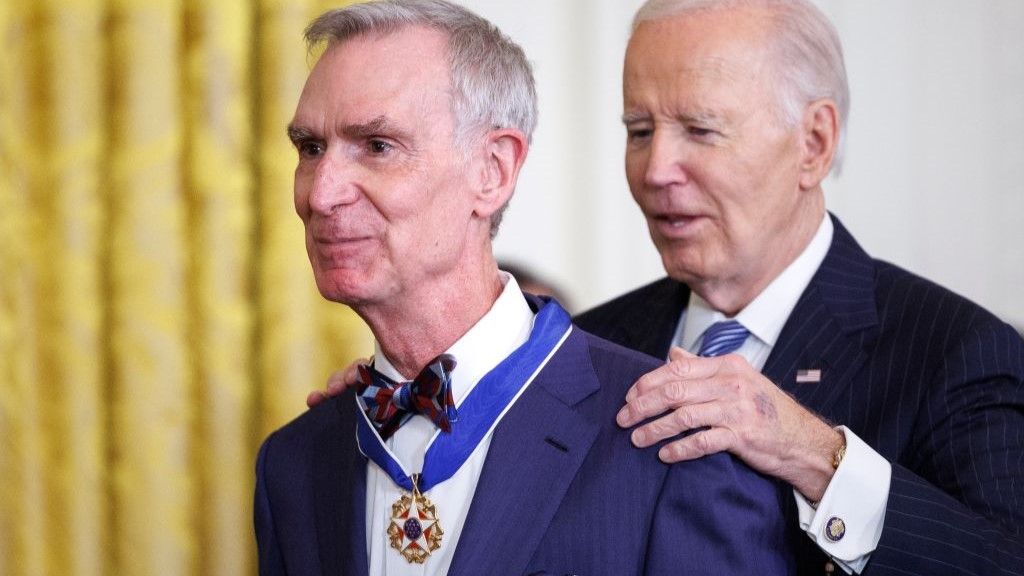
Read MoreBill Nye ‘The Science Guy’ awarded Presidential Medal of Freedom
Bill Nye was recently awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in recognition of his dedication to science education. Nye, popularly known as Bill Nye the Science Guy, is an American science educator, television presenter and CEO of the Planetary Society. Nye was among 19 honorees to receive the Presidential Medal of Freedom — United States’ highest civilian honor — at a White House ceremony held on Jan. 4. “Bill Nye has inspired and influenced generations of American students as ‘Bill Nye the Science Guy,’” officials wrote in a statement from…
Read MoreAstronaut Set to Patch NASA’s X-ray Telescope Aboard Space Station
4 min read Astronaut Set to Patch NASA’s X-ray Telescope Aboard Space Station NASA astronaut Nick Hague will install patches to the agency’s NICER (Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer) X-ray telescope on the International Space Station as part of a spacewalk scheduled for Jan. 16. Hague, along with astronaut Suni Williams, will also complete other tasks during the outing. NICER will be the first NASA observatory repaired on-orbit since the last servicing mission for the Hubble Space Telescope in 2009. Hague and other astronauts, including Don Pettit, who is also currently on the…
Read MoreScientists find ‘spooky’ quantum entanglement on incredibly tiny scales — within individual protons
Scientists have used high-energy particle collisions to peer inside protons, the particles that sit inside the nuclei of all atoms. This has revealed for the first time that quarks and gluons, the building blocks of protons, experience the phenomenon of quantum entanglement. Entanglement is the aspect of quantum physics that says two affected particles can instantaneously influence each other’s “state” no matter how widely separated they are — even if they are on opposite sides of the universe. Albert Einstein founded his theories of relativity on the notion that nothing…
Read More